Privacy Policy Analysis (4 pages)
OPENNESS - TAPSCOTTFirst Forum
Collaboration
Transparency
Sharing
Empowerment
WHERE IS THE CONSUMER IN MARKETING?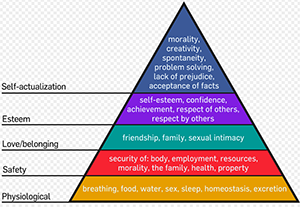
DIFFERENT PERCEPTIONS:
Psychology and Marketing
Problem solving for consumers
View consumer wants and needs as “problems”
Psychology and problem solving
FUNCTIONALISM
What individuals do – how they do it – why they do it?
Means and Ends
Economists and problem solving