Show work for problems 34-39
Cost concepts such as variable, fixed, mixed, direct, and indirect apply only to manufacturers and not to service companies.
True / False
Total variable costs change in proportion to changes in the volume of activity.
True / False
Revenue cycle management is driven by cost control.
True / False
After comparing the product margins between two alternatives the alternative with the higher product margin should be chosen.
True / False
A step-wise variable cost can be separated into a fixed component and a variable component.
True / False
Determining whether a firm's financial position is improving or deteriorating requires analysis of more than one set of financial statements. Trend analysis is one method of measuring a firm's performance over time.
True / False
An avoidable fixed cost is a fixed cost that will be avoided if the service remains/continues.
True / False
In healthcare, “target costing” usually involves the provider of services as the “price setter” and the government as the “price taker”.
True / False
After comparing the product margins between alternative activities of the same magnitude, the activity with the higher product margin should be chosen.
True / False
Asset mix is the amount of working capital an organization keeps on hand to meet its working capital obligations.
True / False
The basic form of cost-volume-profit analysis is often called break-even analysis.
True / False
Profit centers are responsible for both controlling costs and managing/increasing revenues.
True / False
A Line of Credit is considered a long-term commitment.
True / False
The contribution margin per unit is the price at which a unit must be sold in order for the company to break even.
True / False
The dollar amount of sales needed to achieve a target income is computed by dividing the sum of fixed costs plus the target pretax income by the contribution margin ratio.
True / False
The contribution margin ratio is the percent of each sales dollar that remains after deducting the total unit variable cost.
True / False
All of the following factors could contribute to a decrease in health care costs except:
a.
Pharmaceuticals going off patent.
b.
Providers using health information technology in robust ways.
c.
Medical technology continuing to develop new systems.
d.
Hospitals overriding physician preference in supplies.
Which of the following is not a major reason to hold cash?
| a. | Hedge against inflation. |
| b. | For daily operational purposes. |
| c. | Precautionary purposes. |
| d. | Speculative/investment purposes. |
Additional costs incurred solely as a result of an action or activity on a particular set of actions or activities are defined as
a.
Incurred costs.
b.
Incremental costs.
c.
Infallible costs.
d.
Incredible costs.
Credit terms of Accounts Payable “2/15 net 30” mean?
a.
A 2% discount is available if payment is made within 15 days.
b.
A 2% increase is made if payment is made within 15 days.
c.
A. 15% discount is available if payment is made within 2 days.
d.
No discount or premium applies.
On a “per unit” basis, fixed costs will ___________ when volume increases.
a.
Decrease
b.
Stay the same
c.
Increase
d.
Both increase and decrease
Which of the following statements is true regarding product and period costs?
a.
Delivery expense is a product cost and indirect materials is a period cost.
b.
Factory rent is a product cost and advertising expense is a period cost.
c.
Office rent is a product cost and supervisors’ salaries exp. is a period cost.
d.
Sales commissions and indirect labor are both period costs.
A cost with a flat cost line within a relevant range that shifts to another level when volume significantly changes is a(n):
| a. | Flat line cost. |
| b. | Step-wise cost. |
| c. | Curvilinear cost. |
| d. | Incremental cost. |
Revenue Cycle Management can be hindered by
a.
Patients giving correct demographic information.
b.
Lack of clarity about who is responsible for bill payment.
c.
Current health care insurance information.
d.
An accurate/clean final bill.
Sources of Temporary Cash include:
a.
Line of Credit
b.
Commitment Fees
c.
Answers A & B
d.
None of the above
Which of the following is the goal of the U.S. health care system?
a.
Access.
b.
Cost.
c.
Quality.
d.
All of the above.
(2 Points) Which one of the following statements is not true?
| a. | Total fixed costs remain the same regardless of volume within the relevant range. |
| b. | Total variable costs change with volume. |
| c. | Variable costs per unit remain the same regardless of the volume. |
| d. | Total variable costs decrease as the volume increases. |
| e. | Fixed costs per unit increase as the volume decreases. |
An Aggressive Strategy for managing a hospital’s working capital would include
| a. | Maintaining more cash and inventory and decrease access to low-interest short-term debt. |
| b. | Maintaining less cash and inventory and increase access to low-interest short-term debt. |
| c. | Maintaining more cash and inventory and increase access to low-interest short-term debt. |
| d. | Maintaining less cash and inventory and decrease access to low-interest short-term debt. |
| | |
(4 Points) A firm expects to sell 25,000 units of its product at $11 per unit. Pretax income is predicted to be $60,000. If the variable costs per unit are $5, total fixed costs must be:
a.
$215,000.
b.
$275,000.
c.
$90,000.
d.
$125,000.
e.
$65,000.
An Asset Mix strategy related to Working Capital Management includes:
| a. | How an organization chooses to finance its working capital needs. |
| b. | The amount of working capital an organization keeps on hand relative to its working capital needs. |
| c. | Risk of greater return relative to lower liquidity. |
| d. | Coin and currency. |
| | |
Which of the following costs is most likely to be classified as fixed?
| a. | Property taxes. |
| b. | Shipping costs. |
| c. | Sales commissions. |
| d. | Direct labor. |
| e. | Direct materials. |
(2 Points) An important tool in predicting the volume of activity, the costs to be incurred, the sales to be made, and the profit to be earned is:
| a. | Cost-volume profit analysis. |
| b. | Variance analysis. |
| c. | Target income analysis. |
| d. | Least-squares regression analysis. |
| e. | Process costing. |
(4 Points) During March, a firm expects its total sales to be $160,000, its total variable costs to be $95,000, and its total fixed costs to be $25,000. The contribution margin for March is:
| a. | $25,000. |
| b. | $120,000. |
| c. | $65,000. |
| d. | $40,000. |
| e. | $90,000. |
(4 Points) Watson Company has monthly fixed costs of $83,000 and a 40% contribution margin ratio. If the company has set a target monthly income of $15,000, what dollar amount of sales must be made to produce the target income?
| a. | $207,500. |
| b. | $245,000. |
| c. | $37,300. |
| d. | $170,000. |
| e. | $39,200. |
The Working Capital Cycle includes
a.
Obtaining cash.
b.
Billing and Collections.
c.
Providing Services.
d.
All of the above.
(3 Points) A Last year, Wesson Company sold 10,000 units of its only product. If sales decrease by 15% in the current year, how will unit variable cost and unit fixed cost be affected?
| A) | Unit Variable Cost Remains constant | Unit Fixed Cost Remains constant | ||
| B) C) D) E) | Increases Decreases Remains constant Remains constant | Decreases Remains constant Decreases Increases | ||
| a. | Choice A. | |||
| b. | Choice B. | |||
| c. | Choice C. | |||
| d. | Choice D. | |||
| e. | Choice E. | |||
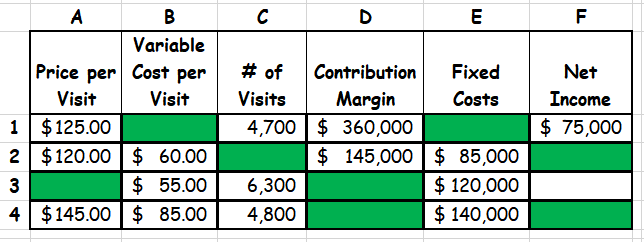
(6 Points) The table below contains selected financial information regarding the four clinics operated by XYZ Hospital. Calculate the missing financial information (the cells in “green”).
(12 Points) ABC Hospital Corporation is preparing its 2022 Q1 Budget. The table below provides the number of hospital encounters, the payor mix, and the dollar amount of expected revenue per encounter (by payor type).
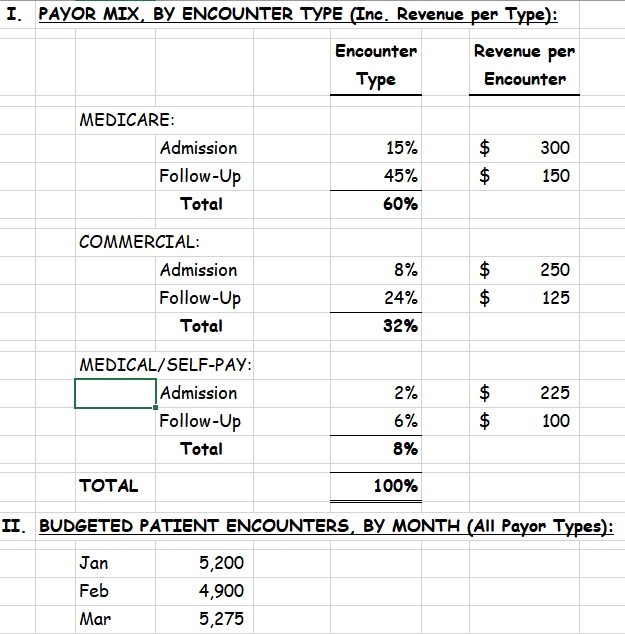
The Hospital also is budgeting Variable Costs to be 52% of Revenue, and monthly Fixed Costs of $350,000/month. Given this information, calculate (1) the 2022 Q1 Revenue, by month, and (2) the 2022 Q1 Pre-Tax Income, by month (Hint: Build an Excel file with the individual months and Q1 total as columns and the other lines of the budget [CM, Fixed Costs, and Pre-Tax income] as rows).
(4 Points) A product sells for $200 per unit, and its variable costs per unit are $130. The fixed costs are $420,000. If the firm wants to earn $35,000 pretax income, how many units must be sold?
| a. | 5,500. |
| b. | 6,500. |
| c. | 5,000. |
| d. | 6,000. |
| e. | 500. |
(10 Points) A major principle of budget reviews (budget vs. actual) is variance analysis. The understanding of the nature of costs, including how they are impacted by activity (sales, for example), allows one to rationally explain what happened, and plan for potential future variances. Please define and briefly describe the nature of costs, and how they are impacted by variances. Include in your response what, if any control, one has on costs. Provide examples, if applicable.
(5 Points) Key Performance Indicators (KPI) are becoming a favorite management tool to help govern financial and operational performance in health care organizations. The better we understand their nature and purpose, the more effective KPI development and implementation occurs. Define and explain (1) what are KPIs, (2) how they are developed and implemented in an organization, and (3) what are the relative strengths and weakness (advantages and disadvantages) associated with KPI development and monitoring. Provide examples, if appropriate, to illustrate your point(s).
Page 9 of 9



