Part 1: Analyze a Financial Statement of an Institution: *** (Length 2 pages) ***Please use the attached financial statement of the “sample University “to answer the below using appropriate headin
| NM | NM | = nonmetal | -3 | -2 | -1 | NM | ||||||||||||
| +1 | +2 | md | = metalloid | md | NM | NM | NM | NM | NM | |||||||||
| +1 | +2 | +3 | md | NM | NM | NM | NM | |||||||||||
| +1 | +2 | +2 | md | md | NM | NM | NM | |||||||||||
| +1 | +2 | +1 | md | md | NM | NM | ||||||||||||
| +1 | +2 | md | NM | |||||||||||||||
| +1 | +2 | |||||||||||||||||
Type I Binary Ionic Compounds
Type I binary ionic compounds contain a metal and a nonmetal AND the metal that is present only forms one type of cation. Metals with only one cation (shaded below with charges). Both the metal and the nonmetal form ions, which is why it is called an ionic compound.
From the following list, cross out those compounds that do NOT belong in the category for Type I binary ionic compounds.
NaCl FeCl2 CaCl2 TiO2 MgO AlBr3 KCl K2S BeF2 Cu2O3 AgCl Zn3N2
Formula and name examples for Type I binary ionic compounds:
KI = potassium iodide BaO = barium oxide ZnF2 = zinc fluoride Na2S = sodium sulfide
Ag3N = silver nitride BeCl2 = beryllium chloride
What type of element is always listed first (metal or nonmetal)? ____________ second? ___________
Is the name of the first element in the compound different from the element? (yes/no)
What is the common ending for all the names? ______________
In zinc fluoride, there are 2 fluoride atoms, are they indicated in the name? (yes/no)
What is the charge on the zinc ion? _______
What is the charge on the fluoride ion? _______
Why do you need one zinc ion and two fluoride ions for the formula for zinc fluoride?
Why do you need two sodium ions for every sulfide ion in sodium sulfide?
As a team, determine the rules for naming type I binary ionic compound when given the formula.
As a team, determine the rules for writing the formula for a type I binary compound when given the name.
Name each of the type I binary ionic compounds listed in question 1.
Type II Binary Ionic Compounds
Type II binary ionic compounds also contain a metal and a nonmetal however the metal that is present here can form more than one type of cation. Metals with multiple possible charges are listed in the periodic table as blank. Type II metals are NOT Type I metals. Again, both the metal and the nonmetal form ions, and it is still called an ionic compound. These metals usually only form two different ions.
From the following list, cross out those compounds that do NOT belong in the category for Type II binary ionic compounds.
AlP FeCl2 Ag2O VBr5 CoS SnF2 K3N SrF2 CuBr AuCl3 ZnO HgS
Formula and name examples for Type II binary ionic compounds:
Fe2O3 = iron(III) oxide or ferric oxide FeO = iron(II) oxide or ferrous oxide
CuS = copper(II) sulfide or cupric sulfide CuCl = copper(I) chloride or cuprous chloride
MnO2 = manganese(IV) oxide or manganic oxide MnCl2 = manganese(II) chloride or manganous chloride
What type of element is always listed first (metal or nonmetal)? ____________ second? ___________
Is the name of the first element in the compound different from the element? (yes/no)
What is the common ending for the nonmetal portion of the names? ______________
In the compound FeO, what is the charge on iron? _______
In the compound Fe2O3, what is the charge on iron? ________
What does the Roman number after the metal name represent?
When the metal name ends in –ic, to what ion does it refer? (higher charge/lower charge)
When the metal name ends in –ous, to what ion does it refer? (higher charge/lower charge)
As a team, determine the rules for naming type II binary ionic compound when given the formula.
As a team, determine the rules for writing the formula for a type II binary compound when given the name.
Name each of the type II binary ionic compounds listed in Question 1 of Type II section.
Type III Binary Compounds
Binary compounds that do not contain metals have covalent bonds instead of ionic bonds. A covalent bond is formed by sharing one or more pairs of electrons. The pair of electrons is shared by both atoms. For example, in forming H2, each hydrogen atom contributes one electron to the single bond.
From the following list, cross out those compounds that do NOT belong in the category for binary compounds containing only nonmetals or metalloids.
CCl4 AlCl3 CO SeF6 SiO2 SrI2 P4O10 TiO2 SeO3 IrCl ZrO2 N2O5
Formula and name examples for Type III binary ionic compounds:
CO2 = carbon dioxide H2O = dihydrogen monoxide
IF5 = iodine pentafluoride BF3 = boron trifluoride
Which element is listed first in the name?
Is the name of the first element in the compound different from the element? (yes/no)
What is the common ending for all the names? ______________
What do the prefixes (di-, mono-, penta-, tri-) in the names above mean?
Is the prefix mono- used when there is only one atom of the first element? (yes/no) Is the prefix mono- used when there is one atom of the second element? (yes/no)
As a team, determine the rules for naming type III binary ionic compound when given the formula.
Name each of the type III binary compounds listed above.
Compounds Containing Polyatomic Ions
Polyatomic ions are ions that as a group have a set charge. Polyatomic ions are usually recognized in a formula by the grouping of more than one nonmetal elements after a metal. Your book has a table listing polyatomic ions. Use your book’s table to fill in the following table with the appropriate names/formulas of the polyatomic ions.
| Name | Formula | Name | Formula |
| ammonium | chlorite | ||
| nitrate | C2H3O2-1 | ||
| NO2-1 | CrO4-2 | ||
| OH-1 | carbonate | ||
| cyanide | SO3-2 |
P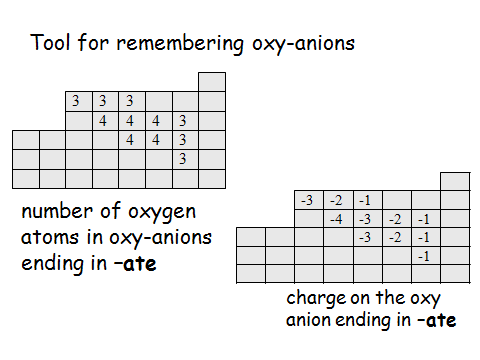 olyatomic ions containing oxygen (oxyanions) are somewhat special.
olyatomic ions containing oxygen (oxyanions) are somewhat special.
carbonate = CO3-2
Match the location of carbon on the periodic table with the two figures on the right.
What number is in the carbon location on the left figure? To what does this number refer?
What number is the carbon location on the right figure? To what does this number refer?
What element must all oxyanions contain?
What is the ending of the name of the ion determined from these tables?
Determine the formula for the following oxyanions using the figures above. Phosphate _________ Silicate ________ Bromate ________ Iodate ________ Sulfate ________ Nitrate ________
perchlorate = ClO4¯ chlorate = ClO3¯ chlorite = ClO2¯ hypochlorite = ClO¯
When comparing the oxyanions above, is the charge of the chlorate ion the same as the charge for the other chloro-oxyanions?
How many less oxygen atoms does chlorite have compared to chlorate?
How many more oxygen atoms does perchlorate have compared to chlorate?
How many less oxygen atoms does hypochlorite have compared to chlorate?
What name ending(s) can help you identify the presence of an oxyanion in a compound?
If sulfate is SO4-2, what would the formula for sulfite be?
In the table below, fill in the name and formula for the oxyanions in the shaded column. Use the figures on the previous page
In the table below, fill in the name and formula for the rest of the oxyanions.
| Element | per-___ -ate ion | ____-ate ion | _____-ite ion | hypo-____-ite ion |
| Bromine (Br) | ||||
| Iodine (I) | ||||
| Phosphorus (P) | ||||
| Nitrogen (N) |
Use your knowledge of Type I and Type II metals as well as the appropriate polyatomic name/formula to fill in the following table.
| Name | Formula | Name | Formula |
| sodium carbonate | Cu(NO2)2 | ||
| iron(II) nitrate | calcium sulfate | ||
| MnSO4 | ammonium nitrate | ||
| Ca(ClO)2 | KCN |
Check your work:
Were the polyatomic ions correctly identified for the above table? Remember when you have parentheses, you must identify the polyatomic ions by looking inside the parentheses and the numbers outside the parentheses just indicate how many of that polyatomic ion you have.
Are the compound formulas you filled into the table above neutral in charge?
Do all type II metals in the table above have their charge indicated by either a Roman numeral or their Latin name with an –ous or –ic ending?
Are all type I metals listed without a Roman numeral?
Acids
Acids are compounds that when dissolved in water, produce hydrogen ions (H+). Naming acids can also be tricky. Use the following chart and try to classify each acid below to an area on the chart.
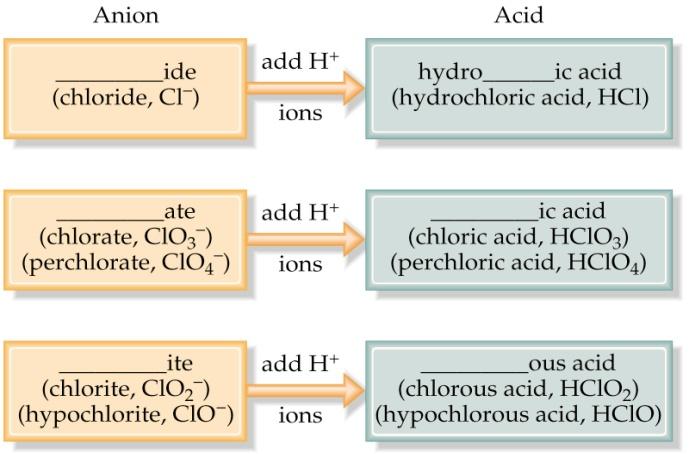
Given that the ion formula is NO2-1, how can one determine the name of the ion, acid formula, and acid name?
Ion name:
1) Based on the –ate determination figures, what is the formula for nitrate? Is NO2-1 the nitrate ion or the nitrite ion?
Acid formula:
According to the figure above, what must be added to create an acid? What is the charge of the ion?
How many of the hydrogen ions must be added to NO2-1 to make a neutral acid (zero charge)?
What is the acid formula for the acid created when hydrogen ion(s) are added to NO2-1?
Acid name:
Based on your answer to Question 1 above, does the name for the NO2-1 ion end in –ite or –ate?
Use the figure above to determine how the name changes when we have the compound HNO2. Name the acid, HNO2.
Fill in the following table:
| Acid Formula | Acid Name | Ion Formula | Ion Name |
| HCl | hydrochloric acid | Cl¯ | chloride |
| NO3¯ | |||
| sulfuric acid | |||
| HBrO3 | |||
| PO4-3 | |||
| HBr | |||
| carbonic acid | |||
| C2H3O2 ¯ |
Page 8 of 8



