i have attached file
2420-Lab 5- Culture Media and Contamination
Directions:Answer following questions after reading the information and watching the video from the link below. Use color RED for your answers. Submit the completed document on eCampus for grading. Refer to
the textbook Openstax Microbiology- Chapter 9
Link: Cultivation of Bacteria-Media, Virtual Edge Experiment-3B
This document has 17 questions to answer, some may have sub-questions.
Students MUST use scientific terminology while answering all questions
For each wrong answer 0.5 points will be deducted
Read the information from textbook from chapter 4 review sections 4.5 (pages 103-105) and 4.6 (pages 106-107) to answer the following questions.
Natural Growth requirements of bacteriaList the major elements required for bacterial growth along with their function.
List the trace elements required for bacterial growth along with their function.
What is a “limiting” nutrient?
What are growth factors?
What is meant by fastidious bacteria? How are these used in research and industry?
Define the following and give one example of an organism that belongs to each category:
Autotroph
Heterotroph
Photoautotroph
Photoheterotroph
Chemolithoautotroph (chemoautotrophs):
Chemoheterotroph (chemoorganotrophs):
Media can be SELECTIVE; allowing only certain types of microorganisms to grow on it. The addition of any antibiotic to a media makes it selective (i.e. only microorganisms that are resistant to that antibiotic would be able to grow in/on that media).
Media can be DIFFERENTIAL; allowing different types of microorganisms to grow on it, but depending on the organism’s metabolism, different microorganisms may appear differently
A culture medium can be both selective and differential.
Link: Cultivation of Bacteria-Media, Virtual Edge Experiment-3B and the textbook chapter 4 (sections 4.5 and 4.6) (Nester- McGraw Hill) to answer the following questions:
What is a complex (or undefined) medium? Give one example.
Describe a situation that would require you to use complex medium in the lab.
What is a chemically defined (or defined) medium? Give one example.
Describe a situation that would require you to use chemically defined (or defined) medium in the lab.
What is selective media?
Describe a situation that would require you to use selective medium in the lab.
What is differential media?
Describe a situation that would require you to use differential medium in the lab.
What are the components of the following media?
Nutrient broth
GSA
TSA
EMB
MSA
Blood agar
McConkey agar
Out of types of media listed above in question 15 which ones are
Complex
Defined
Selective
Differential
Selective and Differential
Observe the pictures and answer questions:
The plate shown below has E. coli growing in the yellow area. True OR False. Explain your answer.
The plate shown below has E. coli growing in the A area. True OR False. Explain your answer.
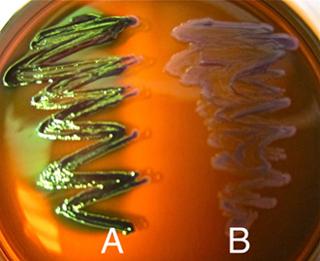
If a drinking water supply is contaminated with fecal bacteria like E. coli, which of the above tests would you use to confirm?
Streptococcus pyogenes causes strep throat. Which of the above tests would you use to confirm an infection with Streptococcus pyogenes? What results of this test would conform if one has strep throat?
Based on the results on the McConkey’s agar plate below, which letter represents
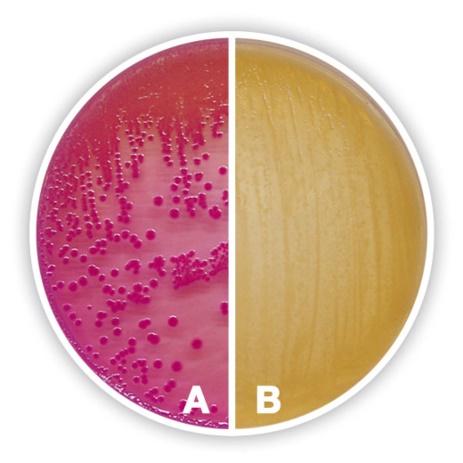
Lactose fermenting bacteria like E. coli
Non-lactose fermenting bacteria like Salmonella typhimurium
Hers is an experiment shown on the Virtual Edge- 1A that we complete in the lab.
After viewing the video and looking at the results you will realize the following:
Our fingers and overall skin carry germs so any time we touch our skin and then touch anything else including food or an inanimate object, we transfer germs. These germs could be bacteria, viruses or fungi.
You don’t get sick every day which actually means not all germs make you sick. Some do but at what extent you will get sick will depend on your immune system too.
Does this mean you have to take extreme care about sanitizing everything you touch? Not really. Exposing to many germs is necessary to prime our immune system! (Under current “COVID” conditions you have to!).
OPTIONAL: Such experiment can be performed at home by
cutting equal size pieces of apple or potatoes with a clean (sterile) knife in clean containers
rubbing each one with clean/sterile cotton swabs with different things including keys, cell phone, washed and unwashed fingers, lemon juice (as a preservative)
covering each container with a piece of clean foil
keeping in a warm place (room temperature- around 25oC or 77 oF) for 3-5 days observing twice a day.
If you happen to do this experiment at home, share pictures with the class. (Unfortunately, under current difficult conditions, I won’t advise anyone to specially go out and buy anything. After completion of the experiment, the used pieces should be disposed off into trash by wrapping in a plastic bag. None of this should be consumed by anyone including humans and pets. Be extra careful with children and pets.



