Hey, there I have one assignment for the subject of Economics. Regarding assignments, all the information are given the thing is you have to read it carefully and follow it step by step. I need good a
Running head: RESTAURANT PRICING DISCUSSION 0
Restaurant Pricing Discussion
Subject Name: Economics for Managers
Course Code: MPE781
Sample Last year
Date Due: 01st May 2018
Table of Contents:
Answer 1…………………………………..…………………………………………………..3
Answer 2 (a)…………………………………………………………………………………..5
Answer 2 (b)………………………………………………………………………………….6
Answer 3……………………………………………………………………………………...7
Answer 4 (a)………………………………………………………………………………….8
Answer 4 (b)………………………………………………………………………………….8
Answer 5………………………………………………………………………………………9
References list………………………………………………………………………………..11
Restaurant Pricing Discussion
Answer 1:
The popular restaurant charges a lower price than the other seafood restaurant with the same products. In addition, the popular restaurant is said to have a higher number of customers during prime hours while the opposite restaurant which charges higher prices has a lower number of customers. The reason why the popular restaurant has higher customers is that it charges a lower price on its products. The demand for food from the popular restaurant is high yet the restaurant still charges a lower price in order to maintain customers. Increases in price will most likely lower number of customers who visits popular restaurants. In economic terms, consumers are rational decisions maker and they evaluate decision in accordance with areas they will receive optimum benefits.
Additionally, consumers of seafood have perfect information about the price for particular products and if the product price goes up the customer for seafood might shift to other restaurants because there is indifference in the price of the two seafood restaurant. The popular restaurant can only be forced to charge the price if the cost of operation is high and the restaurant wants to pass the cost of operation to customers so that they can maximize profits. This decision is risk more so when it involves a customer who has relevant knowledge about the cost seafood. The restaurant might be charging a lower price for its products but on the other hand, it enjoys abnormal profit because customer cares less about the queues.
The other factors which make popular culture not to raise its prices for seafood are because the restaurants may have some knowledge about disposable income of their customers. Customers who have a higher value of disposable income are more likely to purchase more even when the cost of food is high. In this case, popular restaurants have to maintain low pricing so that it can continue attracting more customers. A strategy of offering low price will help the restaurant gains a competitive edge in the market. Lowering price for its products will make other restaurants close business hence leaving the popular restaurant to have a monopoly of power. Having monopoly of power the restaurant can raise it product price because they will be no other restaurant to compete with.
The other restaurant can lower its product price to attract more customers but the decision to lower prices to most customers may be linked to quality and therefore the firm may not gain a substantial number of the customer even when the firm lowers its prices. On the contrary, the restaurant may incur more losses. Charging higher price help the restaurant meeting expenses for the empty seats and expense related to catering, depreciation cost, utilities and other cost related to the operation. The burden of operation cost is factored in the foods sold by other firms charging a higher price, therefore, reducing the price in order to compete with popular it may lead to the closing of business hence leaving popular restaurants to enjoy a monopoly of power.
The graph below explains what might happen when popular raises the price of its seafood.

Figure 1: Goods demanded after the company increases its prices.
If popular restaurants increase its prices from P1 to P3 in order to match the price offered by other firm quantity demanded will shift from Q1 to Q3.
The same graph can be used to explain the trend of good demand after other seafood's lower it prices. Lower of price from P1 to P2 will lead to increase of quantity demanded from Q1 to Q3.
Quantity demand may represent a number of customers will be visiting the restaurants.
Answer (2a)
If the seller is strictly required to sell its goods in short run under perfects competition the seller is more likely to record super-normal profit. The graph below illustrates the supernormal profit or losses achieved in short run.
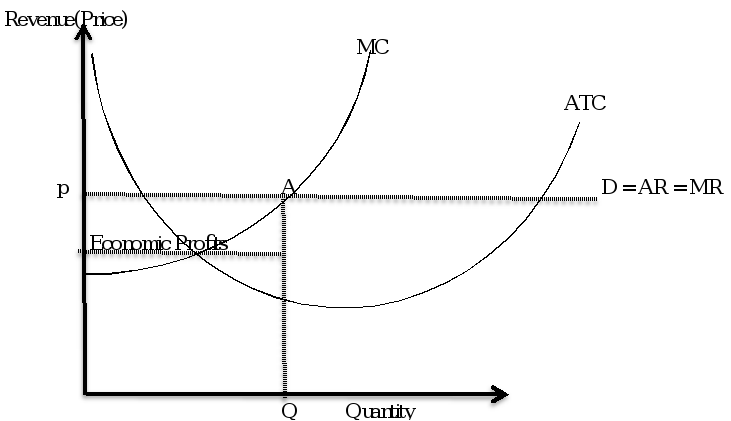
Figure 2: Perfect competition firm in short run.
In this kind of market in long-term firms will enter the market so long firms are making a supernormal profit in short run. Therefore in long term, the industry is more likely to earn normal profit. If the industry is earning losses, firm may not enter the market or some will exit from the market while those left behind may raise prices in order to drive more profits.
Answer (2b)
According to the information presented from the case study, the restaurants operating in this market are more likely to operate in the perfectly competitive market. This is because the features revealed in the extract resemble a perfectly competitive market. For example, the producer and consumer have perfect knowledge and it is assumed that the customer's and producers make rational decision to maximize their self-interest while consumer maximizes their own value for money. Customers who visit popular restaurant have perfect knowledge about the market and are more likely to make a rational decision on which restaurants will help them maximize their value for money.
The restaurant owners know how much they gain from the operation and that why other restaurants are reluctant to lower their prices while the popular restaurant is reluctant to raise its products prices. Even though this information is not clear in the extract, the firm in this market has absolute rights to leave the market and enters. The firm having empty seats can leave the market at will but the revenue they gain from the operation prohibits them from leaving the market. They can only leave the market after they start recording lower profits. In addition, according to the extra, the firm or restaurant in this market produce a homogenous product. The seafood sold in this restaurant is identical to other restaurant majoring in seafood in the area.
Other services offered in this market are homogenous in nature. In this market, no firm has power to influence prices and therefore restaurant prices are determined by market forces. In this extra, the other seafood restaurants have slightly higher price than a popular restaurant and because the firms decided to increase its price then there is a slightly lower number of customers who visit this shops. The restaurant can make super-normal profits in short run and normal in the long run after other firm shows interest in the market. The profit will be spread among all firms in the market so long as the restaurants are charging all most similar.
Question 3:
Exclusivity, in this case, entails creating a unique offer that other firm cannot match. The popular restaurant is able to employ exclusivity through restricting quantity supplied while keeping prices low. The following graph shows the potential gains and losses to profits if the seller chooses to restrict the quantity supplied under the value from exclusivity.
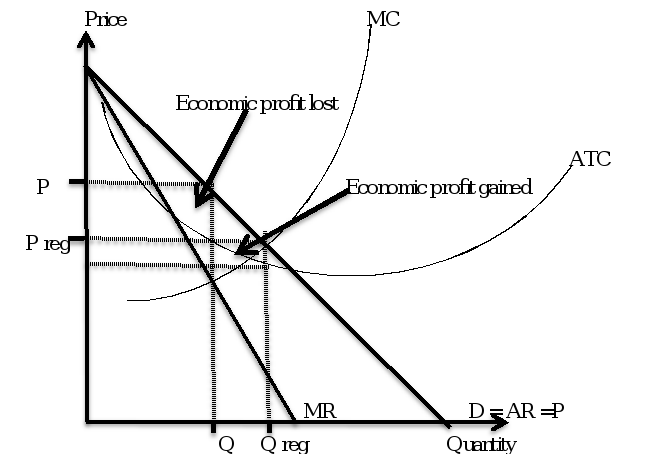
Figure 3: Indicating restriction of quantity supplied under in monopoly market
According to the information above, the firm under monopoly market restricts goods in order to drive more demand and gain to a competitive edge in the market. The figure reveals that if the company restricts price and quantity supplied then the firm will be able to gain economic profits while on the other under if the firm fails to restrict price or quantity the firm is more likely to incur economic profit lost. The profit maximization is where MR is equal to MC. If ATC cover is equal to AR the firms are more likely to earn supernormal profits.
Answer (4) a:
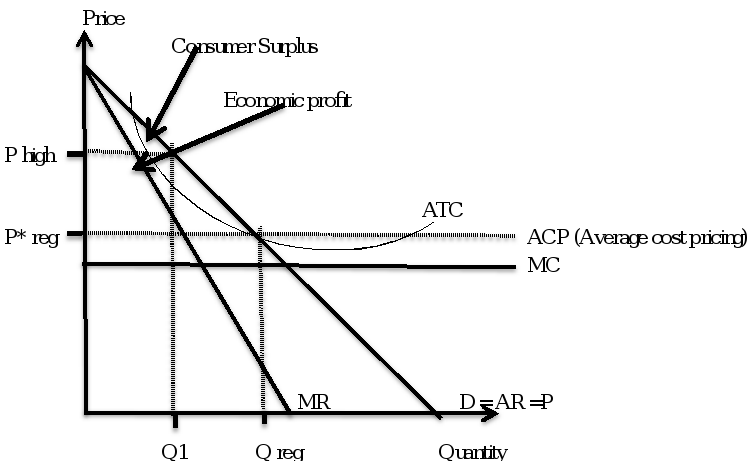
Figure 4: Price Discrimination graph
Q* reg is the legal price charged which is required to be charged by to all customer but the restaurant decide to offer price discrimination by charging higher at Q1. The company is able to attain economic profit by charging higher. When the restaurant is required legally to charge a price equal to average total cost, the Price P* reg expand to Q* reg. At this point monopoly firm make zero profits but if it charges little higher the firm is able to make profits. (Gifford, D.J., and Kudrle, R.T., 2009)
Answer (4) b:
Price discrimination is a scenario of charging a different price for the same goods or services. To achieve price discrimination a firm should identify market segments on which to charge that price (ARNOLD, 2010). The market must be kept separate by times and nature of use which means that the firm will have to charge this prices at predetermined times. For example, when a firm charges lower price because the firm utilizes the economics of scale to produce its products that action make other business operating in the same market segment to quit the market if the firm is not able to match the price offered by the low-cost firm. As results, the firm left will later increase its products price in order to gain abnormal profits.
A firm operating as monopoly firm is not exposed to competition from other firm and therefore it may become inefficient. Customer depending on this firm has no choice but to tolerate with the firm inefficient. Therefore, monopoly services or a product is threats to competition. Charging higher due to the quality of a product makes other firm majoring in the same sector products obsolete and the customer assumes the products are of poor quality. This action endangers young firm. The young firm may not have competitive powers which could match those of other big firms which have dominated the markets for long.
Therefore, if a large firm employs a strategy of differentiating products into quality then the young firm may suffer. Other firms may decide to merge with big firms in order to gain a more competitive edge than other small firm hence threatening the survival of small firms.
Answer 5:
The demand curves do not behave in simple ways to all components. For example, the price of gold is inelastic demand always which means that even if the demand for the Gold decline there is high chance that the cost will still be high. On the other hand, if the supply of Gold increases which is a hypothetical scenario, the price of Gold might not be low but the price will still remain to be high. Each day the price of Gold keeps on increasing in value. The price of a house appreciate each day and therefore the value decline if the area is linked to issues like earthquakes or floods but its rare for the price of a house to decline. On other hands, demand for company stock depends on a variety of factors which are considered before one settle for a particular firm.
Firm market performance for several years is a consideration before someone decides to purchase the stock. Also, the stock return value is another consideration. Most rational traders consider the firm which offers a higher return. The law of demand still holds in some scenarios but not always considering that the purchase of goods or services is influenced by satisfaction one get form the purchase. For example, if company stock offers a higher return, traders will be interested to purchase more but there is a limitation of income level. Therefore considering the law of demand assumption, then the law of demand still holds in all instances. The demand curve will shift to the right if the customer will expect the demand to increase.
If customers are uncertain about the future price of goods the demand for goods shifts to the right. (Fridolfsson, Sven-Olof, 2007). Customer tends to purchase more if they are uncertain about the future price of the products. The action of purchasing products while the price of products is low help customer save on cost. Therefore customer assumes they will save if they purchase now because the future price is uncertain. Other customers who lack the same information may not purchase the products because they assumed the new products being introduced will be of goods quality than the previous one for example, if the customer are uncertain about the price of cell phones some will purchase when cell price is low while other will wait until new brand is realized. Some assume the products sold at a lower price may not be of good quality.
References
ARNOLD, R. A. (2010). Economics. Australia, South-Western Cengage Learning.
Gifford, D.J., and Kudrle, R.T., 2009. The law and economics of price discrimination in modern economies: time for reconciliation. UC Davis L. Rev., 43, p.1235.
Fridolfsson, Sven-Olof. "A consumer surplus defense in merger control." Contributions to Economic Analysis 282 (2007): 287-302.
Hartman, R., 1972. The effects of price and cost uncertainty on investment. Journal of economic theory, 5(2), pp.258-266.
D2l.deakin.edu.au. 2018. Demand and supply curve analysis. retrieved 28 April 2018 <online> https://d2l.deakin.edu.au/d2l/le/content/633492/viewContent/386246 /View.
D2l.deakin.edu.au. 2018. Price discrimination strategy. retrieved 28 April 2018, <online> https://d2l.deakin.edu.au/d2l/le/content/633492/viewContent/3862477/View



