I need help with the attached labs projects.
| Reebop Lab Lab Directions |
This activity was modified from the original created by the Center for Biology Education/University of Wisconsin. Perform the lab at home. Submit your lab answers according to the directions and grading rubric below.
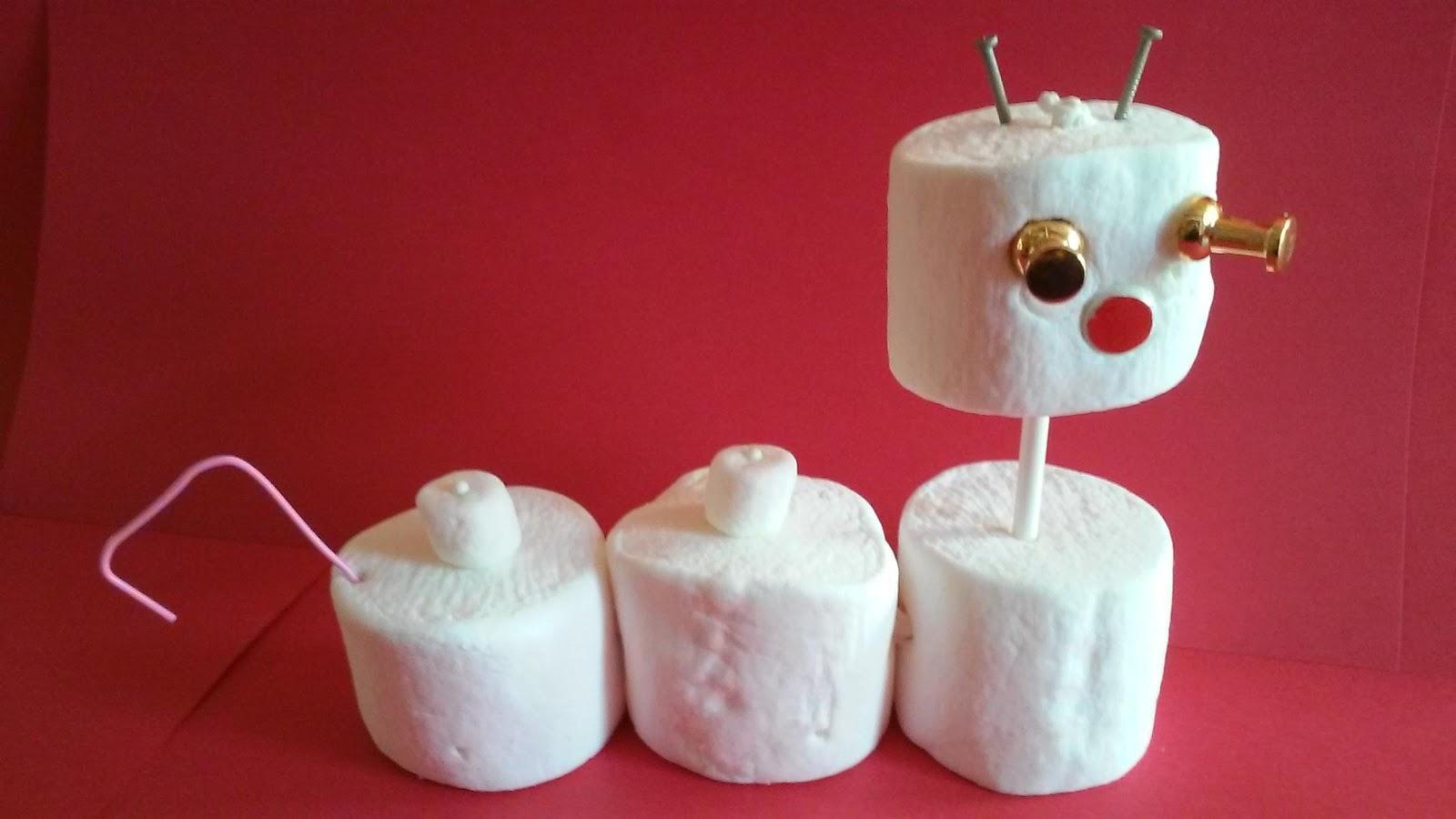

Overview: Reebops (Marshmella magicus) are an imaginary species that reproduce at a rapid rate. In this activity, you will assume the role of two Reebop parents reproducing to make an offspring. You will simulate meiosis, fertilization, and then build your baby Reebop by decoding the alleles on the chromosomes. Some basic facts about Reebops:
Reebops have 8 homologous chromosome pairs, each with one trait.
The 8th chromosome is a sex chromosome. It determine the sex of the baby and carries the gene for eye type.
Goal: Mate two reebops to create a baby Reebop! Record and analyze your data.
Lab Materials:
Scissors
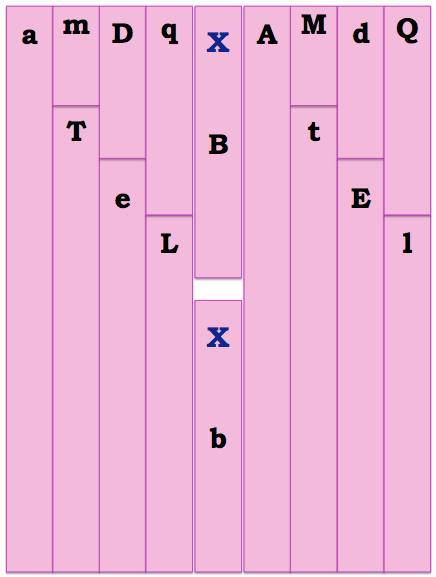
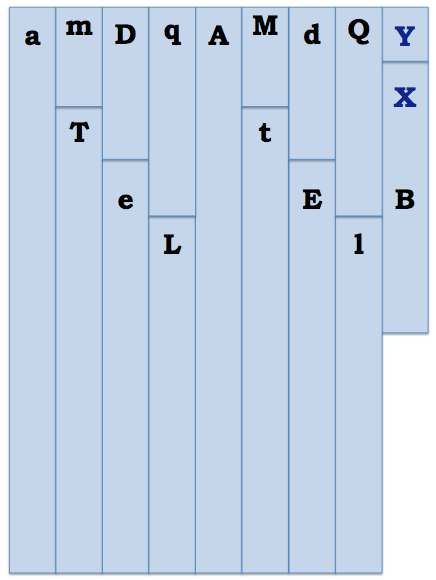
Printed copies of the mom (pink) and dad (blue) chromosomes (p. 5,6)
Materials from your home (see Rebop Decoder Key) OR make a digital drawing of baby (see resources in the sidebar)
Directions:
1. Print and cut out the parent chromosomes from the last page of this lab.
If you are not printing in color, mark them so you keep track of mom vs. dad chromosomes.
2. Create parents.
Match up homologous chromosomes (by length) for mom. Repeat for dad. Record the parent genotypes in Data Table 1. Use the Reebop Decoder Key to determine genotypes and record in Data Table 1. Use Reebop Decoder Key to build parent Rebops (you can do this with raw materials or create it digitally). Take pictures and place in Data Table 1.
3. Make a prediction.
What do you think your baby reebop will look like? Look at the Reebop Decoder Key and your parent genotypes you have placed in Data Table 1. Do some Punnett Squares. Which genotypes/phenotypes are most likely with these two parents? Write a hypothesis (prediction) for the baby’s genotype and phenotype in Data Table 1 with an explanation.
3. Simulate meiosis for each parent.
Spermatogenesis: Place all the father’s (blue) chromosomes face down, and match them up by size. Select one chromosome of each size to make up a sperm with 8 chromosomes. Note: the sex chromosomes will not match up.
Oogenesis: Using the pink chromosomes, repeat the same process to create an egg.
Set the unused chromosomes aside. You should now have two piles of chromosomes: 8 blue chromosomes (sperm) and 8 pink chromosomes (egg.)
4. Simulate fertilization.
Combine your sperm and egg. BOOM! You just make a baby! That was easy.
5. Congrats! Your baby Reebop is born!
Turn over the chromosomes and record the following in Data Table 1:
Name your baby reebop and determine it’s sex.
Baby’s genotype and phenotype (using the Reebop Decoder Key) for each trait.
6. Build your baby!
Use Reebop Decoder Key to build your baby Rebop (raw materials or digitally.) Take a picture and place in Data Table 1.
7. Answer Discussion Questions.
8. Submit Lab (Data Table, Discussion Questions)
Table 1. Reebop Mating Data
| Reebop | Genotype | Phenotype | Picture of Reebop |
| Mom | list all letters here Example: AABbccDd…. | list phenotypes here 2 Antenna ... | insert picture here (built with household objects from Reebop Decoder Key or digitally drawn) |
| Dad | | ||
| Prediction for Baby | | Explanation: (no picture needed) | |
| Baby Name: ________ Baby’s Sex: ____ | |
Discussion Questions.
1. Compare your baby to his/her parents. Does s/he have the same genotype? Does s/he have the same phenotype? Why or why not?
2. Compare your prediction to the actual baby’s genotype or phenotype. Chances are you were not 100% accurate. Explain why or why not.
3. The picture at the top of the lab is an older sibling of your baby! Which two laws from Mendel support the idea that siblings are not identical even though they come from the same parent?
4. Which traits in Reebops appear to “blend” and show incomplete dominance?
5. Which traits in Reebops appear to show complete dominance?
6. The parents in this cross actually have 12 other Reebop babies. Of them, 6 males and 1 female child is blind. Why does a difference exist in the number of females with blindness than without blindness? Hint: Use a Punnett Square to support your argument.
Grading:
The following criteria will be used to evaluate your lab:
| Criteria | Points Possible |
| Hypothesis Prediction included in Data table that includes genotype, phenotype and explanation | 10 |
| Results Data Table
| 30 |
| Discussion Questions
| 60 |
| TOTAL | 100 |
Reebop Decoder Key
*use toothpicks to connect body parts as necessary*
| Trait | Genotypes/Phenotypes | Suggested Materials to Use |
| Body Segments (does not include head) | DD or Dd = three segments dd = two segments | regular marshmallows |
| Humps | MM = 2 humps Mm = 1 hump mm = no humps | mini marshmallows |
| Legs | LL = four legs Ll = two legs ll = no legs | toothpicks |
| Tail | TT or Tt = curly tail tt = straight tail | paperclip |
| Nose | QQ = red Qq = green qq = yellow | Colored candy or objects (gumdrops/thumbtacks) |
| Antennae | AA = two antennae Aa = one antenna aa = no antennae | nails or screws |
| Eye Number | EE or Ee = 2 eyes ee = 3 eyes | pins or thumbtacks |
| Blindness | B, BB or Bb = sighted (eyes present) b or bb = blind (remove eyes) | n/a |
| Sex | XX = female XY = male | n/a |

Reebop Lab 7 of 6



