Please do outline for the 3 chapters, follow the outline example. No long paragraphs. Thank you!This is three separate meals: one breakfast, one lunch, one dinner. Make sure to include all Macro and M
After completing Unit 15 and its interactive learning activities, you will be able to:
Recall the basic functions, structures,and food sources of protein.
Summarize the effects of amino acid supplements and protein on muscle mass and strength.
protein Chemical substance in foods made up of chains of amino acids.
hormone A substance, usually a protein or steroid (a cholesterol-derived chemical), produced by one tissue and conveyed by the bloodstream to another.Hormones affect the body's metabolic processes such as glucose utilization and fat deposition. immunoproteins Blood proteins such as antibodies that play a role in the func- tioning of the immune system (the body's disease defense system). Antibodies attack
foreign proteins.
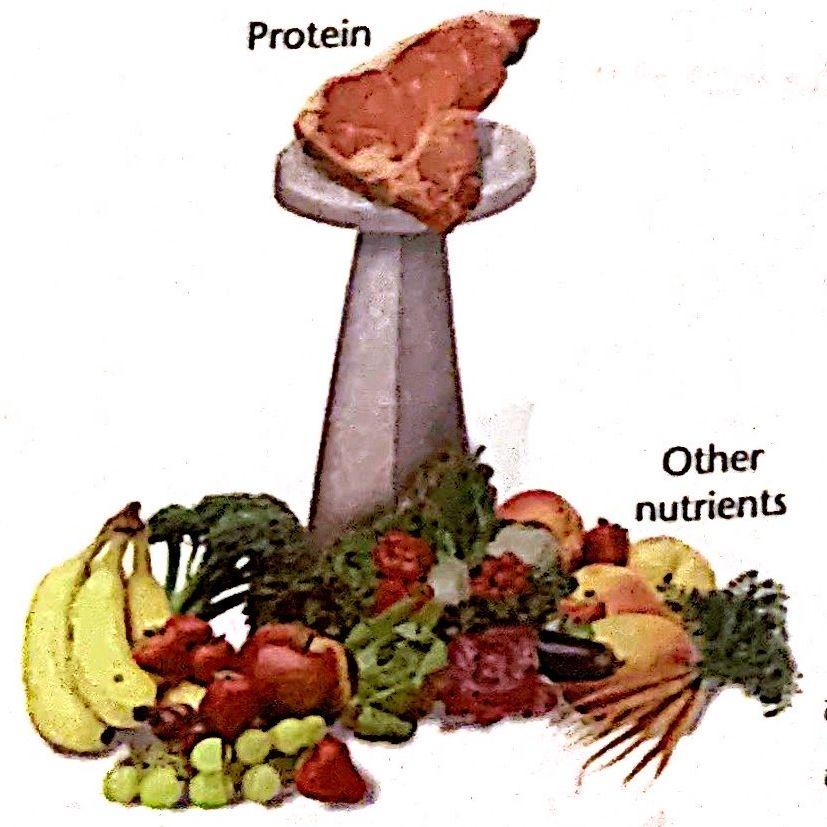
Illustration 15.1 The protein perception.
PhotoDisc
Protein ·Recall the basic functions, structures, and food sources of protein.
The term protein is derived from the Greek word protos,meaning "hrst"The derivation indicates_____importance ascribed to this substance when it was first recognized.Protein is an essential structural component of all living matter and is involved in virtually every biological process that occurs in cells.Protein has a very positive image (Illustration 15.1). The perception is so positive that you don't have to talk about the importance of protein people are already convinced of it.
Key Nutrition Concepts
Content covered in Unit 15 on protein and amino acids relates to the following key nutrition concepts:
·Foods provide energy (calories),nutrients,and other substances needed for growth and health.
·Adequacy,variety,and balance are key characteristics of healthful diets.
Nearly all people in the United States get enough protein in their diets.2 The aver- age intake of protein by adults in the United States is 98 grams per day, approximately twice the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for men (56 grams) and for women of (46 grams). Approximately 16% of total calories in the average U.S. adult diet are supplied by protein.3
High-protein intakes are generally accompanied by high-fat and low-fiber intakes. That's because foods high in protein, such as hamburger, cheese, nuts, and eggs, tend to be high in fat and contain little or no fiber. Even lean meats provide a considerable propor- tion of their total calories as fat (Illustration 15.2).
Functions of Protein
Proteins perform structural and functional roles in the body (Table 15.1). They are an integral structural component of skeletal muscle, bone, connective tissues (skin, collagen, and cartilage), organs (such as the heart, liver, and kidneys), red blood cells and hemo- globin, hair,and fingernails. Proteins are the basic substance that make up thousands of enzymes in the human body; they are a major component of hormones such as insulin and growth hormone, and serve as other substances that perform important biological functions.Tissue maintenance and the repair of organs and tissues damaged from illness or injury are functions of different types of protein. Albumin, a protein made by the liver, is the blood's “tramp steamer” It attaches to and transports fatty acids, calcium, and other substances through the circulatory system to cells throughout the body.4 Protein serves as an energy source at the level of four calories per gram.
The body of a 154-pound man contains approximately 24 pounds of protein.Nearly half of the protein is found in muscle; the rest is prèsent in the skin, collagen,blood, enzymes, and immunoproteins; and in organs such as the heart, liver, and intestines; and other body parts.All protein in the body is continually being turned over, or broken down and rebuilt. This process helps maintain protein tissues in optimal condition so they continue to function normally. The process of protein turnover utilizes roughly nine ounces of protein each day. Yet, we consume only two to three ounces of protein daily. Most of the protein used for maintenance is recycled from muscle and other protein tis- sues being turned over.Proteins play key roles in the repair of body tissues by serving as substances-such as fibrin-that help blood clot (Illustration 15.3) and by replacing tissue proteins damaged by illness or injury.5
Protein serves as a source of energy in healthy people,but not nearly to the extent that carbohydrates and fats usually do. Protein is unlike carbohydrate and fat in that it contains nitrogen and does not have a storage form in the body.In order to_____protein for energy,amino acids that make up proteins must first be stripped of their nitrogen.The free nitrogen can be used as a component of protein formation within the body,or, if pres
15-2 UNIT 15

Proteins and
Amino Acids
NUTRITION SCOREBOARD
1 The primary function of protein is to provide energy. True/False
2“Nonessential amino acids" are not required for normal body processes. Only “essential amino acids" are. True/False
3 High-protein diets and amino acid supplements by themselves increase muscle mass and strength. True/False
Answers can be found at the end of the unit.
15-1
(a)
Enka ross/Shutterstoctk.ccm
nburger(90%lean):45%
(e) xioin roast: 36%
Felicia Martinez/PhotoEdit
(b)Tenderloin:43%
iStockphota.com/svaniophoto