TEST # 5 - CHAPTER 6 Chapter 6: Valuing the Environment Name _________________________________________ Test Score________ Part A: Multiple-choice
TEST # 5 – CHAPTER 6
Chapter 6: Valuing the Environment
Name _________________________________________
Test Score________
Part A: Multiple-choice Questions (40 points)
1. A local forest provides habitat for deer that are harvested by hunters. The hunters receive what type of benefit in this case?
Direct use value
Indirect use value
Option value
Bequest value
Existence value
2. A wildlife preserve provides what type of economic benefits?
Use values only
Non-use values only
Existence values only
Direct and indirect use values only
Both use and non-use values
3. A decision to postpone commercial development of an undisturbed parcel shows an example of what type of economic benefits?
Direct use values
Indirect use values
Existence values
Option values
Bequest values
4. Which one of the following valuation techniques is not based on the value of marketed goods or services?
Hedonic pricing
Avoided cost valuation
Production function valuation
Contingent valuation
Engineering cost valuation
5. An economist estimates the value of a nature preserve by calculating the price premium people pay for houses located adjacent to the preserve. This is an example of what type of economic valuation?
Hedonic pricing
Production function valuation
Contingent valuation
Travel cost method
Engineering cost valuation
6. Asking people to indicate their economic values in a survey is an example of what type of economic valuation?
Travel cost method
Contingent valuation
Hedonic pricing
Production function valuation
Avoided cost valuation
7. Valuing environmental services based on the prices of marketed goods is called ...
Travel cost method
Contingent valuation
Hedonic pricing
Production function valuation
Avoided cost valuation
8. Which one of the following techniques would most likely be used to estimate the value of preservation of a remote arctic wildlife preserve?
Hedonic pricing
Travel cost method
Production function valuation
Engineering cost valuation
Contingent valuation
9. Which one of the following techniques is an example of the replacement cost method of economic valuation?
1) Contingent valuation
2) Hedonic pricing
3) Travel cost method
4) Habitat equivalency analysis
5) Cost-effectiveness valuation
10. Which one of the following statements is false?
Bequest value is the value of environmental services to future generations
Willingness-to-pay tends to be smaller than willingness-to-accept for the same service
The production function approach to valuation considers the cost of constructing facilities to provide environmental services
Contingent valuation can be used to estimate existence values
The value of just knowing a wild species exists is called indirect use value
11. Which one of the following statements is true?
A low discount rate is always better for environmental protection
A high discount rate is always better for environmental protection
A discount rate of zero is always best for environmental protection
Discounting will decrease the magnitude of future costs and benefits
High discount rates should be used to evaluate long-term impacts
12. Suppose the pure rate of time preference is 1%, the growth rate of consumption per capita is 3%, and the elasticity of the marginal utility of consumption is 2. This suggests a value for the social rate of time preference of ...
2%
4%
5%
7%
9%
13. Suppose there is a 30% chance that an oil spill will occur in an area and the economic damage of the potential spill is $1 million. What is the expected value associated with the spill?
$3,000,000
$1,000,000
$300,000
$30,000
$3,000
14. If people are risk averse regarding environmental damages...
Low discount rates should be used
High discount rates should be used
Expected values will understate ecological damages
Irreversible actions should be taken
Contingent valuation responses will not be valid
15. The precautionary principle is most likely to be applied when some impacts ...
Involve option values
Are irreversible
Are converted to present values
Are estimated using the avoided cost approach
Involve indirect use values
16. The precautionary principle is least likely to be applied to which of the following
environmental issues?
Building a new road
Global warming
The approval process of a new pesticide
Timber harvesting in a rainforest
Storage of nuclear waste
17. Which one of the following statements is true?
All projects that provide positive net benefits should be approved
Cost-effectiveness analysis determines the best policy to achieve a given end
All projects with a benefit/cost ratio of less than one should be approved
Positional analysis determines the single proposal that provides the greatest net benefits
Cost-benefit analysis always provides estimates for all costs and benefits associated with a project
18. Suppose a legislature passes a law that mandates a 50% cut in toxic emissions. What type of analysis would most likely be used to determine how to implement this policy at the lowest cost?
Contingent valuation
Cost-effectiveness analysis
Positional analysis
Precautionary principle
Safe minimum standard
19. An analysis approach that considers the relationship of a proposed policy to social objectives is called ...
Contingent valuation
Cost-effectiveness analysis
Hedonic pricing
Positional analysis
Risk aversion
20. Which one of the following statements is true?
Cost-benefit analysis can give an accurate measure of all costs and benefits
Cost-effectiveness analysis is always preferred to cost-benefit analysis
Some costs and benefits will not be quantifiable in many cost-benefit analyses
Policymakers should never use cost-benefit analysis due to its analytical weaknesses
Cost-effectiveness analysis relies on economic techniques to determine policy objectives
Part B: Spreadsheet Analysis “Net Present Value Criterion” (10 points)
Complete (in Microsoft Excel document) the following problem:
Louisiana Drilling and Exploration, Inc. (LD&E) has the funds necessary to complete one
of two risky oil and gas drilling projects. The first, Permian Basin 1, involves the
recovery of a well that was plugged and abandoned five years ago but that may now be
profitable, given improved recovery techniques. The second, Permian Basin 2, is a new
onshore exploratory well that appears to be especially promising. Based on a detailed
analysis by its technical staff, LD&E projects a ten-year life for each well with annual net
cash flows as follows:
| Project | Probability (P) | Annual Cash Flow (CF) |
| Permian Basin 1 | 0.08 0.84 0.08 | $500,000 1,000,000 1,500,000 |
| Permian Basin 2 | 0.18 0.64 0.18 | 300,000 900,000 1,500,000 |
In the recovery-project valuation, LD&E uses 20% and 32% discount rate for Permian Basin 1 and Permian Basin 2, respectively. Both projects involve land acquisition, as well as surface preparation and subsurface drilling costs of $3 million each.
a). Calculate the expected value of annual cash flows for each project.
b). Calculate the NPV for each project.
c). Which project is preferred using the NPV criterion?
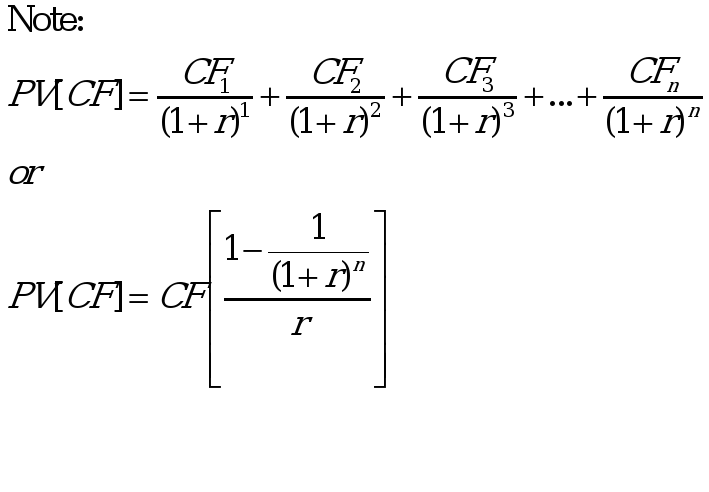
NPV = PV(CF) – PV(costs)
6



