ASSIGNMENT
Milestones Schedule and Critical Risks Assessment
Introduction
This paper provides a thorough and in-depth depiction of Meal Machine’s milestones schedule and details of the critical risks assessment including: what steps should be followed to reach the designated milestones, Meal Machine’s preferred timing and objectives including a Gantt chart representing the start-up process and the tasks involved, the organization’s contingency plans that are in place so that the firm is equipped to handle complications before, during and after the project is complete, and how the business overall is going to overcome obstacles and challenges that may arise throughout the process.
The Milestones Schedule and Critical Risks Assessment
The milestones schedule provides the estimates of a timeline for a projects life. The milestones comprise all the projects’ tasks and the temporary steps required for the project to be efficiently implemented. In most cases, the schedule always includes the milestones for project planning, construction and development, evaluation and reports on the implementation. The dates are normally based on the anticipated grant reward; however, the dates can change in respect to the grant prize. On the other hand, the critical risks assessment ensures that the major elements of a projects risks are identified, it specifies and describes the methods for risk identification, and outlines the risk evaluation process and an explanation of the risk-mitigation process (Schatteman, 2015).
The milestones schedule and critical risks assessment for Meal Machine seeks to understand the evolution of different project activities, as well as the possible risks encountered in the sales and marketing plans of the food truck business. The various tasks that are expected to transpire through the project include: marketing of the products, designing of sales strategies and techniques, and releasing of product. The tasks are expected to be completed in four weeks which is enough time to complete the project because Meal Machine is not an immense or large company (Schatteman, 2015).
Preferred Timing and Objectives
As noted earlier, the preferred timing in business of the company is four weeks which will include marketing and creating awareness of the product. This can be attributed to the simplicity and availability of the required technology to aid in the production process (Carbone & Tippett, 2014). The marketing of the product is expected to rely on the company’s pricing strategy, positioning of the product, and packaging methods. The sales tools to be used include demos, competitive positioning and prospect presentation. The product will also be presented to the target audience in the market within the named time. Thus, within a four-week period the company is expected to have produced the product and will be ready to market the product. The attached Gantt chart shows how Meal Machine is planning to realize its set milestone schedule and objectives.
As we know, timing is everything and requires major consideration along with many factors which include: general economic conditions, the position of the food truck industry within the market and the windows of opportunity. While in the initial process of planning, the overall objective in the food truck industry is the potential demand and how well are the competitors performing, while also taking into consideration financial long term, capital flows, and performance of the business within the industry. Lastly, making the best timing decisions and fulfilling unmet needs, along with the estimated period of time with which the start-up may be able to effectively compete in the market and seize every marketable opportunity (Shrestha, 2008). The complexities of the entrepreneurial venture dictate that the founder conduct the aforementioned multifaceted analysis in order to select the timing of the launch (Okun, 2013).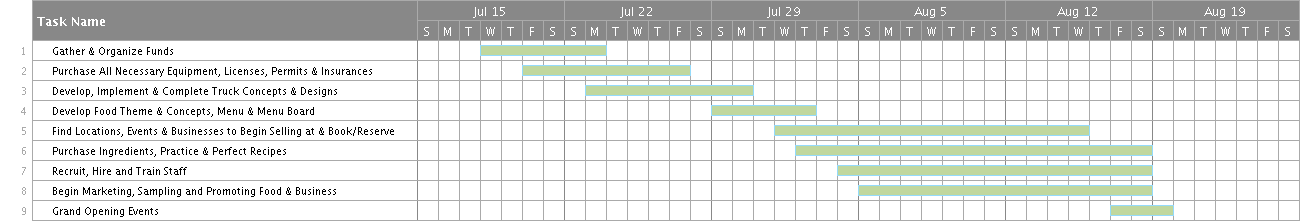
(Entrepreneur Media, Inc., 2011; Daciuk, 2018; Created at https://app.smartsheet.com/b/home)
Contingency Plans
Meal Machine must have a solid contingency plan if it wishes to be successful in its operations. The company should develop various strategies with which to effectively handle all forms of risk that might arise during or after the project. First of all, Meal Machine will purchase reliable insurance coverage to accommodate any risks that might inhibit the success of the project. There are various natural risks, preventable risks and other unforeseen industrial risks that might occur during the project. Meal Machine therefore, needs to have an elaborate insurance plan to be prepared for such risks (Carbone & Tippett, 2014).
The insurance policy serves as a contingency plan in dealing with the potential setbacks in the firm’s operations and business overall. It is also feasible for the company to consider reorganizing its operations and structures to effectively offset the adverse issues that might be experienced during the project. The Gantt chart illustrates some of the contingency plans that the company can employ.
It is wise to say that every business has major risk factors that will affect its operations and cause a profit loss as a result of poor response to those factors. Meal Machine will use the four-step process to prepare a contingency plan that will address some setbacks we may face as food truck business. Those four steps are identifying the key risk, prioritizes the risks, create contingency plan, and maintain the plan (Myrick, 2018). Identifying the key risks will help us address some potential areas that may cause problem in the future. According to a case study (Faw & Tuttle, 2014), some of the risk factors that a food truck organization such Meal Machine may face are: water safety, sanitation knowledge, and food handling practices. The study indicates that most food trucks that were assessed for critical risk factors were documented for health code violations such as no water in the water tank or a leak in a pipe/sink and lead to businesses being temporarily shut down; this violation leads to unsanitary behaviors such as employees not washing their hands and produce not being washed (Faw & Tuttle, 2014). In addition, the study concluded that some of the food truck refrigerators were not operating accordingly and consequently, it affected the food temperature causing it to be out of a safe range (Faw & Tuttle, 2014). Lastly, the food tucks had no sanitation solution to maintain a clean surface in the food truck (Faw & Tuttle, 2014).
To minimize the risks, Meal Machine will properly train every employee on food handling safety and ensure they are knowledgeable about health code regulations. In addition, every food truck will perform a daily self-inspection before, during and after operating hours (Myrick, 2018). Employees must be aware of safe food temperature requirements and ensure that all foods are cooked at a proper temperature for a minimum of fifteen seconds as well as refrigerated at proper temperatures (Myrick, 2018). Lastly, all employees must wash their hands throughout their shift and ensure all food contact surfaces are entirely and safely sanitized (Myrick, 2018). By maintaining our contingency plan, our organizations will remain a healthy and clean food environment.
Conclusion
As shown, Meal Machine is adequately prepared and has organized an efficient, detailed and methodical milestones schedule and has evaluated the critical risks assessment for the business. Through preferred timing and objectives, the organization has developed a plan that corresponds with the goals and milestones of the firm including producing, marketing and presenting the product as well as depicting the goals and milestones in the form of a Gantt chart for clarity. Furthermore, the organization plainly described and explained the contingency plans in place including insurance policies, a four step risk identification process and training, processes and procedures that will act as preventive measures to avoid issues and complications within the business.
Capstone Project Overview – Meal Machine
Context
A business investment takes precedence when an opportunity to establish a business is presented. We live in an era of creative innovation where things have been made simple to obtain food. Food is not only for thought, however, but for the necessity of survival. The ever-growing food industry is tough based on its extreme competitive edge, yet financially beneficial if strategized properly. Everyone loves food, in 2017 based on Comen’s (2018) article Americans spent $130.6 Trillion in 2017 a 2.67 % increase compared to 2016.
Those statistics alone are a clear indication on what a small investment in the food industry can generate for one’s business. With that said we present the opportunity to start a food truck based business that caters to all flavors of life. Our food truck will be the talk of town, offering a wide range of comfort foods that caters to everyone from children up to the elderly. With a highly competitive edge we take pride in our ability to run and maintain a food truck like no other. With so many options to choose from we are confident that our food truck will leave you wanting more.
Mission
Meal Machine is focused on providing fresh, unique, high quality, locally grown, delicious food to everyone we serve. We care about our customers, our employees and our community and always provide imaginative, convenient, and exciting meal choices while charging fair prices and supporting our community and local economy in any way we can. We offer healthy and satisfying meals while not skimping on what our customers and community wants (Myrick, 2017).
Vision
The Vision for Meal Machine is to become the communities place to go to find quality, fresh, delicious food on the go and to be the food truck that locals recommend and that everyone looks for to grab a bite to eat. We want to be highly recognized not only in our own community but the surrounding communities and to become a brand that is not only recognized but called upon for events and gatherings (Myrick, 2017).
Competitive Advantage
Food trucks are known to have the highest competitive advantage in all of the food industry including mobile food and restaurants. To stand out in the fierce competition, Meal Machine will focus on providing affordable prices, excellent service, and deliver variety of food that will fulfill the consumer’s needs. To maintain affordable prices Meal Machine will have to control all costs by understanding the operating costs, perform monthly cost comparisons, and maximize the usage of ingredients throughout the menu. (Competitive Advantage: Keep Your Food Truck On Top, 2018).
Consumers who prefer food trucks over restaurants are usually looking or something that has a rapid delivery with excellent service. Therefore, Meal Machine will provide honest service and make each customer feel valuable. In addition, Meal Machine will train employees on how to sell and recommend foods on the menu. Lastly, Meal Machine will provide a menu that offers all kind foods such as: taco’s, pizzas, and burgers among other American food favorites. Thus, the consumer can find any of their cravings at their fingertips. Meal Machine will use social media as a resource to keep consumers informed of their location, and to let consumers know where to find them at any given time.
Business Opportunity
The nature of the business opportunity in this sector is quite advantageous. The main benefit of this business is that it is dealing with the daily life needs of the customers. As per the social variations, there is always a chance of change in the trendy requirements. However, the customers can never get away from basic requirements as it is a core part of their lives (Ghandour, 2014). Despite the number of competitors available in the business, there is still a lot of sales opportunity in the sector. The purchasing power of the consumers is limited; however, their population is high. The main strategy of the business is to carry out enough number of sales that will be easily completed. The business will also provide a fair chance to establish its brand name in the area. Afterward, the business can consider the expansion in other areas of the country and other countries.
Analysis of Environment and Industry for the Capstone Project–Meal Machine
Introduction
Within this document is the environmental analysis and industry analysis for the Meal Machine. This analysis includes an industry analysis using the five forces of competition including: the threat of new entrants, competitive rivalry, bargaining power of customers, bargaining power of suppliers and the threat of substitute products or services, in addition to a description of the sources of Meal Machine’s competitive advantage, the details of global expansion using the modes of entry, and an identification of the outlook, forecast and trends of Meal Machine found using the elements of the external environmental analysis (Hitt, Hoskisson, & Ireland, 2015).
Industry Analysis
Threats of New Entrants:
The threat of entry into a modern division relies upon the hindrances to entry that are available, combined with the response of existing competitors that must be normal by the contestant. On the off chance that the obstructions are high and additionally the newcomer can expect a clear striking back from set up competitors, the threat of entry is low. Meal Machine also has threats for new entrants to come into the business (Investopedia Staff, 2017).
Competitive rivalry:
Meal Machine has a contention between competitors which happens when at least one of the competitors feel the weight or see the opportunity to enhance their competitive position in their mechanical segment. The serious contention is the consequence of various basic elements, which are specified and independent (Investopedia Staff, 2017).
Bargaining power of customers:
The bargaining power of customers of Meal Machine is low. Buyers agree to the price fixed by Meal Machine and hence the customers bargaining power is low. Purchasers contend in the mechanical segment by constraining down prices, consulting for superior quality or more administrations and influencing competitors to rival one another to the detriment of the productive industry or threaten to incorporate vertically in reverse (Investopedia Staff, 2017).
Bargaining powers of Suppliers:
Meal Machine has the power to bargain as the fast food industry has a strong supplier power. They can fix the price according to the quality of meals they supply to customers. Suppliers can exercise their bargaining power with the participants in an industrial sector by increasing their prices, or by decreasing the quality of the goods and services acquired and threatening to integrate vertically forward (Investopedia Staff, 2017).
Threat of substitute products or services:
Meal Machine has a threat of substitute products or services because fast foods are very common in all places. Thus, there will be competition among the substitute products. In the junk food industry, substitutes that may influence benefits are alleged home-cooked meals (Healthy Ready-Made Meal Delivery, 2015).
Competitive Advantage
When it comes to business and competitive edge, the workforce and the community are the driving force behind the majority of competitive advantages. If the staff is better at innovation, creation, and developing relationships with others, than an organization is more likely to attain a competitive advantage. As most know, competitors might have the ability to duplicate and reproduce an organizations product, but will never be able to duplicate an organizations people. With superior ability and resources, that allows one to simply outperform. Technology is another great example of a competitive edge. Technology escalated as a foremost facet in competitive advantage, specifically with the industrial revolution. In the beginning, technology encompassed industrial machinery, transportation technology, energy, office equipment, and consumer products (Mar, 2013).
Throughout the 20th century, information technology and biotechnology surfaced as foremost elements (Mar, 2013). Additionally, a good example of a competitive edge includes both capital and natural resources. Capital, and access to natural resources, were customarily the foundation of most competitive advantages. The significance of capital has diminished over time. For instance, capital is the prime competitive advantage in longstanding industries such as transport. If an organization owns a railway that boasts select routes, it's challenging for the competition to build a competing route. New industries, such as information technology are less capital intensive (Mar, 2013).
Modes of Entry
Based on the modes of entry, including exporting, licensing, strategic alliances, acquisitions and new wholly owned subsidiaries, the most beneficial and strategic option for Meal Machine would be a new wholly owned subsidiary. The Country chosen for the new wholly owned subsidiary and global expansion process is Canada due to its closeness and accessibility. Due to the capacity of the Meal Machine business, it would be simplest to create a new wholly owned subsidiary because it gives Meal Machine complete control over the business and has higher potential for above-average returns (Hitt, Hoskisson, & Ireland, 2015). There are many benefits to using this mode of entry including financial consolidation and focus, the ability to directly or indirectly control the operations of the subsidiary and the ability to implement new strategies quickly (Basu, 2018).
Culturally speaking, there are not many or any barriers. Primarily Canadians do not work as much as Americans, they take more breaks and get more vacation time (Abadi, 2018). Although, their business culture varies slightly, and even more so from region to region, most of their culture is similar to that of the United States. Currently, Canada is in good standing and stable both politically and economically seeing expansion and growth in many areas (Canada Economy, 2018). Furthermore, Canada already has a large market for food trucks and even hosts a free food truck festival in Vancouver expecting up to 90 food trucks (DH Vancouver Staff, 2018). Lastly, depending on the region that the business functions in, there may be some language barriers as the majority of Quebec speaks French, however, most of the country speaks fluent English (Office of the Commissioner of Official Languages, 2018).
External Environmental Analysis
To determine the outlook, forecasting, and the trends of Meal Machine, we would have to use the four parts of the External Environmental Analysis. This includes scanning, monitoring, forecasting, and making an analysis (Hitt, et al, 2015). Through scanning we can identify early signals of change in the general environment (Hitt, et al, 2015). We will use scanning to have full understanding the seven parts of general environment. For example, Meal Machine can use specific software to help identify events, and targeted customer (Food Trucks, n.d.). Through monitoring, we can observe the changes in the environment and spot the highlighted trends (Food Truck Industry Growth Trends, 2017). Meal machine would have to use new technology to commercialize its market, and to stay connected with its stakeholders.
To succeed we must have the ability to contain and control stock on hand, closeness to key markets, and have the required licenses (Food Trucks, n.d.). Nevertheless, forecasting will help determine what can occur with events and tends, and how quickly can it escalate (Hitt, et al, 2015). Effective forecasting will help Meal Machine outperform the market, and make sure the decision will support its investors. Some of these decisions may include new ways of tending to our market in an efficient and timely manner. Lastly, assessing will help us determine the timing of the environmental change and its effect on the firm (Hitt, et al, 2015). This may include industry threat of other vendors offering unique foods, competitive technology, or other regulation that may affect profit (Food Trucks, n.d.).
Conclusion
This dissertation demonstrated the environmental analysis and industry analysis for Meal Machine. This analysis included an industry analysis using the five forces of competition including: the threat of new entrants, competitive rivalry, bargaining power of customers, bargaining power of suppliers and the threat of substitute products or services, as well as a description of the sources of Meal Machine’s competitive advantage, the details of global expansion using the modes of entry, and an identification of the outlook, forecast and trends of Meal Machine found using the components of the external environmental analysis.
Organizational and Operational Plan – Mean Machine
Introduction
This document will provide the Organizational Plan and Operational Plan for Meal Machine. Within will be a detailed examination and explanation of the Organizational Plan, including: the configuration of the management team including their talents and skills and how they contribute to the organization; an outline of the McKinsey 7-S Model discussing strategy, structure, systems, shared values, style, staff and skills and how it applies to the organization; and a description of how the business-level strategy corresponds with the corporate-level strategy for the organization.
Additionally, the Operational Strategy will be evaluated and expressed including: the supply chain the organization uses and how the organization brings value into the supply chain; the main partners and suppliers of the organization as well as their locations and the contingency plan in place for the organization; how the organization will optimize its operational effectiveness; and a discussion of the primary and support activities such as financial, human resources, and information systems management from the perspective of a value chain.
Organizational Plan
The Organizational Plan below begins with a description of the management team including who they are, their skills and talents and what they add to the organization. This is followed by the outline of the McKinsey 7-S Model where strategy, structure, systems, shared values, style, staff and skills will be explained and discussed in relation to the organization. Lastly, an explanation of how the business-level strategy corresponds with the corporate-level strategy for the organization.
Management Team
Since Meal Machine is a smaller business, the management team is minimal and consists of four managers who represent different departments of the organization. Jessica is the Owner, CEO, and general manager of Meal Machine and oversees all functions and operations of the business. This includes inventory management, business expansion, finding locations and businesses to work with, website management and general daily operations. Jessica has eight years of management experience, fifteen years in customer service and a passion for cooking and serving exceptional food with quality ingredients.
The second manager on the team is Tanya and she is the CMO, or the Chief Marketing Officer. Tanya is responsible for Marketing the business and works with the rest of the team to create new ideas to promote the business via signage, social media, radio and other advertising to ensure customers know where to locate the food truck and what the menu is for the day. Tanya is obtaining her bachelor’s in Entrepreneurial Studies and is a motivated and dedicated individual that acts as a great support to the organization and is constantly working to develop it and promote it.
The third Manager is Mays and she is the CFO, or the Chief Financial Officer and manages the finances of the organization. Mays handles the overall financial accounting including expenses such as fees for registration, permits and licensing, inventory, equipment purchasing and maintenance, salaries, fuel, and more (Myrick, 2017). Mays is extremely driven and devoted to her skillset of financial accounting. Also, she is obtaining her bachelor’s in financial accounting and is extremely knowledgeable and manages her department exceptionally.
The fourth Manager is Saah and he is our Public Relations Manager and Event Coordinator. He manages public relations and events to ensure the business is well publicized, becomes well known in the community, and safeguards our relationships with the community. He develops and progresses positive and beneficial relationships with all of the community including partners and suppliers, such as local growers and grocers, event planners and venues and other local businesses that could use our services for either everyday meals or catering events. Saah is hardworking and inspired to foster and grow the business and the positive relationships that will keep it successful and is also working to achieve a bachelor’s degree.
McKinsey 7-S Model
To analyze and identify Meal Machines current standing and its envisioned objective, we will look at the seven key internal elements known as Mckinsey’s 7- S’s. In which, are strategy, structure, systems, style, staff, skills, and shared values (Jurevicius, 2013). Those seven areas are divided into two categories: hard element, and soft elements (Jurevicius, 2013). The hard elements are much easier to identify and manage (Jurevicius, 2013). While the soft elements require disciplinary management and may potentially create sustained competitive advantage (Jurevicius, 2013). The first element is Strategy; the Strategy of the business will look at how the business will use its resources to win the market. Meal machine strategy is to provide a variety of tasty meals at the consumer finger tips. We plan on using mobile apps to provide the options of ordering online and offer delivery services.
In addition, we plan on partnering with local business or other industries such as universities to stay in trend with festivals and other events. Structure, will embody the organization’s units and division, and the responsibility of each division (Tice, 2011). Since Meal Machine is a small business, the structure of the organization will be comprised of four different divisions: the managers of Meal Machine will also be the designated drivers and the cooks of Meal Machine, as well as the expediter, and the server. The CEO and managers will supervise and determine what events to attend, where the inventory is purchased, the cost of menu items, and determine other financial decisions that affect the business’s profit. The information will be shared through informal channels, such as email, face to face or phone collaborations.
As for systems, Meal Machine will use a specified operating system that will track each food truck location, the inventory invoices, and keep track of the number of meals purchased monthly. The style of the organization will signify the means that Meal Machine management. Top management will have an approachable leadership model making each employee feel as a part of the Meal Machine family. Each year employees will be given a review to identify some of the opportunities management can work on. In addition, there will be a monthly collaboration where employees can share new ideas and talk about potential changes in the business. Meal Machine is food on the go restaurant, therefore, each food truck will need approximately one manager and three employees.
As mentioned above, each employee will have his/her own to task to complete. To keep employees motivated and well trained, we will provide one day a month where employees can have a free meal of their choice and enjoy competitive games between team members. Lastly, the firm’s employees must have skills to remain coachable, and consistent with their work. For example, the chief must be able to manage the food truck while ensuring the meals ingredients and recipes are being followed. The expeditor must have the ability to work under pressure. The sever must memorize the meal menu and its prices, and ensure the orders are prepared in an efficient and timely manner. Mckinsey 7- S’s will help Meal Machine identify it’s the strengths and weaknesses of its performance. Thus, each element is internally connected to the other.
Business and Corporate Level Strategy
Cost leadership allows us to highlight the important aspect of the overall market that we target to serve, our primary focus is to maintain a competitive advantage among our competitors while formulating a strategy that exceeds the business needs (Hitt, Hoskisson, & Ireland, 2015). So, in doing so we recognize the past mistakes companies have made. We must also understand that the response received from our customers is our strategic plan in order to target an area that allows us to also meet and execute our business strategy. Decision making allows us to organize by avoiding repeating past mistakes; those who have done nothing must realize their vulnerability.
In order to understand what makes a great and successful business, we must always put the needs of our customers first. Corporate strategy concerns two different questions: what businesses the corporation should be in and how the corporate office should manage the array of business units (Porter, 2015). Corporate strategy and its plan of action to diversify the company, is both the darling and the stepchild of contemporary management practice—the darling because CEOs have been obsessed with diversification since the early 1960s, the stepchild because almost no consensus exists about what corporate strategy is, much less about how a company should formulate it (Porter, 2015). Through the differentiation strategy, firms provide customers with products that have different, and valued, features; differentiated products must be sold at a cost that customers believe are highly competitive (Porter, 2015).
Operational Plan
Presented below is the Operational Plan breakdown for Meal Machine. The Operational Plan contains details about the supply chain and what Meal Machine contributes to it, our partners and suppliers and the contingency plan in place in regards to them, how our business will optimize its operational effectiveness, and a summary of our primary and support activities such as financial, human resources, and information systems management from the perspective of a value chain.
Supply Chain
The supply chain of Meal machine will consist of raw material, production chain, and delivering the final product to the consumer. Since Meal Machine is in the food service industry, most of its material will be raw material. According to a case study titled “15 Case studies on Local Food Supply Chains” (Park, 2010) a local food supply chain is more likely to have a diverse collection of products and have detailed information of where and by whom their products are produced. In addition, the study demonstrates the prices influence by the demand relationship, it’s local supply, and production differentiation (Park, 2010). Therefore, most of Meal Machine’s raw material will be obtained from local farmers. Since Meal Machine is in the food service industry, most of the production chain will occur in the food truck kitchen. Moving forward, delivering the product to our customer we must focus on packaging of the meals, and keep transportation fuel cost to a minimum.
Partners and Suppliers
When venturing into the food service business one must account for the overall health and benefit of all the customers catered to. We know and understand that we are in a world of high tech and innovative entrepreneurs that are constantly creating the next best thing for the business of their choice. When it comes to food and running a food service business, it’s imperative that we not only build business relationships with local partners and growers but also our many supply chains within grocery stores. Our key suppliers will be our many high end, and organically grown products and produce purchased from grocery stores. Overall, we always have access to many ‘go to’ Grocery Stores such as: Sprouts, Trader Joes, Fry’s Foods, and Wholefoods Market just to name a few.
These Grocery stores will insure that we meet and exceed the highest expectation of great tasting and quality products and produce will that will cater to our customers. We will have a wide range of various items that meets the needs of customers that may or may not have special dietary needs. We understand that food is vital to the body which fuels us to operate at max capacity, and our food suppliers have insured us that they will always provide us with grade A quality in meats, fruits, and vegetables by keeping everything we purchase in season and locally grown. There is no way we can succeed as a business without the support of and professional business relationships from our suppliers.
Although local grocers are a large portion of our partners and suppliers to our our organization, we pride ourselves on supporting and working with the community in as many ways as we can. Additionally, we enjoy using farm fresh ingredients grown by the same community that purchases our products. By doing this, our customers know that by purchasing from Meal Machine means supporting their neighbors and their farming community, and in the end their own economy. The absolute best thing about using local growers and farmers is that you can find a farmer’s market or local farm stand in any area you go, the only thing that really changes is the product they sell. With that in mind, wherever our business goes, we can still stick to our vision and mission and utilize the community’s resources and support the community.
In addition to the benefit of utilizing the community’s resources, local farmers and farmer’s markets anywhere we go, many cities boast multiple famer’s markets which are comprised of different suppliers and various products (Montelongo, 2017). Knowing what area we are going to be in and which market, we are able to build our menu and products based on our suppliers and partners and what they are offering. This gives our business a competitive advantage as we can always provide what the community desires in ingredients, flavors and local support, in addition to our superior quality we provide in our meals and customer service. Furthermore, this provides our business with a sustainable contingency plan as we are able to purchase our ingredients and products from multiple local suppliers, growers and farmers and always have multiple possibilities and options.
Operational Effectiveness
Operational effectiveness deals with the management techniques and tools that can be employed to accomplish similar operations as our rivals but more resourcefully. It is from operational effectiveness that concepts such as a learning organization and continuous improvement have emerged. Corporations utilize tools such as benchmarking to ensure that they are in the truck with the best practices in the industry. Leadership, performance evaluation, change management, re-engineering of business process and business process improvement are significant models in operational effectiveness.
To optimize operational effectiveness in Meal Machine, we will have to apply several strategies. First, we need to focus on quality. Quality aims at reducing rework and waste, making more monetary savings in the process, and improving the outcomes hence making the organization more efficient. Quality should employ tools such as the six sigma, total quality management and statistical control of the process (Crespo Marquez, Bianchi & Gupta, 2018).
Secondly, we should improve the forecasting. Every organization tries to forecast on its capability and demand when selling goods and services, buying and managing of inventory, supply chain control, and proper staffing. The truth is that many organizations aren’t good at forecasting. This leads to poor market operations, hence losses and wastes. Improving the forecasting will greatly propel the effectiveness of Meal Machine.
Thirdly, we will introduce thinking that is customer-centric. The key point here is putting the customer first. We should put ourselves in the position of our customers to determine what they need from us. A customer-centric strategy for a company is truly incredibly efficient ( Crespo Marquez , Bianchi & Gupta, 2018).
Fourth, we will employ some old-fashioned re-engineering of the business process (Crespo Marquez, Bianchi & Gupta, 2018). By effective re-engineering of our process, the business will identify the wasteful procedures regarding how best the business can undertake and develop more efficient processes. Reengineering, however, requires the maximum involvement of the employees because they are the ones who have the vital knowledge on how things are done.
Primary and Support Activities
Value chain normally separates the activities of an organization into nine activities. Four activities belong to the support category while five belong to the primary ones. The support activities are the infrastructure of the firm, procurement, development of technology and human resource management. On the other hand, the primary activities are operations, inbound logistics, outbound logistics, sales and marketing, and service (Kunchala, 2018).
Inbound logistics in Meal Machine will deal with receiving, warehousing, management of inventory and controlling the input resources. Operations are the activities that create value in which input are transformed into outputs. Outbound logistics in Meal Machine will be involved accessing the final goods and services to the buyer through warehousing, order fulfillment and more. Sales and marketing involve devising strategies to get the buyer to buy the good or service through a selection of the channel, advertising and promotion, pricing and many more. Service activities are activities that improve the value of the product by customer support, maintenance and many more. The mentioned activities have been found to be generic and each of them involves precise operations that vary in every business sector (Kunchala, 2018).
In supportive activities, procurement in Meal Machine involves buying the raw materials and other inputs used in creating the value of firm activities. Development in technology deals with research and development, mechanization of the process and the technological advancements to support the activities of the value chain. Human resource management in Meal Machine involves the hiring of staff, continuing to make developments and training and compensation of the employees (Kunchala, 2018). Lastly, firm infrastructure is concerned with activities that involve the legal, quality management, financial resources among others.
Conclusion
This paper clearly and effectively expressed the Organizational Plan and Operational Plan for the food truck business Meal Machine. We analyzed and explained of the Organizational Plan, including: the configuration of the management team including: Jessica as CEO and General Manager with management experience, Tanya as CMO with Entrepreneurial background and focus, Mays as CFO with Accounting experience and emphasis and Saah as the Public Relations Manager and Event Coordinator with a framework built on developing relationships and cultivating community affiliations; an outline of the McKinsey 7-S Model discussing our strategies, structure, systems, shared values, style, staff and skills and how we will use this model to identify our strengths and weaknesses and improve our business; a description of how the business-level strategy corresponds with the corporate-level strategy via customer-centric focus and learning from previous mistakes.
Moreover, the Operational Strategy was assessed and conveyed including the details of: the supply chain our organization uses including raw materials, our production chain, and delivering the final product to the consumer and how our organization brings value into the supply chain by purchasing locally and supporting the community; the main partners and suppliers of the organization including local grocers, growers, and farmers which can be located in any area we service and the contingency plan in place for the organization which allows us to use our flexibility to purchase from the great variety of available local grocers, growers and farmers; how our organization will optimize its operational effectiveness by focusing on our customers and our quality; and lastly a discussion of our primary and support activities including financial, human resources, and information systems management from the perspective of a value chain.
References
Crespo Marquez, A., Bianchi, C., & Gupta, J. (2004). Operational and financial effectiveness of e-collaboration tools in supply chain integration. European Journal of Operational Research, 159(2), 348-363. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2003.08.020
Hitt, M. A., Hoskisson, R. E., & Ireland, R. D. (2015). Strategic management: Competitiveness & globalization: Concepts (11th ed.). Stamford, CT: Cengage Learning
Jurevicius, O. (2013, December 20). Conquer the Challenge of Expansion with McKinsey 7s. Retrieved from https://www.strategicmanagementinsight.com/tools/mckinsey-7s-model-framework.html
Kunchala, K. (2018). Value Chain Analysis: Primary & Support Activities. Retrieved from http://www.mbahelp24.com/value-chain-analysis-primary-support-activities/
Montelongo, O. (2017, February 08). 10 Must-Visit Farmers Markets in Metro Phoenix. Retrieved from https://www.phoenixnewtimes.com/restaurants/10-must-visit-farmers-markets-in-metro-phoenix-9030386
Myrick, R. (2017). Food Truck Financial Expenses For Your Business Plan. Retrieved from https://mobile-cuisine.com/business-plan/food-truck-financial-expenses-business-plan/
Park, K. (2010, July 20). 15 Case Studies on Local Food Supply Chains. Retrieved from http://publications.dyson.cornell.edu/docs/smartMarketing/pdfs/SmrtMktg Jul2010.pdf
Porter, M. E. (2015, May 20). How Competitive Forces Shape Strategy. Retrieved from https://hbr.org/1979/03/how-competitive-forces-shape-strategy
Tice, W. (2011, October 26). McKinsey 7S Model: A strategic assessment and alignment model. Retrieved from https://whittblog.wordpress.com/2011/04/24/mckinsey-7s-model-a-strategic-assessment-and-alignment-model/



