Please look at this file
Name____________________________ (12 points)
Part I – Complex IV – a crucial enzyme in Oxidative Phosphorylation

Figure 1. Oxidative Phosphorylation in Eukaryotes. The green box highlights Complex IV.
Complex IV is the last enzyme in the electron transport chain. Its function is to transfer four electrons to one O2, which combine with 4H+ to form two H20 molecules. While doing this it transports H+ across the inner mitochondrial membrane, contributing to making a H+ gradient.
1. When the H+ move down their concentration gradient is energy released or required?
2. When H+ move down their concentration gradient through ATP synthase what is made? Does the synthesis of this molecule release or require energy?
In order for Complex IV to be fully active it must associate with two cardiolipin molecules. Cardiolipin is a type of phospholipid in the mitochondrial inner membrane. A change in the amount of cardiolipin would decrease the activity of Complex IV.
3. What would happen if cardiolipin levels were changed? Please consider what would happen to the following and explain why.
Electrons
H+
ATP levels
Part II – Changes in phospholipid levels are the result of SERAC1, a mitochondrial gene.
Table 1. Three codons in different parts of the mitochondrial gene SERAC1. These three codons were mutated in four patients with MEGDEL syndrome.
| Template DNA RNA | amino acid | Mutated Template DNA RNA | Mutated amino acid | |
| Codon 1 | 3’ CCA 5’ | Gly | 3’ CTA 5’ | |
| Codon 2 | ||||
| 5’ GGA 3’ | 5’ GAA 3’ | |||
| Codon 3 | 3’ TCG 5’ | 3’ TGG 5’ | ||
If these mutations play a role in MEGDEL syndrome, then they must affect the function of SERAC1, but what does SERAC1 do?
SERAC1 is present in all eukaryotes and is highly conserved, especially its lipase domain (Fig. 2). The three amino acids (Gly401, Gly404 and Ser498) affected by the mutations (Table 1) are all located within this lipase domain and are fully conserved down to the fruit fly (identical in all species known). The SERAC1 lipase domain is proposed to play a role in the phospholipid conversion pathway (Fig. 3).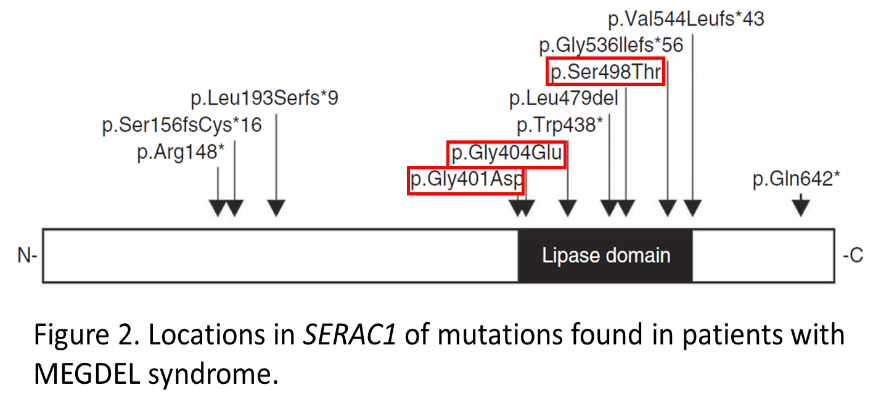
PG 34:1 is a precursor for Cardiolipin, while PG 36:1 is a precursor for BMP. It is proposed that SERAC1 plays a role in converting PG 34:1 to PG 36:1. 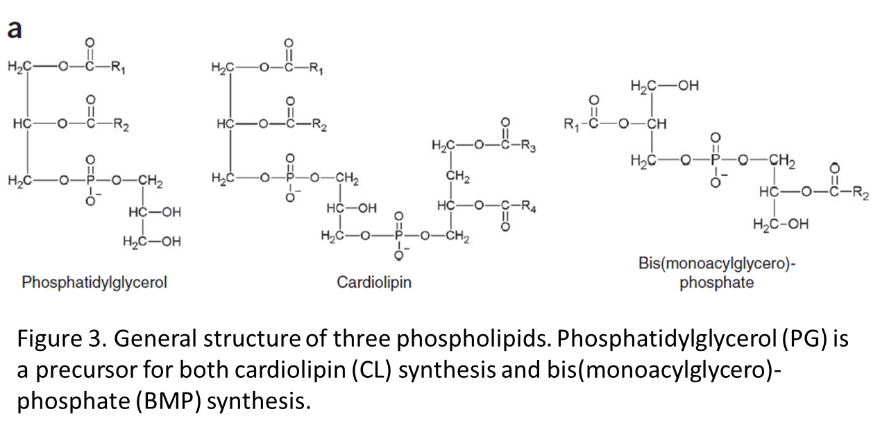
Form a hypothesis about how each mutation would affect SERAC1 function. Do you think the mutated versions would work better, worse, or about the same?
Hypothesis:
Based on your hypothesis form a prediction about each lipid (PG 34:1, PG 36:1, cardiolipin, and BMP) level in MEGDEL patients.
Prediction:
Wortmann, S.B., Vaz, F.M.,…de Brouwer, A.P.M. 2012. Mutations in the phospholipid remodeling gene SERAC1 impair mitochondrial function and intracellular cholesterol trafficking and cause dystonia and deafness. Nature Genetics. 44(7): 797-802. doi:10.1038/ng.2325
Part III –Effect of SERAC1 mutations on phospholipid levels
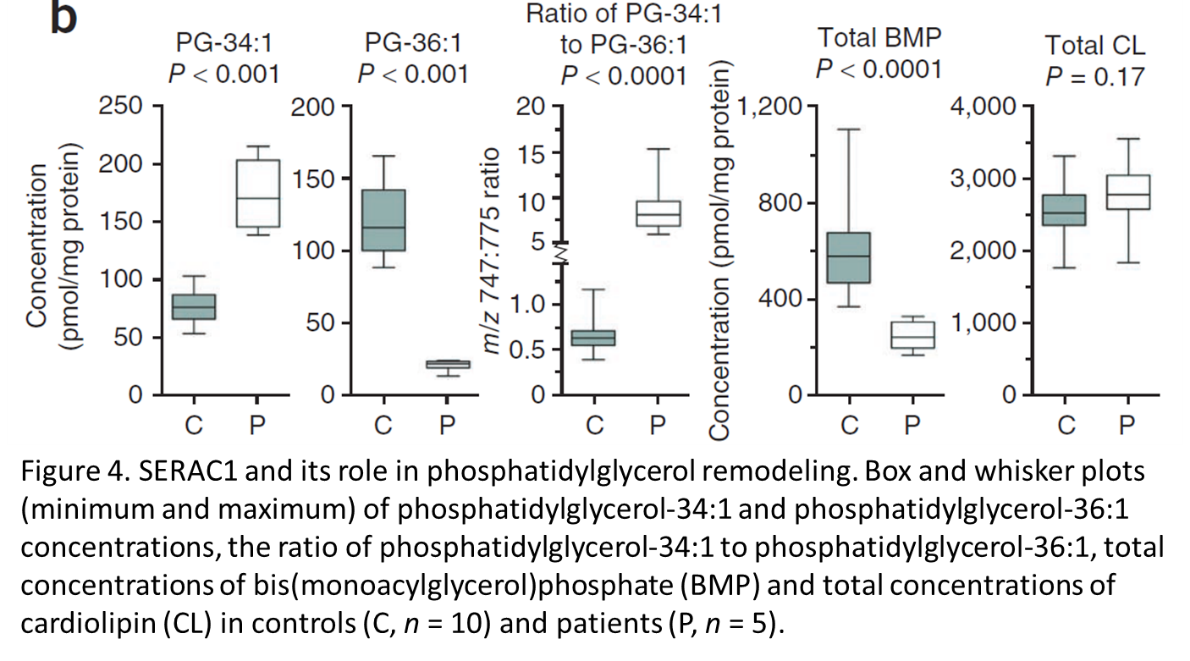
4. What conclusions can you make from the results in Figure 4?
a. How have the mutations affected phosphatidylglycerol 34:1 levels?
b. How have the mutations affected phosphatidylglycerol 36:1 levels?
c. How have the mutations affected BMP levels?
d. How have the mutations affected cardiolipin levels?
e. How have the mutations affected SERAC1 enzyme function?
f. Based on these results, how do you think these mutations in SERAC1 will affect oxidative phosphorylation in MEGDEL syndrome patients? Explain your answer.



