Part A: Your Marketing Plan Overview For this assignment, you will document your hypothetical company’s background information and mission statement, your company’s short-term and long-term goals, an
Running head: PART A: MARKETING PLAN YOUR COMPANY NAME 1
Part A: ABC Marketing Plan (Change to your name of business here)
Your Name
MKT500 Marketing Management
Strayer University
Dr. Lisa Amans
Date submitted
Introduction (note this is not bold)Write an introduction to your company. Describe your hypothetical company, its location (why did you choose this location), and the product it makes or the service it provides, and introduce the contents of your marketing plan.
Mission StatementDevelop your company’s mission statement (do not confuse a mission statement with a tag line, slogan, or positioning statement). Also, your mission statement should resonate with your consumers/customers as well as with your employees and stakeholders – remember to see the purpose of a mission statement and rationalize yours. Do not just state a mission statement without rational – answer why. See textbook, page 21.
Goals
Write an introduction to this section here (minimum of three sentences). Note, your goals should be realistic, practical, and SMART (i.e., S. – specific; M. – measurable; A. – assignable; R. – realistic; and T. – time based). What does your company need to accomplish in the short and long term; consider revenue and profit goals?
Short TermText starts here – Decide the main goals that you would like to achieve within the next year (short term). Determine the most appropriate ways to measure short term goals. Note: Consider the following metrics: tracking downloads of Website content, Website visitors, increases in market share, customer value, new product adoption rates, retention, rate of growth compared to competition and the market, margin, and customer engagement. For information on Website analytics, visit Google Analytics at http://www.google.com/analytics/why/
Long TermDecide the mains goals that you would like to achieve within the next five (5) years (long term). Determine the most appropriate ways to measure long term goals. Note: Consider the following metrics: tracking downloads of Website content, Website visitors, increases in market share, customer value, new product adoption rates, retention, rate of growth compared to competition and the market, margin, and customer engagement. For information on Website analytics, visit Google Analytics at http://www.google.com/analytics/why/
Environmental AnalysisDevelop an environmental analysis that includes competitive, economic, political, legal, technological, and sociocultural forces. Include an introduction of these elements. Write an introduction to this section (minimum of three sentences). See textbook pages 45-51.
Competitive AnalysisCompetitive analysis here - (who is the competition – direct and indirect, why do you consider them to competition, what do they do well, what might be a weakness?).
Economic AnalysisEconomic analysis here - (Through this factor, businesses examine the economic issues that are bound to have an impact on the company. This would include factors like inflation, interest rates, economic growth, the unemployment rate and policies, and the business cycle followed in the country).
Political and Legal AnalysisPolitical and legal analysis here. Separate the topics if you have significant analysis. (Political and Legal: Here government regulations and legal factors are assessed in terms of their ability to affect the business environment and trade markets. The main issues addressed in this section include political stability, tax guidelines, trade regulations, safety regulations, and employment laws).
Technological AnalysisTechnological analysis here – (How technology can either positively or negatively impact the introduction of a product or service into a marketplace is assessed here. These factors include technological advancements, lifecycle of technologies, the role of the Internet, and the spending on technology research by the government).
Sociocultural Forces AnalysisSociocultural forces here – (With the social factor, a business can analyze the socio-economic environment of its market via elements like customer demographics, cultural limitations, lifestyle attitude, and education. With these, a business can understand how consumer needs are shaped and what brings them to the market for a purchase).
SWOT and Needs AnalysisDevelop both a SWOT analysis and needs analysis for your product. Each analysis should examine three (3) each of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for your company. Suggestion is to write an introduction (minimum of three sentences) and create a SWOT table (use APA formatting, label Table 1, etc.). Include an analysis, not just the table. Rationalize why you choose these SWOT elements. See textbook page 21.
Table 1
SWOT Analysis
| Strengths
| Weaknesses
|
| Opportunities
| Threats
|
Note: Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for xxxx company.
Include three strengths and explain the importance (think features and benefits to customer). Strengths are internal; what you can control.
WeaknessesInclude three weaknesses and impact to the business and/or customer. Weaknesses are internal; what you can control.
OpportunitiesInclude three opportunities and explain the importance (think features and benefits to customer). Opportunities are external; what is happening outside your company you can take advantage of such as new technology.
ThreatsInclude three threats and impact to the business and/or customer. Threats are external; what is happening outside your company that will impact your business such as new government policies or laws.
ConclusionSummarize the plan to this point (minimum of three sentences) and you should not include any new thoughts (just summary).
References (note this is centered and not bold and on a separate page)Use at least three (3) academic resources as quantitative marketing research to determine the feasibility of your product / service. Three academic references are proficient. In order to receive most points as exemplary, submit four or more.
These academic resources should be industry specific and relate to your chosen product / service. Quality, academic references are peer-reviewed and found in scholarly journals published in the last 5 years. A good way to incorporate is by using Journal of Marketing, as an example, for your theories and consumer behavior observations.
Newspapers, magazines, and other Websites do not qualify as academic resources and although you should reference if you use, they do not count towards your minimum.
Listing your references without applying them in your text (citations) is not acceptable!!! See proper formatting in APA hints on page 7 of this document.
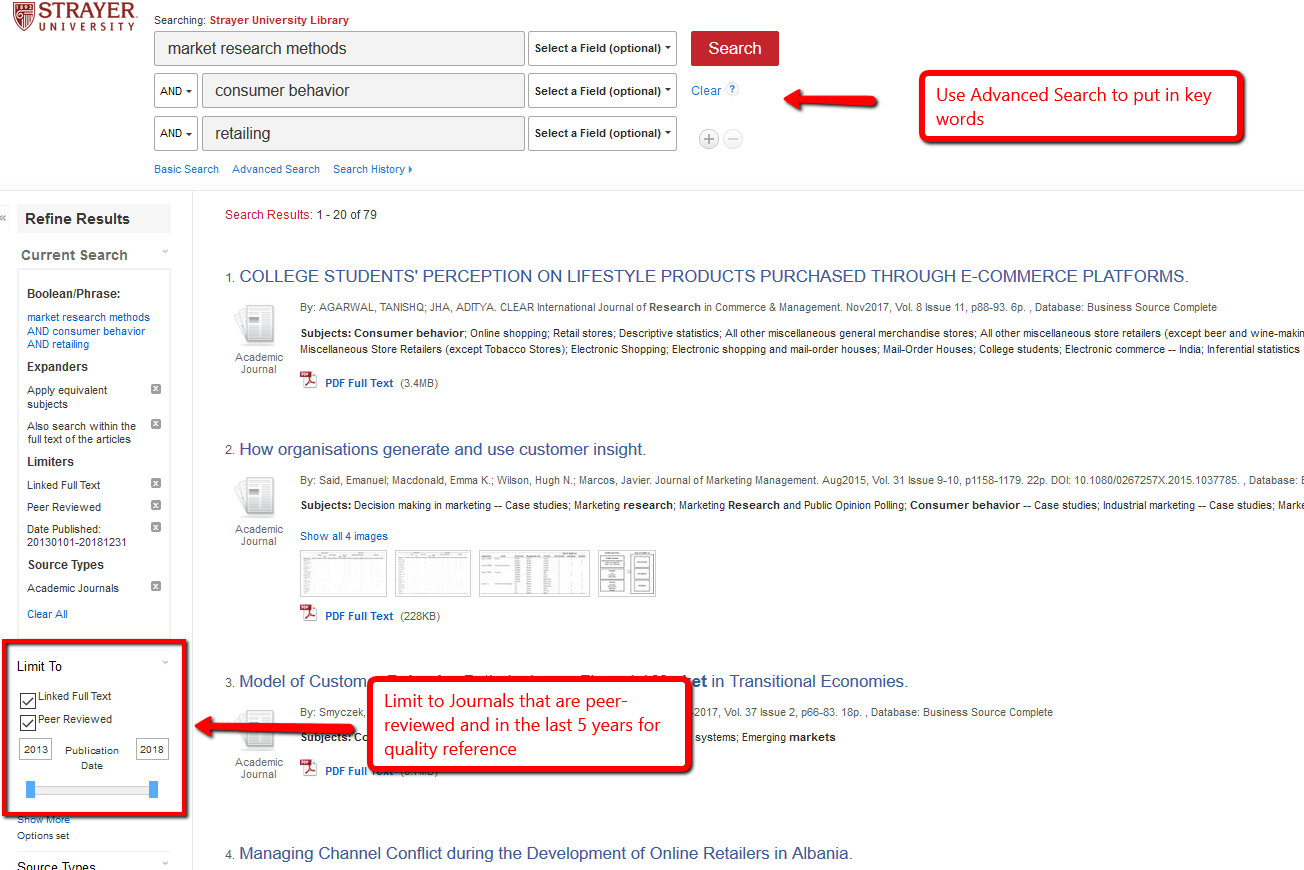
Below are tips and notes to guide you writing an APA paper. Use this information as a reference and ask if you have any questions.
Tips and Notes:NEVER plagiarize: Plagiarism: act of using someone else’s ideas, words, figures, unique approach, or specific reasoning without giving appropriate credit.
Always include an introduction for your Heading 1 topic (example: Environmental Analysis) to explain to the readers what they learn in the section you are introducing.
Paragraphs should be complete, such as a minimum of three sentences:
“Put only one main idea per paragraph.
Aim for three to five or more sentences per paragraph.
Include on each page about two handwritten or three typed paragraphs.
Make your paragraphs proportional to your paper. Since paragraphs do less work in short papers, have short paragraphs for short papers and longer paragraphs for longer papers.
If you have a few very short paragraphs, think about whether they are really parts of a larger paragraph—and can be combined—or whether you can add details to support each point and thus make each into a more fully developed paragraph.” (https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/606/02/ )
http://blog.apastyle.org/apastyle/2011/12/the-long-and-the-short-of-it.html
http://arc.aje.com/editing-tip-sentence-length/
Don not use (or minimize):
they (minimize, pronouns, use actual names/titles for clarity)
these
there are
thing
it
this
I
we
you
one or ones
some
a lot
a ton
really
very
Use of contractions – spell out
Use of conjunctions: https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/598/1/ An independent marker word is a connecting word used at the beginning of an independent clause. These words can always begin a sentence that can stand alone. When the second independent clause in a sentence has an independent marker word, a semicolon is needed before the independent marker word.
Ex. Jim studied in the Sweet Shop for his chemistry quiz; however, it was hard to concentrate because of the noise.
Some common independent markers are: also, consequently, furthermore, however, moreover, nevertheless, and therefore.
Findings: are past tense
Use of italics: https://owl.english.purdue.edu/engagement/2/1/45/ : only Italicize the titles of magazines, books, newspapers, academic journals, films, television shows, long poems, plays, operas, musical albums, works of art, websites.
APA Guidelines:
American Psychological Association (2010). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (6th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
APA Website: www.apastyle.org
Updated APA guideline notes on ELCSE website under Student Resources (http://www.aug.edu/elcse/ELCSE_APA_Guidelines.pdf)
Sample paper – guideline to Headers: https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/01/
Numbers: https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/01/
Formatting Tables and Figures
https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/19/
https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/20/
How to cite: https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/01/
Paraphrasing within text:
In a 1989 article, Gould explores some of Darwin’s most effective metaphors.
Author cited in text:
Gould (1989) attributed Darwin’s success to his gift for making the appropriate metaphor.
Author not cited in text:
As metaphors for the workings of nature, Darwin used the tangled bank, the tree of life, and the face of nature (Gould, 1989).
Multiple works within the same parenthesis:
Several studies (Balda, 1980; Kammil, 1988; Pepperberg & Funk, 1990) confirm the use of metaphors increases learning.
First citation in text:
Wasserstein, Zappula, Rosen, German, and Rock (1994) found. . .
The use of metaphors was found to be helpful (Wasserstein, Zappula, Rosen, German, & Rock, 1994)
Subsequent citations (3 or more authors):
Wasserstein and colleagues (1994) found
Wasserstein et al. (1994) found
The use of metaphors was found to be helpful (Wasserstein et al., 1994)
Authors With the Same Last Name: To prevent confusion, use first initials with the last names.
(E. Johnson, 2001; L. Johnson, 1998)
Direct quote from author: (use sparingly):
Gould (1989) explains that Darwin used the metaphor of the tree of life “to express the other form of interconnectedness-genealogical rather than ecological-and to illustrate both success and failure in the history of life” (p.14).
Direct quote without name of author:
Darwin used the metaphor of the tree of life “to express the other form of interconnectedness-genealogical rather than ecological” (Gould, 1989, p.14).
References:
References are listed on separate page, header is centered, do not bold
Notice no first names used, only initials and in alphabetical order.
Only citations that appear in the text should appear on the reference page
Everything cited in the text should appear on the reference page.
References are double-spaced, flush left with subsequent lines indented 5 spaces
Examples:
Online Periodicals General format:
Author, A. A. (date). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume(number), page numbers. doi: xx.xxxxxxx
Example:
Herbst-Damm, K. L., & Kulik, J. A. (2005). Volunteer support, marital status, and the survival times of terminally ill patients. Health Psychology, 24, 225-229. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.24.2.225
Book General format:
Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (year of publication). Title of work: Capital letter also for subtitle (number ed.). Location City, State Abbreviation: Publisher.
Example:
Anderson, A. B., Smith, S. D., & Jones, J. C. (1978). A distant mirror: The calamitous fourteenth century (3rd ed.). New York, NY: Knopf.
DOIs are unique strings of numbers used to identify online articles’ content and provide a persistent link to their location on the Internet.
When DOIs are present, no longer have to include URL.
When DOIs are not present, include URL
https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/01/
Finding DOIs: http://www.crossref.org
Example without a DOI:
Sillick, T. J., & Schutte, N. S. (2006). Emotional intelligence and self-esteem mediate between perceived early parental love and adult happiness. Applied Psychology, 2(2), 38-48. Retrieved from http://ojs.lib.swin.edu.au/index.php/ejap



