Discussion Management of Information Systems Cultural and Legal Differences Discuss cultural norms or laws of one country that differs from the norms or laws of another country. Give an example of the
Week 5 Lecture 1 - Challenges of IS
Management of Information Systems
Challenges of IS
The Internet connects people and organizations from all over the globe. The Internet significantly reduces physical distances between trading organizations and time zone limitations on trade speed. Without the Internet, global commerce would decrease, and business travel and extended business transactions would increase. The Internet facilitates global trade through its compression of distance and time.
Although the Internet has made connecting easier, the world consists of a massive quantity of significantly diverse cultures. The world is becoming a global village. However, in international commerce, there are still cultural differences to consider. Cultural differences can be found between Middle Eastern, European, Asian, African, American, and other regions. Cultural differences can be demonstrated by different perspectives, different ways of dress, individualism, collectivism, power distance, ethics, and human rights policies.
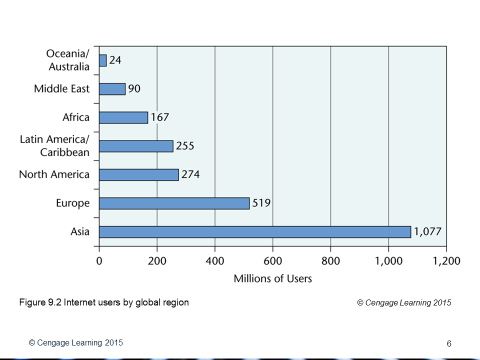
Figure 5 Internet users by global region © Cengage Learning 2015
The web facilitated the global exchange of information which spurred global business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-consumer (B2C) commerce. Global companies must tailor their websites to local consumers. These companies must offer websites in the local language of the consumer. Ideally, local teams should maintain the local versions of websites.

Figure 6 Percentage of non-English speaking Internet users © Cengage Learning 2015
When designing, or planning global information systems, particularly Web, or mobile technologies, legal, cultural and other differences in implementations must be taken into account. While assessing whether to leverage IT for international communication and commerce, significant challenges must be considered. Some challenges are technological barriers, regulations, tariffs, electronic payment mechanisms, different languages, cultures, economics, and political considerations. Another challenge, in addition to legal and cultural issues, is the integration of disparate supply chain management systems. Legal considerations are differences and copyright laws, differences in consumer protection, and differences in privacy laws.
Week 5 Lecture 2 - Decision Support and Expert Systems
Management of Information Systems
Decision Support and Expert Systems
Structured and unstructured problems
A structured problem has a process to solve it already defined. An unstructured problem has a number of factors that may not be fully understood, to consider and no defined process by which to solve it. Most problems faced by managers are on a spectrum between structured and unstructured; these are called semi-structured problems.
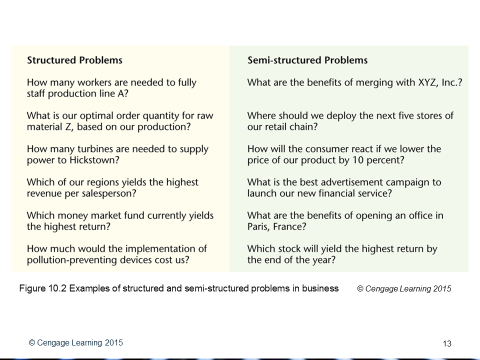
Figure 7 Structured and semi-structured problems © Cengage Learning 2015
A fully unstructured problem is one that does not allow the manager to select rationally any manageably small number of alternatives from which to select the optimal one.
Decision Support System
A sensitivity analysis is a what-if test that measures the degree that a change in one factor will affect other factors. Decision support systems (DSSs) are used to save time in decision-making. A DDS is a computer-supported information system designed to help knowledge workers select alternatives in problem solutions. A spreadsheet is an excellent tool for building a DSS since it offers other calculations, and functions for statistical and financial analysis.
Spreadsheet programs are an excellent tool for building DSSs thanks to their good modeling power. They offer many arithmetic, statistical, and financial analysis functions. If the students already know how to use net present value formulas, you may want to assign the building of a simple DSS to analyze the NPV of three or four alternative investment options. After they decide which alternative is the best, they should answer the question “How would your answer change if the interest rate goes up by 2% per annum?” This demonstrates a “what if” analysis.
Expert System
When it is not possible to exploit a DSS, an expert system can be used to solve problems and make decisions in a relatively narrow domain. An expert system emulates the knowledge of an expert to solve problems and make decisions.



