See the attached file
CIS350/3501
Please provide necessary steps to gain the partial credit if your final solution is not correct.
Make an effort to write in a readable fashion. We will skip over (and therefore not grade) non-readable portions.
Note, there are 9 problems on 8 pages.
- (15 points) Time Complexity
Give a tightest possible bound for the Big-Oh runtime complexity of the following program fragments or functions in terms of the value of the input parameter n:
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
a[i] += a[j] + i + j;
sum = 0
for (i = 0; i < n*n; i++)
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)
sum++;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < i*i; j++)
x++;
int simple (int n)
{
if (n < 1000 )
return 1;
else
return n + simple (n – 1);
}
int verysimple (int n)
{
if (n <= 1 )
return 1;
else
return n * verysimple (n/2);
}
(10 points) Binary Search Trees
(a) Show a result of inserting 4, 2, 3, 1, 7, 5, 6, 9, 8 into an initially empty binary search tree.
(b) Show the result of deleting the root.
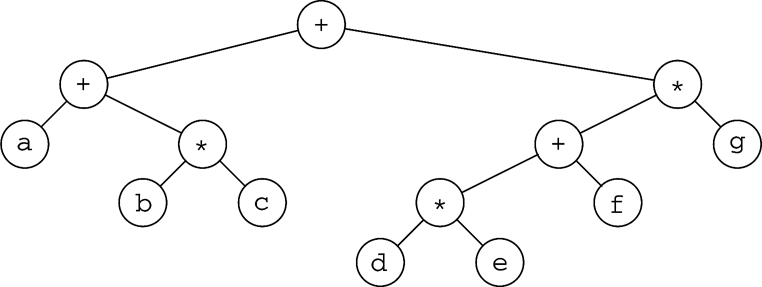
(6 points) Give the prefix, infix, and postfix expressions corresponding to the following tree:
(8 points) AVL Trees
Show a result of inserting 1, 2, 3, 6, 5, 4, 8, 7 into an initially empty AVL tree.
(12 points) Hashing
Draw the result of hashing 58, 13, 18, 3 into a table if the h(x) = x mod 5. The initial hash table size is 5. If you cannot fit everything into the table (when a collision chain is longer than 4), then you have to rehash (reset the table size to 11 and update h(x) = x mod 11), but show both tables. For collisions use: a) separate chaining; b) linear probing; c) quadratic probing; and d) double hashing h2(x)= 3 – (x mod 3).
(6 points) Splay Tree
Show the tree after the search for key 1 in the following splay tree:
(3 points) What is the main difference between a B-tree and a Binary Search Tree? What is the main difference between a B-Tree and a B+ Tree? What are the main applications of B+ tree?
(12 points) Max Binary Heap
Show the results of using the linear-time algorithm to build a max binary-heap using the input: 4, 5, 25, 12, 19, 10, 15, 14, 6.
Show the result of deleteMax to the following max binary heap.
[30, 20, 25, 10, 15, 9, 5, 8, 4, 3]
Show the result of adding 27 to the following max binary heap.
[30, 20, 25, 10, 15, 9, 5, 8, 4, 3]
(8 points)
Write a recursive function that take only a pointer to the root of a binary search tree, BST, and print all the items in BST in the decreasing order.
struct BinaryNode
{
Comparable element;
BinaryNode *left;
BinaryNode *right;
};
int printTreeDecreasingOrder(BinaryNode *node, ostream & out)
{
}
What is the running time of your routine?
8



