Good day, I am seeking assistance to review 2 papers and write 1 rubric for each paper.
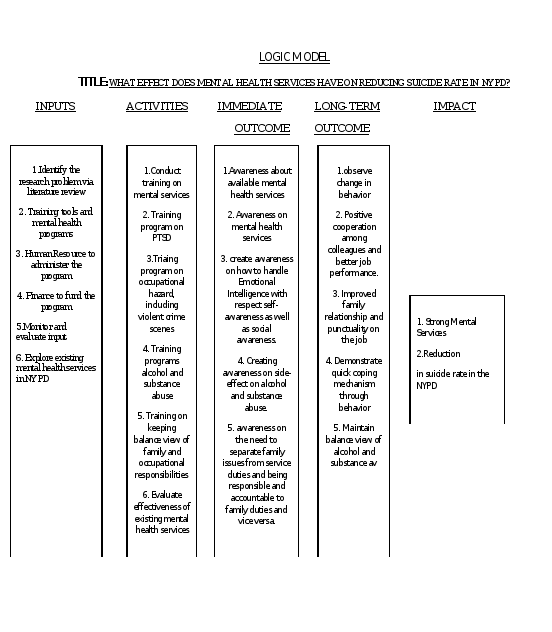
TITLE : HOW CAN MENTAL HEALTH SERVICES IN NYPD BE IMPROVED IN PREVENTING SUICIDE
RESEARCH QUESTION: What effect does mental health service in NYPD have on reducing suicide tendencies among NYPD?
GOAL: The goal is to explore how evidence based mental health services can help reduce suicide rate among NYPD officers.
OBJECTIVE 1: to explore the effectiveness of the current mental health services in the NYPD.
OBJECTIVE 2: Based on the finding from objective 1 to conduct a new mental health service to selected NYPD and evaluate its impact on suicide.
Hem, E., Berg, A., & Ekeberg, &. (2001). Suicide in Police—A Critical Review. Suicide and Life‐Threatening Behavior, 31(2), 224-233.
The article discusses that police officers are a high-risk group for suicide tendencies. They are often exposed to violent crime scenes which may sometime cause fear on the job. As the article explores the recent worldwide studies on suicide rate among police officers. The results were that, while some articles show elevated suicide rates in suicide, other studies show inconsistent results. These findings suggest that there is the need for further systematic research. On the other hand, the review failed to address the effectiveness of the currently available to NPPD. Therefore, there is the need to explore the effectiveness of the current mental health services currently available to NYPD officers in coping with suicide tendencies.
Violanti, J. (2004). Predictors of Police Suicide Ideation. Suicide and Life‐Threatening Behavior, 34(3), 277-283.
The second literature review shows that further inquiry in processes that leads to suicide in the police occupation is necessary. How? The study mentioned some major contributing factors leading suicide tendencies in police occupation. The article focuses on psychological traumatic police work experience, the development of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in officers, and the inordinate use of alcohol associated with this condition. Furthermore, the study focuses on symptoms, causes and prevention. Therefore, the combined impact of PTSD and alcohol abuse led to a ten-fold increase risk for suicide ideation. Several demographic correlates of suicidal ideation have been found to include age, gender, ethnicity, marital status and social support. Moreover, psychosocial correlates of ideation are depression, family discord, personal stress and abuse of alcohol. Studies of PTSD is unique symptoms brought about by exposure to a traumatic and most often violent crime scenes which may cause intense fear on the job. Studies of veterans with PTSD have reported an increase risk of suicidal behavior. the review failed to explain if any, the effectiveness of mental health services available to suicide ideation within the police force in the NYPD. Therefore, there is the need to conduct a study specifically on the effectiveness of mental health services in the NYPD.
Arnetz, B. B., Arble, E., Backman, L., Lynch, A., & Lublin, A. (2013). Assessment of a Prevention Program for Work-related Stress among Urban Police Officers. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 86(1), 79-88. doi:http://dx.doi.org.lehman.ezproxy.cuny.edu/10.1007/s00420-012-0748-6
The method used was ANOVA. In this, a random sampling of 37 police cadets received complementary training in psychological and technical techniques to reduce anxiety and enhance performance when giving a series of police critical incidents. Then there was another random sample of 38 cadets also receiving training as usual was followed in parallel. Assessment of somatic and psychological health and stress biomarkers was done at baseline, immediately following training and 18 months as a regular officer. Comparison was done using two-way repeated analysis of variance (ANOVA) and logistic regression. The findings were as follows: (1) the results show that, the intervention group improved their general health and problem-based coping as compared to the control group. (2) they also demonstrated lower levels of stomach problems, sleep difficulties, and exhaustion. The training was associated with an OR of 4.1 (95% CI, 1.3-13.7; P< 0.05) improved GHO. The study reveals that somatic symptoms such as coping, mental well-being, sleep quality, exhaustion, blood hormone sampling and analysis and statistics was conducted in the control and the intervention groups. Series of logistic regression models were reviewed to compare the two groups improvements across the study’s duration. In this, three such models were tested and adopted. the study discusses that preventive mechanism by way of training can reduce suicide tendencies.
Loo, R. (2003). A Meta‐Analysis of Police Suicide Rates: Findings and Issues. Suicide and Life‐Threatening Behavior, 33(3), 313-325.
Meta-analysis is a quantitative formula. It is an epidemiological study design used to systematically assess the results of previous research to derive conclusions about the body of the research. The study was conducted using (101) sample from the literature. The review identified issues researchers need to address, which includes the use of long-time frames. The reporting of more complete suicide statistics, including breakdowns by year, sex, and ethnic groups; and the rates for population comparison groups. The study gave further evidence of rate of suicide across different regional groups and population comparison. The review also showed true suicide rate is higher than officially reported rate. Regarding suicide ratio, it is important to note that the review identified that police suicide neglect important information about population suicide rate which is very essential in evaluation within the larger context of suicide in different countries and regions around the world. The increase rate in some places were not uniform, while decrease rates were due to under reporting. Therefore, there is the need to conduct a new study to determine the current trend in police suicide and design effective mental health service program and reduce suicide tendencies among NYPD officers.
Janik, J., & Kravitz, H. (1994). Linking Work and Domestic Problems With Police Suicide. Suicide and Life‐Threatening Behavior, 24(3), 267-274.
The review specifically mentioned increase rate of suicide in New York, Chicago and some other major cities around the world. Tennessee, London and Canada. The study found that harassment by administrators may exert a protective effect against attempting suicide. Therefore, those who are primarily concerned with harassments, rather tends to ignore other existing problems simply because, they focus unidirectionally on the harassment to the exclusion of all others, perhaps denying their other problems. Some officers feel increasingly isolated from members of their administration. officers cite stress from administration who they feel may not be knowledgeable about their street experiences. Interestingly, the study shows that, the general mortality rate of police suicide occurred due to improved medical procedures, better training and wearing of bulletproof vests. These findings prove that there is the need to evaluate the current mental health services in the NYPD in order to redesign, improve and ensure effectiveness on mental health services to reduce suicide rate in the NYPD.
Introduction:
Police suicides are usually caused by many stressors. Police occupation itself is a high risk due to work overload, shift work, and exposure to violent and life-threatening situations, among other many other factors. On the other hand, the police organization is another source of stress due to departmental protocols, as well as local and federal policies. For instance, there is the lack of support and proper recognition from management and the autocratic leadership styles. Work-shift, temporal assignments, temporal postings and transfers create a huge burden on police families. Unfortunately, family disruptions can also contributing factors in police suicide tendencies. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorders (PTSD), alcohol and substance abuse are benign factors that can potentially trigger suicide tendencies in the NYPD as established in the above review.
Therefore, as indicated above there is the need to conduct studies into police suicide and determine causes and symptoms in order to design effective mental health training programs to reduce police suicide in the NYPD. Different stages of evaluation including surveys should be conducted during the study. Other area of interest in the study includes racial and gender bias. Gays, lesbians and transgender (LGBT) discrimination within the NYPD.
The contributing factors are not studied well especially among NYPD officers. Therefore, the current proposal will explore existing mental health service that is given to NYPD and based on the findings design a new mental health program to reduce the suicide rate among NYPD.
BODY:
The study showed that there is an increase of suicide rate among police officers because of the unique nature of the job1. The police officers occupation is one of the most highly risk for suicide tendencies. There is many reasons for this. Police officers are constantly expose to violent crime scene. The task of police is very stressful job by its nature. The findings from the review as already noted indicate that there is the need to conduct new study within the NYPD in order to validate the research question above. The review show that most of the data are out-of-date and therefore current study is required. A systematic and methodical study into nationwide and specifically NYPD suicide is required in order to accept or reject the proposed Hypothesis.
Previous studies have found many contributing factors to police sucide2. PSTD is one of the contributing factors the paper discussed. The second contributing factors is alcohol use. The third contributing factor …In the second article review, the focus was on PTSD as a contributing factor of police suicide due to the traumatic and violent crime scenes that officers are exposed to while on duty. However, the article failed to show or explain what is causing the PTSD among NYPD. The article also failed to explain what if any coping mechanism is available by way of mental health services to deal with PTSD. This is a mental health problem and requires mental health services to solve the problem.
The ANOVA method used in the third review shows that the invention group improved better with coping mechanism such as mental well-being, sleep quality, exhaustion etc. therefore studies using the ANOVA method is needed conduct studies in the NYPD or the above-mentioned research question
The fourth review on “Meta-Analysis show that more transparency from the police department nationwide is needed in order to establish a valid report on police suicide. The data from the review specifically on NYPD suicide was either out-moded or insufficient and therefore inconclusive. The NYPD local and federal law enforcement agencies need to cooperate fully with researchers and make data readily available so that more studies can be conducted in order to establish authentic and reliable data report on the subject.
The fifth article “Living Work and Problems with Police suicide” shows how harassment by administrators can exert negative pressure on officers even to the point of committing suicide. Therefore, constructive survey at regular intervals should be part of the mental health services offered to train officers before recruitment, in-service and after service.