1) Word count: 350 words plus minus 10% no more than that 2) References: Chicago format 3)Use "Outsourcing" as the recommendation 4) Refer to "BUS296 - TMA 2019 UILG" page 8 for journal articles to b
Introduction
SMRT Corporation Ltd (SMRT) is a public transport service provider that established in 1987. Their primary business is to provide, manage and operate train services on the North-South Line, East-West Line, Circle Line, Bukit Panjang Light Rail Transit and the upcoming Thomson-East Coast Line (SMRT Corporation 2019).
Positioning Map
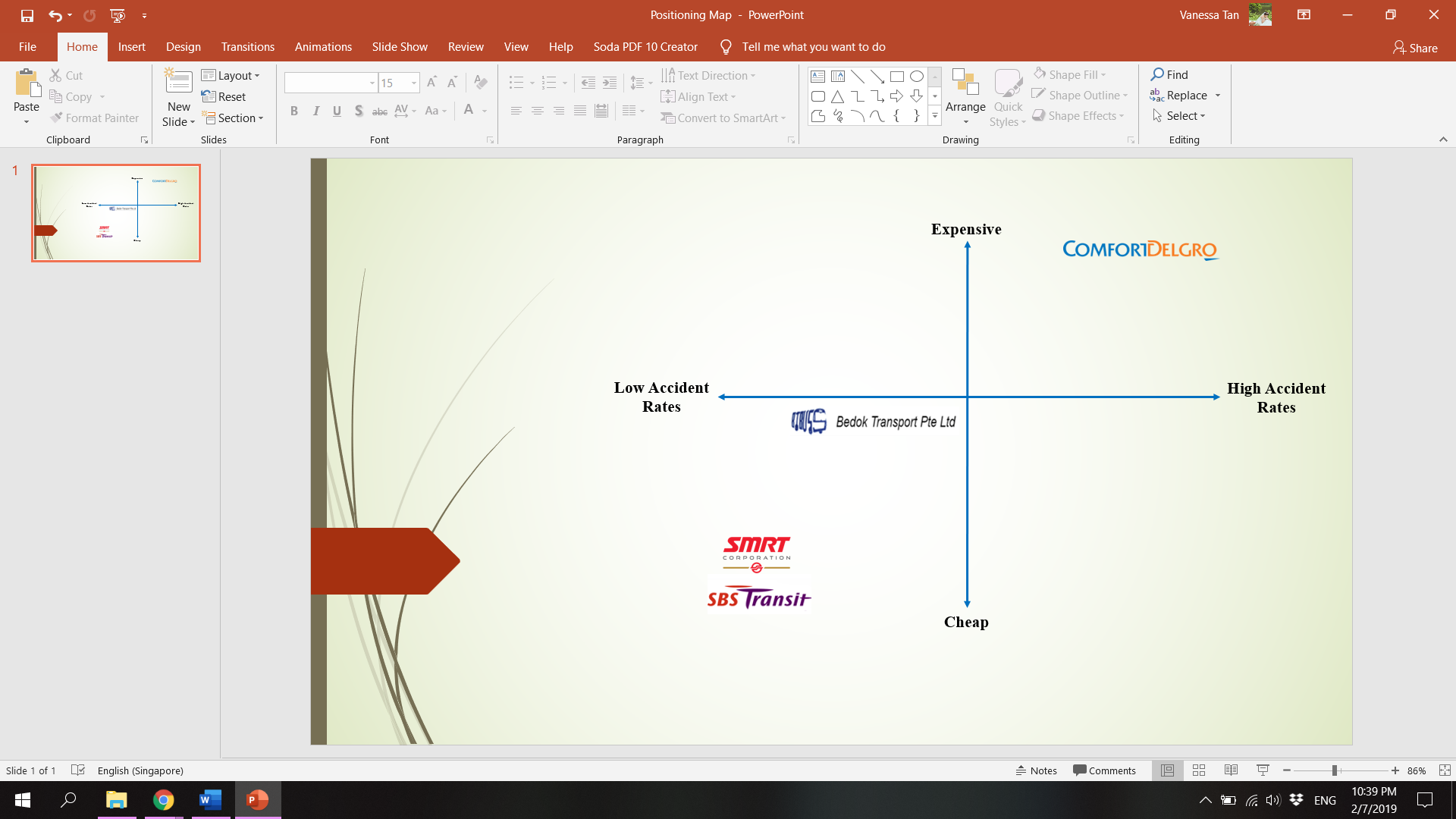
Situational Analysis
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
SMRT train service is a safe and secure mode of transport with least number of fatalities over the last 32 years since its establishment.
SMRT is the largest train service operator with over 75% share of the nation’s rail length in Singapore.
Weaknesses
There are insufficient maintenance staffs to perform maintenance works on the track, trains and wiring to ensure that such incidents of track faults, train faults and power faults are greatly reduced. Commuters begin to lose trust in SMRT due to the frequent breakdown of trains and all the track faults that occurs especially during peak hours leading them to think that the trains are not dependable. This had resulted in negative disconfirmation of the commuters and sharing their negative experiences on their social media.
There is a delay in the announcement to the commuters when there are any train delays due to track faults or train faults. Not only that, SMRT service staff were not equipped with the necessary skills and crisis management plans to brighten the mood of the commuters.
Opportunities
SMRT can consider to tie-up with international players to expand to overseas for exposure.
SMRT can also consider to expand its taxi and bus segments within Singapore.
Threats
The revenue for its fares business could remain stagnant as it is regulated by the Public Transport Council.
SMRT could have lose its rail market share if it loses its new rail tenders to competitors
Concluding from SWOT Analysis
Due to the insufficient manpower to perform the regular track and train maintenance work which lead to the often breakdown and delay in the train services, SMRT must seek to address this issue so as to reduce the number of service failure.
Target Market
The target market consists of commuters, both genders, all races and ethnic groups that are living, working and studying in Singapore. Their education level ranges from pre-school onwards These are the commuters that uses the transportation daily for leisure, schools and work purpose.
Positioning
SMRT Corporation Ltd their vision is moving people, enhancing lives. Their mission is to be the people’s choice by delivering a world-class transport service and lifestyle experience that is safe, reliable and customer-centric. SMRT believes that with a safe and reliable transport services, it helps to enhance the lifestyle experience of their commuters. SMRT core values are 1) Safety & Service Excellence 2) Mastery 3) Responsibility & Respect 4) Teamwork 5) Nurture and 6) Integrity (SMRT Trains 2018).
Marketing Objectives
To reduce the time taken for its service recovery measures to less than 5 minutes by 31 July 2020.
To reduce the number of complaints to no more than one per month by 31 July 2020.
To achieve 70% of market share by 31 July 2020.
Audit
The service failure is a train fault that affected the East-West Line on 15 March 2019, Friday morning during rush hour. At 5.45am, a train fault occurred near Clementi MRT station and affected the stations between Jurong and Queenstown. Due to the train fault, it affected the North-South Line which is the interchange for East-West Line at Jurong East station. SMRT tweeted before 7am to inform commuters that an additional 30 minutes is to be added to their travelling time due to a track fault. At 7am, train services at the affected stations resumed progressively. However, few minutes later, train services went down again and at 7.10am, SMRT tweeted that free bus services were available. Train services was not cleared as of 7.50am.
4.1 People
The service failure had caused a lot of inconvenience to the commuters due to the delay. Most commuters travel on scheduled trips. If you get late for some few minutes, you may miss a crucial function. Commuters value their time very much. A single second wasted could have significant negative impacts on the commuters. Some commuters are traveling to work, others, to school, others to catch a flight. Delaying their trip means that either someone will be late to work, late to class or even end up missing a flight. The company damaged their reputation just by causing such delays. No commuter would want to use services for a company that does not value their time. Even the most loyal customers will turn against you if you don’t provide quality services. The failure to conduct enough research early enough to mitigate the problem has caused many commuters to look for other options of transport. It significantly affects the organization as they are losing their customers to their competitors (Gummesson 2017, 17).
Although SMRT may come up with strategies to reduce the incidence of delayed trips, that will not convince commuters to trust them again. Since its inception, the organization has been operating efficiently until recently where it has experienced inconveniences and delays in its operations. As a commuter, it feels so bad for a trusted organization to waste your valuable time that you could otherwise be doing something constructive. The management of the company needs to conduct extensive research as soon as possible to determine the cause of the delays and develop appropriate strategies to mitigate the problem (Erevelles 2016, 901).
4.2 Mood States
According to mood state theory, it aims is to determine the emotional state of commuters as they are using the services provided by SMRT Corporation. Service environments play an important role in service delivery because environments can reach a positive reaction, while strengthening customer perceptions and retention (Jiun-Sheng 2011, 355). However due to the track fault on the 15 March 2019, it has caused a delay in commuting especially for East-West Line and the North-South Line which are the two longest routes as compared to the other lines provided. This hence would delay many more commuters that are commuting to their destination as the fault was ratified a few hours later. This service experience has led to commuters feeling frustrated as it would cause them to be late in heading to their destination. Not only did the fault cause frustrations, there are other factors as well such as packed train stations that leads to humidity which fuel the frustration by the commuters. A company employing proactive interaction focuses on anticipating future events by learning from mistakes and by predicting potential failures and taking preventive initiative to change or control future outcomes (Shin 2017, 167) However SMRT has failed to engage in proactive interaction which hence led to many negative disconfirmation. All these frequent train faults have led to commuters having brand loyalty and faith in the service provided by SMRT Corporation. Not only did the train fault happen, SMRT Corporation took about an hour before free buses were available to those commuters that are affected by the delay. All these negative disconfirmations has led to less brand loyalty due to negative emotions by the commuters and hence negative feedback were spreading over the social media and other internet platforms. The service staff from SMRT Corporation did not reach out to the commuters to lighten their mood and hence this is a failure as well from them.
4.3 Financial Risks
The increase in the financial risk has resulted in the commuters negatively perceive that it is not reliable in engaging SMRT services when they have an important event or meetings to attend. This is because there is no value in consuming its services as eventually, the service failure had resulted in the commuters to seek other modes of transportation to the said destination.
Based on the Journal of Marketing, commuters make a service purchase based on financial risks consideration (Petersen 2015, 45). When they find that a service is unreliable and will have greater to their financial risks, they will not be loyal to SMRT during urgent agenda of that day.
SMRT will lose its royal commuters when a service failure happen as commuters will not take risks in taking their free shuttles provided by SMRT because the affected commuters crowd is large and time to queue to get on the shuttle will further delay the time to reach the destination. As there is no monetary compensation for service failure as such, most commuters will not be satisfied with SMRT as it disrupts their expenses on that day. Commuters were forced to spend additional on alternative mode of transport to reduce the impact on the event of their day. The situation during service failure can affect the satisfaction of the commuters in engaging the SMRT services again and make a switchover decision (Riaz 2016, 421).
Erevelles, Sunil, Nobuyuki Fukawa, and Linda Swayne. 2016. "Big Data consumer analytics and the transformation of marketing." Journal of Business Research 62 (2): 897–904. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2015.07.001.
Gummesson, Evert. 2017. "From Relationship Marketing to Total Relationship Marketing and Beyond." The Journal of Services Marketing 31 (1): 16-19. http://libproxy.murdoch.edu.au/login?url=https://search-proquest-com.libproxy.murdoch.edu.au/docview/1862042489?accountid=12629.
Jiun-Sheng, Chris Lin and Liang Haw-Yi. 2011. "The Influence of Service Environments on Customer Emotion and Service Outcomes." Managing Service Quality 21 (4): 350-372. http://libproxy.murdoch.edu.au/login?url=https://search-proquest-com.libproxy.murdoch.edu.au/docview/875621001?accountid=12629.
Petersen, J. Andrew, Tarun Kushwaha, and V.Kumar. 2015. "Marketing Communication Strategies and Consumer Financial Decision Making: The Role on National Culture." Journal of Marketing 79 (1): 44-63. https://www-jstor-org.libproxy.murdoch.edu.au/stable/43784381.
Riaz, Zeeshan and Ishfaq Khan Muhammad. 2016. "Impact of Service Failure Severity and Agreeableness on Consumer Switchover Intention." Journal of Marketing and Logistics 28 28 (3): 420-434. http://libproxy.murdoch.edu.au/login?url=https://search-proquest-com.libproxy.murdoch.edu.au/docview/2080876644?accountid=12629.
Shin, Hyunju, Alexander E. Ellinger, David L. Mothersbaugh, and Kristy E. Reynolds. 2017. "Employing Proactive Interaction for Service Failure Prevention to Improve Customer Service Experiences." Journal of Service Theory and Practice 27 (1): 164-186. http://libproxy.murdoch.edu.au/login?url=https://search-proquest-com.libproxy.murdoch.edu.au/docview/1857602224?accountid=12629.
2019. SMRT Corporation. Accessed June 28, 2019. https://www.smrt.com.sg/About-SMRT/Our-Identity.
SMRT Trains. 2018. "Trains Operations Review 2018." Operations Review.



