Econ questions and answers in detail, please.
CHAPTER 18: Using Input Market Analysis
CHAPTER 18
Using Input Market Analysis
CHAPTER ANALYSIS
This chapter presents applications that use the tools developed in Chapters 16 and 17. In order to analyze real-world labor markets, the correct labor supply curve must be used. This is because there are differences in the elasticity of supply between the aggregate supply curve and the industry supply curve. Be sure to notice which supply curve is used in the applications, when it is appropriate to use supply and demand analysis, and when it is appropriate to use the income-leisure model.
ILLUSTRATIONS
Markets and the Jim Crow LawsThe Jim Crow era in the South is identified with the period from the late nineteenth century to the middle of the twentieth century when a legally enforced system of racial segregation existed. There is a growing literature documenting the effects of market forces on economic discrimination prior to the Jim Crow era. This literature shows that market forces often did not generate segregation, and that the white majority responded by enacting legislation that mandated segregation. These laws were passed because the marketplace did not generate the results that the politically powerful wanted.
Studies have found that segregation of streetcars was fought by the streetcar companies,1 railroads were integrated prior to legislation that prohibited the practice,2 and competitive pressure in southern labor markets tended to equalize equal payments for equal work.3 Jennifer Roback concludes, "The evidence indicates that the law, not the market, was the chief oppressor of blacks in the Jim Crow era."4
Who's Discriminated Against the Most?
In a study concerning discrimination against minority and women-owned firms in the Louisiana construction industry, owners were asked whether they thought the contracting system used by the state discriminated against various groups. These groups consisted of: African Americans, French-Acadiens, women, and other, which included Hispanics, Asians, and Native Americans. Each targeted group perceived that discrimination against their group was greater than discrimination against any other group. That is, more African Americans believed firms owned by African Americans faced more discrimination than firms owned by women, or by members of other racial or ethnic groups. Similarly, more women believed firms owned by women faced discrimination than firms owned by blacks, and so on. While each group perceived discrimination against themselves to be greater than against any other group, clearly each group cannot be correct.
[See John Lunn and Huey L. Perry, "Justifying Affirmative Action: Highway Construction in Louisiana," Industrial and Labor Relations Review, 46 (April 1993): 464-479.
KEY CONCEPTS
disemployment effect
efficiency wage
REVIEW QUESTIONS
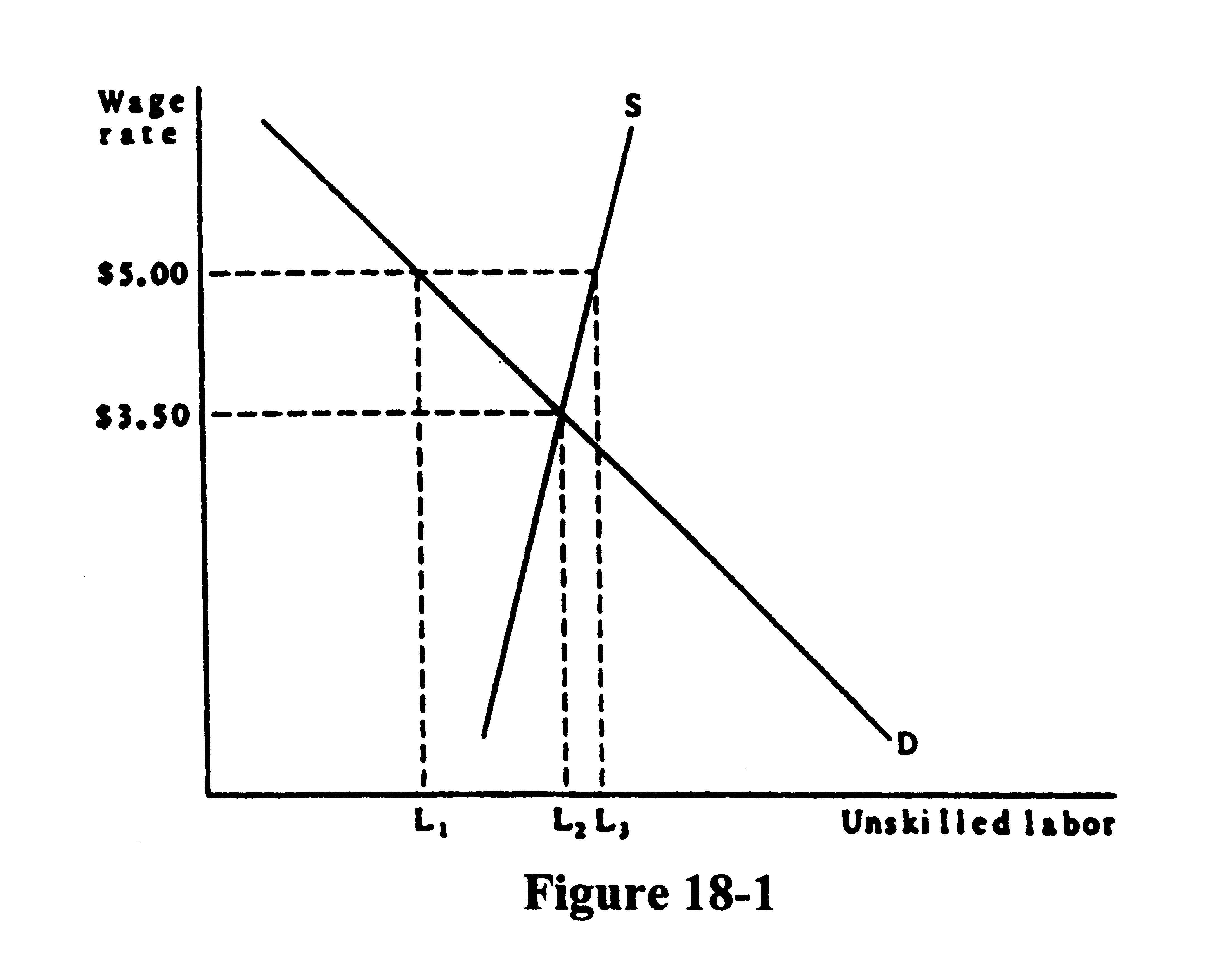
Multiple Choice/Short Answer1. Use Figure 18-1 to answer the following questions.
a. How many unskilled laborers will be hired if there is no minimum wage?
b. How many unskilled laborers will be hired if the minimum wage is $5.00?
c. At a minimum wage of $5.00, how many workers will want jobs?
d. How many unskilled workers are disemployed as a result of the minimum wage?
e. How many unskilled workers are unemployed as a result of the minimum wage?
2. Among unskilled workers, the most productive workers will be most likely to lose their jobs as a result of the minimum wage.
True
False
3. An efficiency wage is
a. another term for the prevailing market wage rate.
b. a wage higher than the prevailing market wage that increases firm’s profits.
c. a wage lower than the prevailing market wage that decreases firm’s profits.
d. the wage rate at which the unemployment rate is minimized.
4. As the minimum wage has risen over time and the share of industries covered by the minimum wage has expanded,
a. the unemployment rate of minority teenagers has risen relative to the unemployment rate of white teenagers.
b. the share of the workers who receive minimum wage that are in poor households has increased.
c. the poverty rate has fallen.
d. All of the above.
5. If the aggregate supply curve of labor is very inelastic, the burden of the Social Security tax
a. falls mostly on consumers because the price of goods increases.
b. falls mostly on the firms.
c. falls mostly on the workers.
d. depends on how much of the tax is collected from employees and how much from employers.
6. The long-run effects of a rise in the Social Security tax is that
a. wage rates will rise.
b. wage rates will fall.
c. wage rates will stay the same.
d. wage rates will fall initially but return to their previous level in long-run equilibrium.
7. One way to make the burden of the social security tax more equitable between employers and employees would be to
a. increase the share of the tax paid by employers.
b. increase the share of the tax paid by employees.
c. raise the social security tax rate.
d. None of the above.
A cartel of buyers reduces the wage rate paid to workers by
a. increasing employment and moving down the labor-demand curve.
b. replacing skilled labor with unskilled labor and capital.
c. lowering the product price, which lowers the value of the marginal product of labor.
d. restricting employment collectively.
A cartel of employers is
a. common since the cartel lowers labor costs and increases profits.
b. common because there are no laws against such cartels.
c. rare because unions have the power to prevent the formation of the cartels.
d. rare because so many firms in different industries would have to coordinate their activities.
10. Which of the following is evidence that the NCAA has established a monopsony-like result for college athletics?
a. Not all athletes graduate from college.
b. Many schools offer illegal inducements to athletes.
c. Revenues for college athletes have increased due to television.
d. All of the above.
11. Who is harmed by the NCAA rules?
a. Sports fans.
b. Athletes in non-revenue generating sports.
c. Administrators of small private colleges.
d. Athletes in revenue generating sports.
12. If some, but not all, employers discriminate against blacks, then we would observe
a. segregated employment patterns but not wage rate differentials.
b. segregated employment patterns and wage rate differentials.
c. wage rate differentials but not segregated employment patterns.
d. neither wage rate differentials nor segregated employment patterns.
13. Racial or sexual discrimination is more likely in nonprofit organizations than in profit-making organizations.
True
False
14. Which of the following explain part of the gap between the wages received by African-Americans and whites in the United States? (More than one answer may be correct.)
a. The median age of African Americans is higher than the median age of whites.
b. On average, whites have more schooling than African-Americans.
c. The percentage of whites that are married is greater than the percentage of African-Americans who are married.
d. A higher percentage of African-Americans than whites live in urban areas.
15. Which of the following explain part of the gap between the wages received by women and the wages received by men? (More than one answer may be correct.)
a. Men work more hours per week than women.
b. On average, men have more schooling than women.
c. Women tend to choose lower-paying majors.
d. The median age of men is higher than the median age of women.
Discussion Questions and Problems
1. Use a two-part graph to show that the effect of the minimum wage on unemployment depends on the elasticity of demand for labor and the elasticity of supply of labor.
2. Some areas have a lower minimum wage for teenagers than for adults. Can you offer any reasons for such a system?
There are people who want a "living wage" law passed, which would require all jobs to provide enough income that a family of four could live on it. What would be the economic effects of such a law?
4. People who are self-employed have to pay the entire Social Security tax themselves. Does this mean that self-employed people bear a larger share of the Social Security tax than workers who are not self-employed? Explain.
5. Analyze the effects of a national health insurance program financed by payroll taxes on workers and employers paid entirely by employers.
Explain why the correct answer to Multiple Choice question #7 is d.
Explain how the NCAA is able to keep wages for college athletes below the marginal value product of the athletes. Is the wage below MVP for all college athletes? Explain.
Who is harmed by the NCAA's cartel-like behavior? Who benefits?
Explain why it is difficult for an input cartel to be successful. If this is so, why is the cartel involving college athletes so successful?
10. What factors other than discrimination might explain the gap between the average wage for women and the average wage for men?
11. Explain why firms that want larger profits are less likely to discriminate when hiring workers.
12. Suppose a study finds that 80 percent of the gap in the wages received by men and women is due to factors such as majors selected, work experience, and hours worked. Does this imply that the remaining gap is due to discrimination? Explain.
SOLUTIONS
Multiple Choice/Short Answer1. a. L2 b. L1 c. L3 d. L2-L1 e. L3-L1
2. False
3. b
10. b. (a) is not evidence since not all students graduated and (c) provides an incentive to colleges to operate sports programs like a business but not evidence of monopsony power.
11. d
12. a
13. True
14. b, c
15. a, c
Discussion Questions and Review
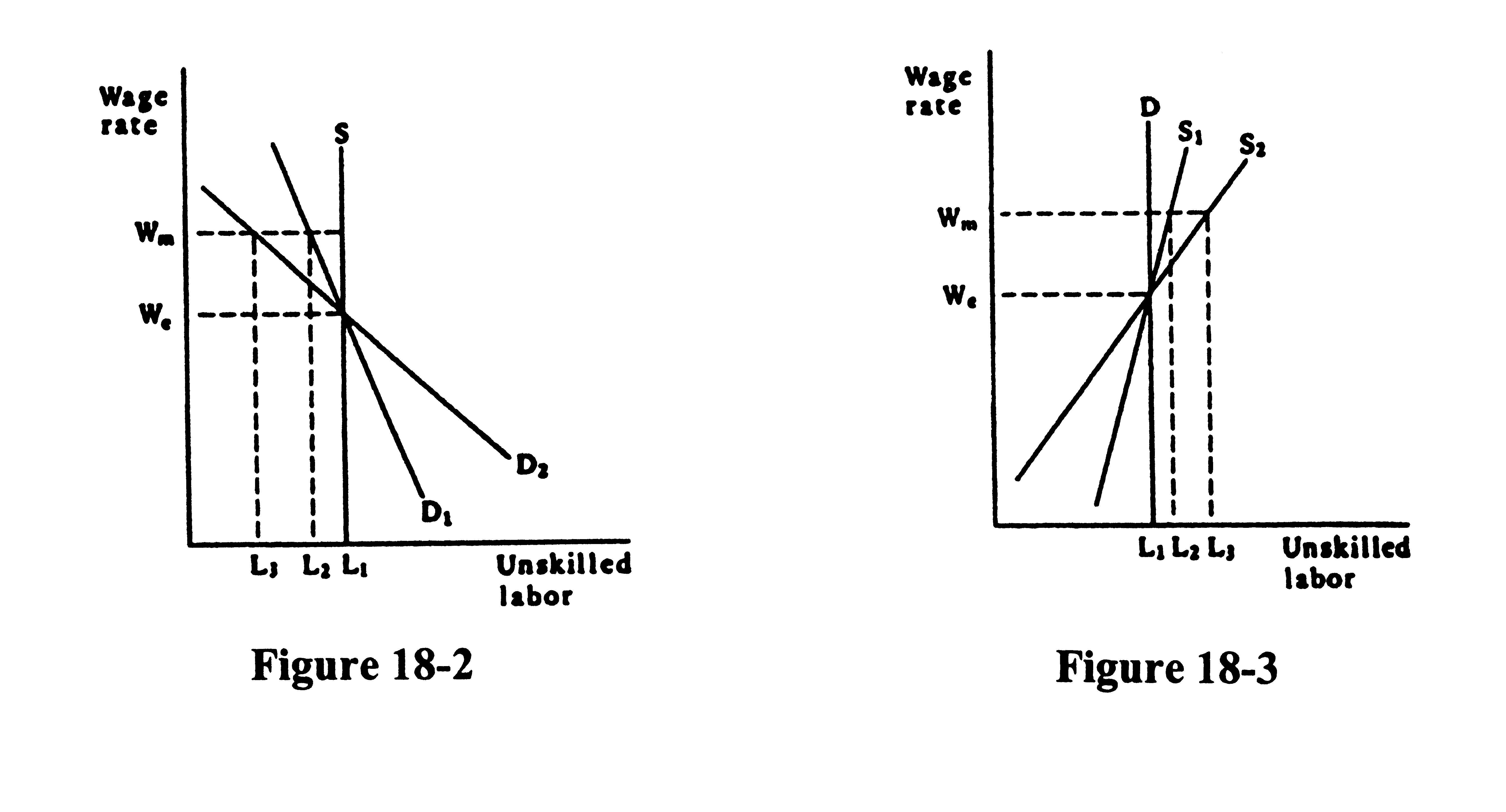
1. The minimum wage will lead to more unemployment the more elastic the demand for unskilled labor and the more elastic the supply of unskilled labor. In Figure 18-2, the supply curve for unskilled labor is vertical, and two demand curves are shown where D2 is more elastic than D1. The disemployment effect of the minimum wage is greater for D2 (L1 - L3) than for D1 (L 1- L2). In Figure 18-3, the demand curve is vertical and S2 is the more elastic of the supply curves. Again, unemployment is greater after the minimum wage is established for the more elastic supply curve.
2. The minimum wage hurts the least productive workers the most. Teenagers are not very productive generally, so the minimum wage affects teenagers more than adults. The unemployment rate is higher among the teenagers, especially black teenagers, so a lower minimum wage would permit more teenagers to find jobs. The jobs provide opportunities for the teenagers to increase their productivity through work experience, which will increase their earning capabilities when they are older.
The "living wage" would have similar effects to the minimum wage. Assuming the living wage would be higher than the minimum wage, the impact on unemployment among unskilled workers would likely increase.
4. The burden of the Social Security tax that is borne by workers does not depend on how the tax is collected. Figure 18.3 in the text shows that the worker bears the entire burden of the tax when the supply curve of labor is vertical. If the supply curve of labor is not vertical, the employer bears some of the burden of the tax. Hence, the self-employed person does bear a larger share of the burden of the tax (all of it) than workers that are not self-employed, as long as the supply of labor is not perfectly inelastic.
5. Figure 18-4 illustrates the effects of the tax. The demand for labor shifts downward by an amount equal to the payroll tax when the employer has to pay the tax. The new demand curve, D', intersects the supply curve at point B, so the workers receive a wage of WA. The tax rate is WB - WA, so the firm pays this amount to the government. The firm's total expenditure on a worker is WB. (Note that the effects are identical to those of the Social Security tax. Compare Figure 18-4 to Figure 18.2 in the text.)

The share of the burden of the tax does not depend on who pays the tax. Instead, the share depends on the elasticities of demand and supply of labor. Altering the share of the tax paid will not affect the actual burden of the tax. Raising the social security tax would not affect the distribution of the burden of the tax.
The NCAA determines the maximum financial rewards student athletes can receive and the maximum number of athletes that can receive the awards. By doing so, the NCAA restricts employment of student-athletes, causing a movement down the supply curve of labor and a lower wage. Colleges that offer athletes more than what is allowed and are caught are punished financially. The wage may not be below MVP for all athletes, especially those in sports that do not generate much revenue.
8. The athletes who earn less than their MVP are harmed. Beneficiaries include athletes in non-revenue generating sports who are subsidized by athletes in revenue generating sports, and coaches who have a comparative advantage in recruiting.
9. An input cartel faces more difficulties than an industrial cartel because specific inputs tend to he hired by firms in many industries. For such a cartel to work, many firms in different industries would have to coordinate their actions with respect to the input owners. The costs of doing so would be enormous. Further, like any type of cartel, cheating and new entry would prevent the cartel's success.
10. If wages are determined by productivity, a wage differential between men and women may be due to productivity differences. Many factors affect productivity such as age, education, experience, and turnover, to name a few. If these factors differ by sex, productivity can differ and the wage differential would not necessarily be the result only of discrimination.
11. If minorities or women are making lower wages because of discrimination, an employer can increase profits by hiring members of the group(s) facing discrimination. Given that labor costs account for about 70 percent of production costs for American firms, a relatively small decrease in labor costs can have a large impact on the firm's rate of profit.
12. No. Other important factors may have been left out.
1 Jennifer Roback, "The Political Economy of Segregation: The Case of Segregated Streetcars," Journal of Economic History, 46 (1986): 893-917.
2 Charles Lofgren, The Plessy Case: A Legal-Historical Interpretation. (New York: Oxford University Press, 1987).
3 Rober Higgs, "Firm-Specific Evidence on Racial Wage Differentials and Workforce Segregation," American Economic Review, 67 (March 1977): 236-245.
4 Jennifer Roback, "Southern Labor Law in the Jim Crow Era: Exploitative or Competitive?" University of Chicago Law Review, 51 (Fall 1984): 1161-1192.
102



