Problem set Micro-economics PLEASE CHECK THE FILES Instructions THERE ARE 34 QUESTIONS AND 2 PARTS • You must explain your answers to multiple-choice questions with one or two sentences. Just markin
ECON 1100
Problem Set 1
Part 1: Multiple-Choice Questions [2 points each]
1. A tax on the sellers of coffee mugs
increases the size of the coffee mug market.
decreases the size of the coffee mug market.
has no effect on the size of the coffee mug market.
may increase, decrease, or have no effect on the size of the coffee mug market.
2. A tax imposed on the sellers of a good will raise the
price paid by buyers and lower the equilibrium quantity.
price paid by buyers and raise the equilibrium quantity.
effective price received by sellers and lower the equilibrium quantity.
effective price received by sellers and raise the equilibrium quantity.
3. If the government levies a $500 tax per car on sellers of cars, then the price received by sellers of cars would
decrease by less than $500.
decrease by exactly $500.
decrease by more than $500.
increase by an indeterminate amount.
4. If a tax is levied on the sellers of a product, then the demand curve will
shift down.
shift up.
become flatter.
not shift.
Figure 1: The vertical distance between points A and B represents the tax in the market.
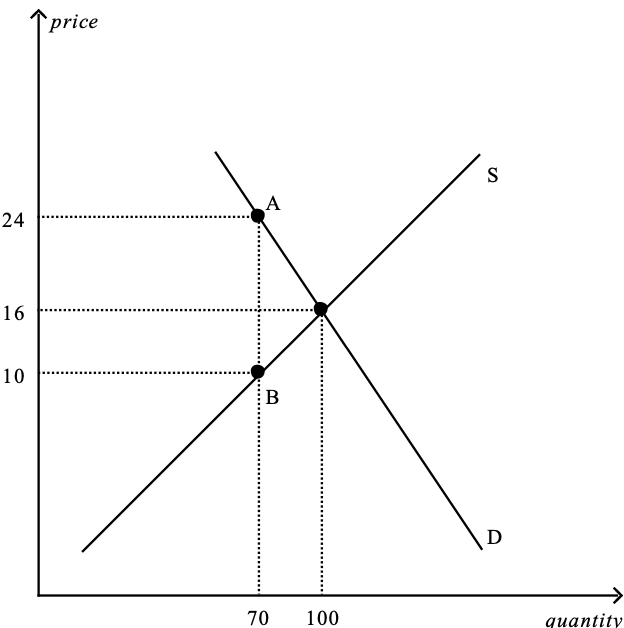
5. Refer to Figure 1. The effective price that sellers receive after the tax is imposed is
a. $6.
b. $10.
c. $16.
d. $24.
6. In which of the following circumstances would a buyer be indifferent about buying a good?
The amount of consumer surplus the buyer would experience as a result of buying
the good is zero.
The price of the good is equal to the buyer’s willingness to pay for the good.
The price of the good is equal to the value the buyer places on the good.
All of the above are correct.
Table 1

7. Refer to Table 1. If the price of the product is $18, then the total consumer surplus is
a. $38.
b. $42.
c. $46.
d. $72.
8. Dawn’s bridal boutique is having a discount season on evening dresses. The increase in consumer surplus comes from the benefit of the lower prices to
only existing customers who now get lower prices on the gowns they were already planning to purchase.
only new customers who enter the market because of the lower prices.
both existing customers who now get lower prices on the gowns they were already
planning to purchase and new customers who enter the market because of the lower prices.
Consumer surplus does not increase; it decreases.
2
9. At Nick's Bakery, the cost to make homemade chocolate cake is $3 per cake. As a result of selling three cakes, Nick experiences a producer surplus in the amount of $19.50. Nick must be selling his cakes for
$6.50 each.
$7.50 each.
$9.50 each.
$10.50 each.
10. PlayStations and PlayStation games are complementary goods. A technological advance in the production of PlayStations will
increase consumer surplus in the market for PlayStations and decrease producer surplus in the market for PlayStation games.
increase consumer surplus in the market for PlayStations and increase producer surplus in the market for PlayStation games.
decrease consumer surplus in the market for PlayStations and increase producer surplus in the market for PlayStation games.
decrease consumer surplus in the market for PlayStations and decrease producer surplus in the market for PlayStation games.
11. To measure the gains and losses from a tax on a good, economists use the tools of
macroeconomics.
welfare economics.
international-trade theory.
circular-flow analysis.
12. When the government places a tax on a product, the cost of the tax to buyers and sellers
is less than the revenue raised from the tax by the government.
is equal to the revenue raised from the tax by the government.
exceeds the revenue raised from the tax by the government.
Without additional information, such as the elasticity of demand for this product, it
is impossible to compare the cost of a tax to buyers and sellers with tax revenue.
Figure 2
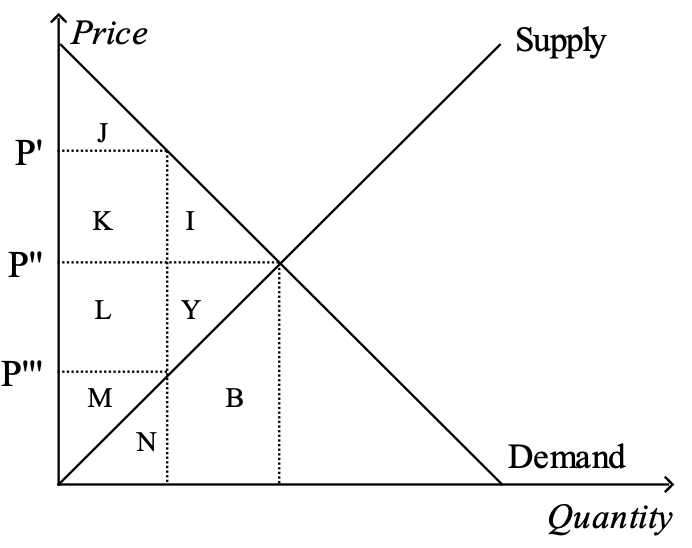
13. Refer to Figure 2. Suppose the government imposes a tax of P' - P'''. The area measured by I+J+K+L+M+Y represents
total surplus before the tax.
total surplus after the tax.
consumer surplus before the tax.
deadweight loss from the tax.
14. Refer to Figure 2. Suppose the government imposes a tax of P' - P'''. Total surplus after the tax is measured by the area
a. I+Y.
b. J+K+L+M.
c. I+Y+B.
d. I+J+K+L+M+Y.
Figure 3
The vertical distance between points A and B represents a tax in the market.
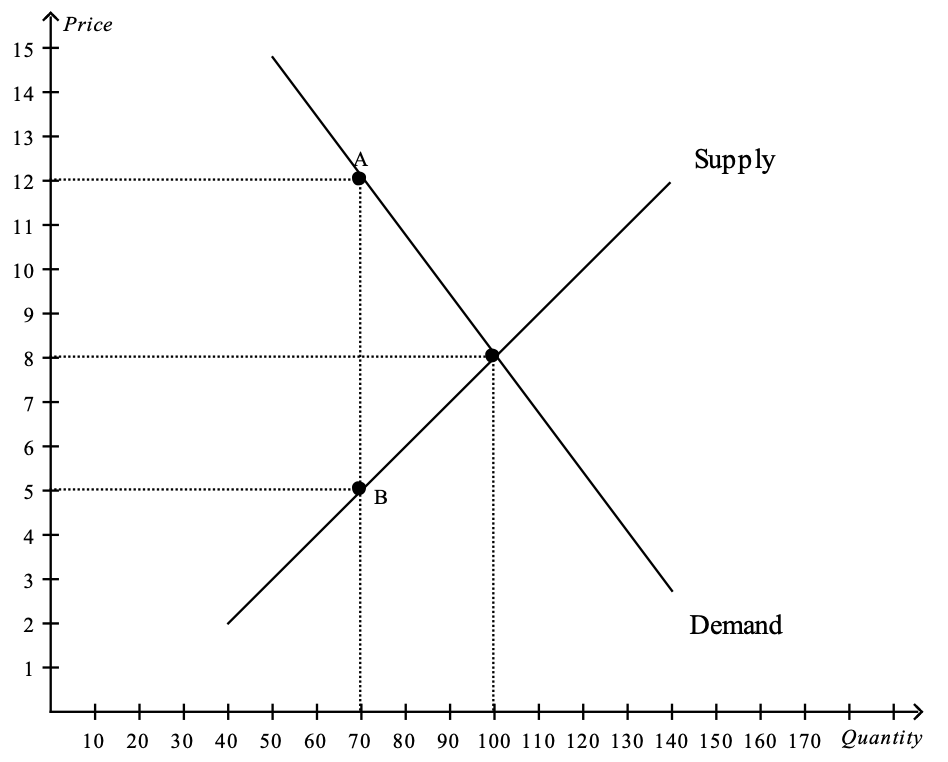
15. Refer to Figure 3. The amount of deadweight loss as a result of the tax is
a. $105.
b. $210.
c. $490.
d. $600.
Table 2
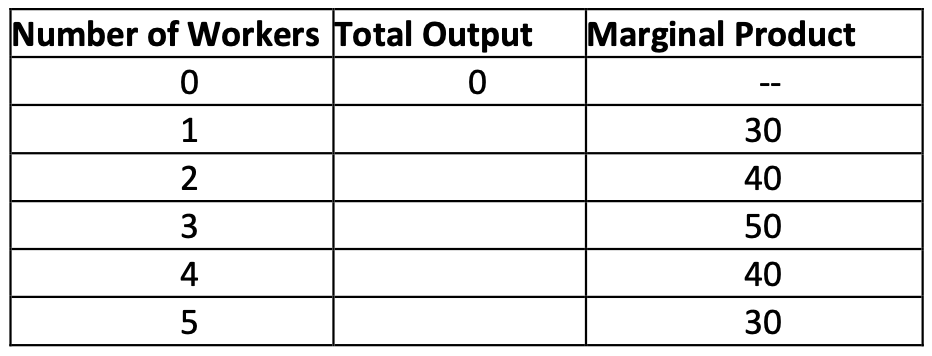
16. Refer to Table 2. What is total output when 2 workers are hired?
a. 10
b. 40
c. 70
d. 120
Table 3
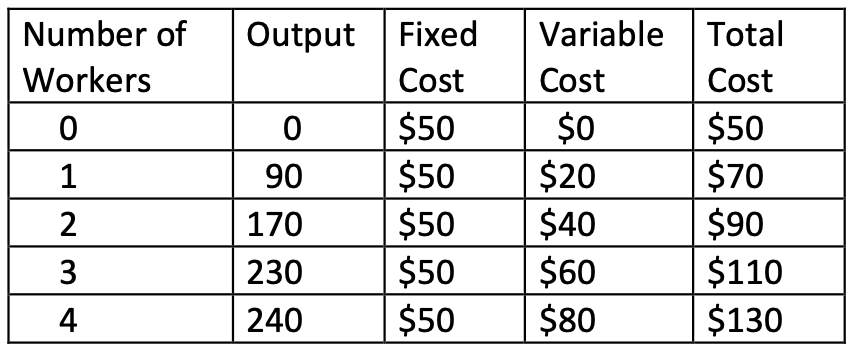
17. Refer to Table 3. At which number of workers does diminishing marginal product begin?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
18. If a firm produces nothing, which of the following costs will be zero?
a. total cost
b. fixed cost
c. opportunity cost
d. variable cost
19. Suppose that a firm has only one variable input, labor, and firm output is zero when labor is zero. When the firm hires 6 workers the firm produces 90 units of output. Fixed costs of production are $6 and the variable cost per unit of labor is $10. The marginal product of the seventh unit of labor is 4. Given this information, what is the average total cost of production when the firm hires 7 workers?
a. $10.06
b. $9.64
c. 81 cents
d. 70 cents
20. Which of the following can be added to profit to obtain total revenue?
a. net profit
b. capital profit
c. operational profit
d. total cost
21. A certain firm produces and sells potato chips. Last year it sold 3 million bags of chips at a price of $3 per bag. For last year, the firm's
a. accounting profit was $9 million.
b. economic profit was $9 million.
c. total revenue was $9 million.
d. explicit costs was $9 million.
22. Gloria has decided to start her own snow removal business. To purchase the necessary equipment, Gloria withdrew $2,000 from her savings account, which was earning 3% interest, and borrowed an additional $4,000 from the bank at an interest rate of 7%. What is Gloria's annual opportunity cost of the financial capital that has been invested in the business?
a. $60
b. $280
c. $340
d. $660
23. Bev is opening her own court-reporting business. She financed the business by withdrawing money from her personal savings account. When she closed the account, the bank representative mentioned that she would have earned $300 in interest next year. If Bev hadn’t opened her own business, she would have earned a salary of $25,000. In her first year, Bev’s revenues were $30,000. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. Bev’s total explicit costs are $25,300.
b. Bev’s total implicit costs are $300.
c. Bev’s accounting profits exceed her economic profits by $300.
d. Bev’s economic profit is $4,700.
Table 4
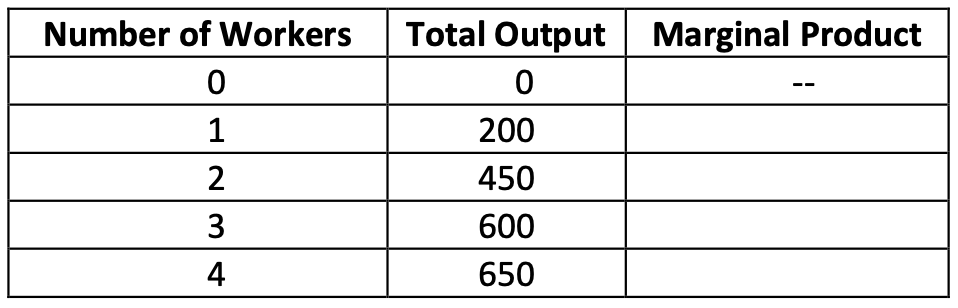
24. Refer to Table 4. What is the marginal product of the fourth worker?
a. 250 units
b. 200 units
c. 150 units
d. 50 units
25. Refer to Table 4. At which number of workers does diminishing marginal product begin?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
26. For a construction company that builds houses, which of the following costs would be a fixed cost?
a. the $20 per hour wage paid to a construction foreman
b. the $30,000 per year salary paid to the company's bookkeeper
c. the $2 per worker-hour paid to the state government for workers’ compensation insurance
d. All of the above are correct.
27. At Bert's Bootery, the total cost of producing twenty pairs of boots is $400. The marginal cost of producing the twenty-first pair of boots is $83. We can conclude that the
a. average variable cost of 21 pairs of boots is $23.
b. average total cost of 21 pairs of boots is $23.
c. average total cost of 21 pairs of boots is $15.09.
d. marginal cost of the 20th pair of boots is $20.
28. Which of the following statements is not correct?
a. The marginal cost of the fifth unit of output equals the total cost of five units
minus the total cost of four units.
b. The total variable cost of seven units equals the average variable cost of seven
units times seven.
c. If marginal cost is rising, then average variable cost must be rising.
d. The marginal cost of the fifth unit of output equals the total variable cost of five units minus the total variable cost of four units.
29. When a firm is experiencing economies of scale, long-run
a. average total cost is minimized.
b. average total cost is greater than long-run marginal cost.
c. average total cost is less than long-run marginal cost.
d. marginal cost is minimized.
Figure 4

30. Refer to Figure 4. The firm experiences diseconomies of scale if it changes its level of output from
Q1 to Q2.
Q2 to Q3.
Q3 to Q4.
Q4 to Q5.
Part 2: Problems [10 points each]
31. John has been in the habit of mowing Willa's lawn each week for $20. John's opportunity cost is $15, and Willa would be willing to pay $25 to have her lawn mowed. What is the maximum tax the government can impose on lawn mowing without discouraging John and Willa from continuing their mutually beneficial arrangement?
32. The table shown reflects the value Tammy places on each donut she eats:
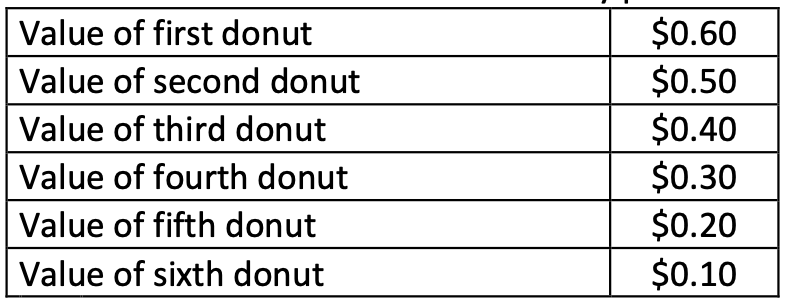
Use this information to construct Tammy's demand curve for donuts.
If the price of donuts is $0.20, how many donuts will Tammy buy?
Show Tammy's consumer surplus on your graph. How much consumer surplus
would she have at a price of $0.20?
If the price of donuts rose to $0.40, how many donuts would she purchase
now? What would happen to Tammy's consumer surplus? Show this change
on your graph.
33. Illustrate on three demand-and-supply graphs how the size of a tax (small, medium and large) can alter total revenue and deadweight loss.
Figure 5
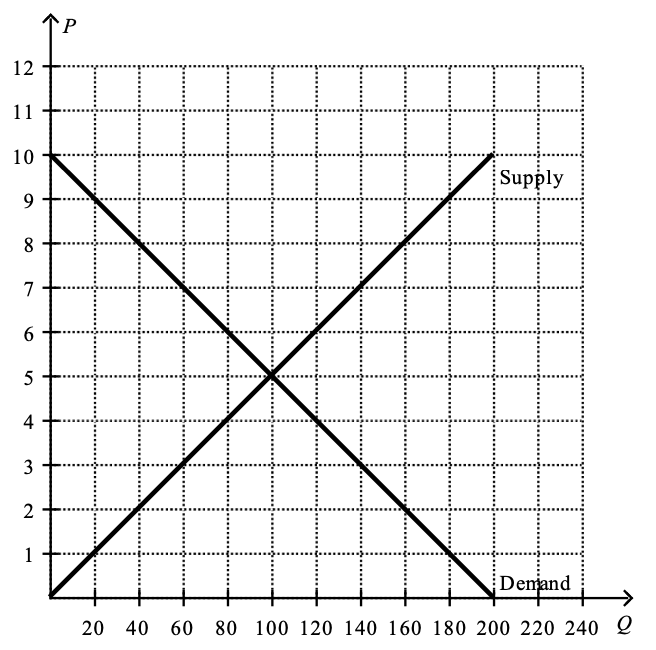
34. Refer to Figure 5 to answer the following two. Show your work clearly.
a. How much is total surplus at the market equilibrium?
b. Suppose the government places a $4 tax per unit on this good. How much is consumer surplus after the tax is imposed?



