12 slides excluding reference Team C: South Korea vs North Korea (Two polar economic opposites, one people) Research each economy assigned to your Team. Compare similarities and differences between yo
Running head: ECONOMICS 1
A comparative study of the economic systems of North Korea and South Korea
Name:
University:
Table of ContentsIntroduction 3
Literature Review 4
Discussion and Collection of Data 7
Analysis of Data 10
Result and Conclusion 11
References 12
Annexure 14
A comparative study of the economic systems of North Korea and South Korea
IntroductionComparative studies based on the economic systems in different countries are not easy to conduct. The comparison of two or more countries can be drawn on the basis of economic systems and other macro-economic variables. It requires in depth research and enormous capabilities in order to make economic comparison of two countries. This paper aims to develop comparison of North Korea and South Korea in terms of their economic systems. The economic system prevalent in North Korea and South Korea are different from each other (Gregory, Paul & Robert, 1985). In North Korea, centrally planned economy is in practice. All the decisions regarding market and other macro-economic factors are centrally planned. The markets involvement in the formation of economic system is low in North Korea. In contrary to North Korea, mixed economic system is prevalent in South Korea (Koo, Bon & Dongho, 1995). It means few decisions are centrally planned and others are planned by markets or private owners. In South Korea, there are family based conglomerates to operate the businesses. Hence, the apparent difference in economic systems of North Korea and South Korea is further elaborated in this term paper with the assistance of economic variables that are uniform in different economies. The comparative study is based on differences in financial system, resource allocation, statistical information, property rights and rural & urban economic system (Financial system of Korea, 2008).
Literature ReviewNorth Korea, one of the world's most halfway coordinated and slightest open economies, faces endless monetary issues. Modern capital stock is about destroyed as an aftereffect of years of underinvestment, deficiencies of extra parts, and poor upkeep. Extensive scale military spending draws off assets required for speculation and regular citizen utilization (Eberstadt & Nicholas, 2007). Mechanical and power yields have stagnated for quite a long time at a small amount of pre-1990 levels. Incessant climate related yield disappointments exasperated endless sustenance deficiencies brought on by on-going systemic issues, including an absence of arable area, aggregate cultivating hones, poor soil quality, deficient treatment, and constant deficiencies of tractors and fuel. All these factors and some other factors in this regard are beneficial for the purpose of this research paper.
The mid 1990s were set apart by serious starvation and far reaching starvation. Critical nourishment help was given by the universal group through 2009 (World Bank, 1995). Since that time, sustenance help has declined essentially. In the most recent couple of years, household corn and rice creation has been to some degree better, albeit residential generation does not completely fulfill request. A substantial segment of the populace keeps on torment from delayed ailing health and poor living conditions. Since 2002, the legislature has permitted casual markets to start offering a more extensive scope of products (Rodrik & Dani 1995). It additionally executed changes in the administration procedure of collective homesteads with an end goal to help farming yield.
In December 2009, North Korea did a redenomination of its money, topping the measure of North Korean won that could be traded for the new notes, and restricting the trade to a one-week window. A simultaneous crackdown on business sectors and outside cash use yielded extreme deficiencies and swelling, constraining Pyongyang to facilitate the limitations by February 2010. Because of the sinking of the South Korean warship Cheonan and the shelling of Yeonpyeong Island in 2010, South Korea's administration cut off most guide, exchange, and reciprocal participation exercises, except for operations at the Kaesong Industrial Complex. North Korea proceeded with endeavors to create exceptional monetary zones and communicated readiness to allow development of a trilateral gas pipeline that would convey Russian common gas to South Korea. North Korea is additionally working with Russia to restore North Korea's run down rail system and together reconstructed a connection between a North Korean port in the Rason Special Economic Zone and the Russian rail system.
The North Korean government keeps on focusing on its objective of enhancing the general way of life, yet has found a way to make that objective a reality for its people. In 2013-14, the administration took off 20 new monetary advancement zones - now totaling 25 - set up for remote financial specialists, in spite of the fact that the activity stays in its earliest stages. Firm political control remains the administration's abrogating concern, which likely will hinder changes to North Korea's present monetary framework.
South Korea in the course of recent decades has exhibited mind blowing monetary development and worldwide mix to end up a cutting edge industrialized economy. In the 1960s, GDP per capita was tantamount with levels in the poorer nations of Africa and Asia. In 2004, South Korea joined the trillion-dollar club of world economies. An arrangement of close government and business ties, including coordinated credit and import confinements, at first made this achievement conceivable. The administration advanced the import of crude materials and technology to the detriment of purchaser merchandise and supported funds and venture over utilization.
The South Korean economy's long haul challenges incorporate a quickly maturing populace, resolute work market, predominance of expansive combinations (chaebols), and the substantial dependence on fares, which contain about portion of GDP. With an end goal to address the long haul challenges and support monetary development, the present government has organized basic changes, deregulation, advancement of business enterprise and innovative ventures, and the aggressiveness of little and medium-sized undertakings.
Discussion and Collection of DataThe data related to the economic factors prevalent in economic systems of North Korea and South Korea is collected for comparative study of economic systems. The comparative study is based on differences in financial system, resource allocation, statistical information, property rights and rural & urban economic system (Republic of Korea, 2003). Facts, policies and figures related to different sectors in the economic system are useful informative gatherings for data analysis. Central Investigation Agency facts regarding the economic conditions of different countries are viable source for comparative study. The database of Central Investigation Agency is used for data gathering (Korea fact book, 2016). Therefore, secondary sources serve as major source of data mining for research purpose. Comparative study of economic systems is better conducted by using secondary research approach. Data from the reports of international organization research institutes is also collected in order to expand the scope of the research.
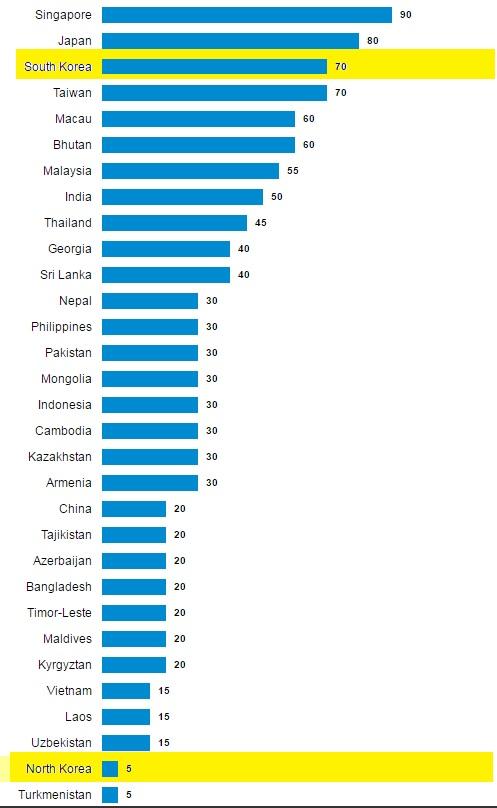
Similar variables are considered for collection of data related to economic systems of North Korea and South Korea. Property rights determine the difference in economic system of North Korea and South Korea. A subcomponent of the Index of Economic Freedom, the property rights list measures the extent to which a country’s laws ensure private property rights, and the extent to which its administration upholds those laws. Higher scores are more attractive, i.e. property rights are better ensured (Property Rights Index - North Korea Compared to Continent, 2015). Scores are from 0 to 100 (see annexures). The file likewise surveys the probability that private property will be seized and dissects the autonomy of the legal, the presence of defilement inside the legal, and the capacity of people and organizations to implement contracts. The Global Property Guide considers assurance of property rights as a critical component influencing the attractive quality of a private land venture.
The Asian money related emergency of 1997-98 uncovered longstanding shortcomings in South Korea's improvement model, including high obligation/value proportions and enormous fleeting outside acquiring. Gross domestic product dove by 7% in 1998, and after that recuperated by 9% in 1999-2000. South Korea embraced various monetary changes taking after the emergency, including more noteworthy openness to outside venture and imports. Development directed to around 4% every year somewhere around 2003 and 2007. Over the time period, the economic system of South Korea has generated reasonable outputs for country.
South Korea's fare centered economy was hit hard by the 2008 worldwide financial downturn, however immediately bounced back in resulting years, coming to more than 6% development in 2010. The US-Korea Free Trade Agreement was approved by both governments in 2011 and became effective in March 2012. Somewhere around 2012 and 2015, the economy experienced moderate development – 2%-3% every year - because of slow residential utilization and venture. The organization in 2015 confronted the test of adjusting substantial dependence on fares with creating residential situated segments, for example, administrations.
The difference in economic systems results in different economic outputs for different countries. Economics facts and figures can be used for measurement of economic systems effectiveness and appropriateness for economies. The other data for comparative study of North Korea and South Korea includes purchasing power parity index. North Korea purchasing power parity is equal to $ 40 billion in comparison to South Korean $ 1.849 trillion purchasing power parity. Property rights determine the difference in economic system of North Korea and South Korea. GDP of North Korea is $ 28 billion in comparison to $ 1.377 trillion GDP of South Korea. Agriculture, industry and services sectors of North and South Korea perform according to the prevalent economic systems. The composition of agriculture, industry and services sectors in GDP of South Korea is 2.3 %, 23 % and 59.7 % respectively. In contrary, the composition of agriculture, industry and services sectors in GDP of North Korea is 22 %, 47 % and 31 % respectively.
Analysis of DataThe data gathered related to the macroeconomic variables of economic systems prevalent in the North Korea and South Korea is analyzed for better understanding of the appropriateness of economic systems. The separation of Korea was resulted after the Second World War. With the passage of time, South Korea with mixed economic system has emerged as leading economy and is part of G-20 countries. The Pro American approach and the involvement of markets in the decision making process has led to the success of South Korea (Taylor, 2013). The economic system adopted by South Korea after the world war is mixed economic system and is in contradiction to the economic system of North Korea. North Korea economic condition is poor right now due to the centralized approach towards decision making in the prevalent economic system. In North Korea, centrally planned economy is in practice. All the decisions regarding market and other macro-economic factors are centrally planned. In contrary to North Korea, mixed economic system is prevalent in South Korea. It means few decisions are centrally planned and others are planned by markets or private owners. In South Korea, there are family based conglomerates to operate the businesses.
The factors considered for comparative study of North Korea and South Korea is all favorable for South Korea in comparison to North Korea. Right to property, wage system, financial viability and other developments in the South Korea are more than the outcomes in North Korea. The extracted data form the comparative study of North Korea and South Korea resembles success of market based economic system over the centralized economic system. The economic system in which markets are allowed to operate independently has more appropriate outputs than any other system. Over the time period, the economic system of South Korea has generated reasonable outputs for country. Gross domestic product and purchasing power parity along with other micro and macro-economic variables are more supportive for South Korea in the basis of economic system than North Korean economic system.
Result and ConclusionWhile concluding, the comparative study regarding the economic systems of North Korea and South Korea results and conclusions are drawn based on the data assembled and analyzed. This paper focused its attention on the economic systems which are in practice in North Korea and South Korea. The results of the comparative study are in support of market economic system. The use of market economic system in any economy is helpful as it opens more opportunities for developments. Centralized economic system is not beneficial at all because it leads to failures on various fronts. The economic system of South Korea over the period has proved itself effective for any growing economy. The impact of economic system on South Korean economy is more effective than the impact of centralized economic system on North Korea. Hence, the study completely explored the differences in the economic systems being adopted by the South Korea and North Korea. Economic indicators present the appropriateness of market based economic system.
ReferencesEberstadt, Nicholas, (2007). The North Korean Economy, Transactions Publishers, New Brunswick.pp.1-13, 127-57
Gregory, Paul R. and Stuart Robert C, (1985). Comparative Economic Systems (2nd edition), Houghton Mifflin, Boston.9-43
Republic of Korea. (2003, 02 14). Retrieved from IMF: https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/scr/2003/cr0381.pdf
Financial system of Korea. (2008). Retrieved from Bank of Korea: http://www.asifma.org/uploadedfiles/resources/financial-system-korea-2008.pdf
Property Rights Index - North Korea Compared to Continent. (2015). Retrieved from http://www.globalpropertyguide.com/Asia/North-Korea/property-rights-index
Koo, Bon Ho and Jo, Dongho, (1995). “Comparative analysis of the North and South Korean economies” in Cho, Lee-Jay and Kim, Yoon Hyung (eds), Economic Systems in South and North Korea: The Agenda for Economic Integration, Korea Development Institute, Seoul.
Korea fact book. (2016). Retrieved from CIA: https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ks.html
Rodrik, Dani, (1995). “Getting Interventions Right: How South Korea and Taiwan Grew Rich,” Economic Policy 20.
Taylor, A. (2013, 04 08). A Crazy Comparison Of Life In North Korea And South Korea. Retrieved from Business Insider: http://www.businessinsider.com/life-in-north-korea-vs-south-korea-2013-4
World Bank, (1995). The East Asian Miracle: Economic Growth and Public Policy, World Bank, 1993, 8-26 (Lee, Chung H., a book review of The East Asian Miracle in Seoul Journal of Economics, Vol. 8, No. 1)
AnnexureProperty Right Index Comparison: North Korea and South Korea