need some help in finishing the paper.
Consider an economy with two sectors, a traditional one labeled T with many producers but all added up in one representative firm for the sector, and an industrial one labeled I composed of a price limiting monopolist. There is only one factor of production in the economy, namely (unskilled) labour, where there are one hundred individuals. The traditional sector produces rice (
) in a competitive market with linear (constant returns) production function
where
denotes the amount of labour used in that sector. The price limiting monopolist on the other hand produces rice with a production function that has increasing returns, which is defined as
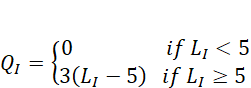
This technology captures the idea that only if a sufficient number of workers hired in the industrial sector, above 5, then the monopolist enters the economy and produces. Note that the monopolist has a higher productivity since its marginal product of labour is 3 while that of sector T is 1. The amount of labour in the economy is distributed in both sectors i.e. for any labour allocation. The price of rice for both sectors is normalized to one, the wage in the traditional sector is denoted
while that in the industrial sector is denoted
where
represents the cost of migrating from the traditional sector to the industrial sector, a switching cost that can be say transportation.
Suppose the demand for rice from the traditional sector is defined as , where
, while the complement
is the demand for rice from the monopolist where Y denotes total labour income in the economy, i.e.
. The distribution of labour among the two sectors determines if the monopolist enters since that would only happen if
is sufficiently large, otherwise it would not, in which case the demand for rice is satisfied only by the traditional sector and
. In what follows we study the conditions under which industrialization through a Big Push would arise or not.
Note that the profit function for the traditional sector is 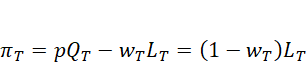 while that for the industrial sector is
while that for the industrial sector is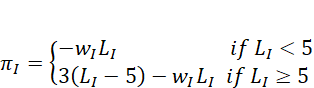
a. Suppose that competition will make profits go down to zero in the long run for the traditional sector. The competitive wage that generates zero profits regardless of the level of used is ____(numeric answer). If d=1 the equilibrium wage the monopolist faces then is ____(numeric).
b. Consider the industrial sector and determine the minimum amount of labour, denoted , for the monopolist to demand in order to have non-negative profits as a function of d. If d=1 then
____(numeric answer).
c. Find the total labour income Y as a function of and d. When d=1 and
=25 then Y=____(numeric answer).
d. Replace the total labour income function Y found in c. into the demand function for traditional rice and
for the industrial rice. When
=0.8, d=1 and
=25 then demand for traditional rice is____(numeric answer).
Up to this point we have assumed a given value for . Now we need to determine the amount of labour supplied in to the industrial sector as a function of
and d.
e. In order to do that equate the supply and demand of rice in the traditional sector to determine as a function of
and
. But since
then using this you can find the supply of labour for the industrial sector denoted
as a function of
and d. If
=0.8 and d=1 then
=____(numeric answer, round to nearest integer)
There are two cases to consider: i) when such that the monopolist enters and attains profits, in which case industrialization arises (Big Push) in the economy in equilibrium; ii) when
such that the monopolist attains non-positive profits and therefore does not enter and the traditional sector is the only one operating in the economy.
f. Under and
does industrialization arise?_____(choose either: YES or NO).
Question 1 options:
| Blank # 1 | |
| Blank # 2 | |
| Blank # 3 | |
| Blank # 4 | |
| Blank # 5 | |
| Blank # 6 | |
| Blank # 7 | |
| |
Consider an industry with nine domestic firms and a market demand function of where
denotes price per unit and
the quantity demanded in the market. Each firm supplies
for
where a is a parameter that measures efficiency, the higher it is the more efficient the firm is.
a. Find the market supply curve for the industry. If the price in the market is say 1 and the parameter a is zero then the quantity supplied in the market is ___ (numeric answer).
b. Find the price and quantity in the industry if there is no free trade as functions of the parameter . When a is zero then the equilibrium price is___(numeric answer) while the equilibrium quantity is___(numeric answer). (Hint: graph the supply and demand curves, where price is in the vertical axis and quantities in the horizontal axis when the parameter a, is zero for your own understanding)
c. Suppose that the economy opens up to world trade where the price in world markets is and market supply curve is horizontal. When a is zero the quantity produced domestically is ____(numeric answer), the quantity demanded is ____(numeric answer) and the amount imported is ____(numeric answer).
d. Suppose the government implements an Import Substitution Industrialization (ISI) policy that imposes a promotional tariff per unit imported such that the price in the domestic economy is now
When
the quantity produced domestically is ____(numeric answer), the quantity imported is ____(numeric answer) Compute the revenue that the government collects with this policy and the deadweight loss from the policy. The revenue for the government is ____(numeric answer) and the deadweight loss from the policy is ____(numeric answer)
e. Suppose the ISI policy is implemented and it is announced to the industry that it will be phased out gradually for a certain period of time and requires domestic firms to achieve efficiency gains, represented as increases in the level of in the domestic industry through "learning by doing" coupled with economies of scale. Find
= ____ (numeric answer) such that the amount supplied by domestic firms at the end of the period is the same aggregate amount under no free trade found above but at the world price
.
Question 2 options:
| Blank # 1 | |
| Blank # 2 | |
| Blank # 3 | |
| Blank # 4 | |
| Blank # 5 | |
| Blank # 6 | |
| Blank # 7 | |
| Blank # 8 | |
| Blank # 9 | |
| Blank # 10 | |
| Blank # 11 |
Match the concept to the appropriate description using the bank of concepts.
_____Comes from the evolution of a country's resource endowment.
_____A means to create a more productive domestic economic structure which raises domestic incomes.
____Sets the stage for a desired structural transformation of import and export patterns
____Countries and/or regions that sequenced first the easy import substitution industrialization strategy with a difficult import substitution strategy afterwards.
____The process of increasing the domestic production of intermediate capital goods and more complex consumption manufactured goods instead of importing them.
____The process of increasing the domestic production of non-durable consumption manufactured goods instead of importing them.
_____Countries that sequenced first the easy import substitution industrialization strategy with an export substitution strategy afterwards.
_____The process of increasing the exports of complex manufactured goods instead of exporting primary goods.
1.An Imperative for Industrialization
2.Difficult Import Substitution Industrialization
3.Industrialization
4.Contests and referees
5.Easy Import Substitution Industrialization
6.Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, China
7.Nascent Infant Industry Tariff strategy
8.Dynamic comparative advantage
9.Export Substitution Industrialization
10.Corruption of civil servants
11.Parastate multinational companies
12.Thailand, Taiwan, Hong Kong, China
13.Latin America and India
Neoliberalism and its emphasis on Smith's invisible hand as a means to attain efficiency and increase the standard of living for workers:
Instruction: You may select more than one answer. Wrong answers and answers that are left blank but should have been marked deduct points from correct marked ones. In any case total points for each question are not below zero.
(please high light the right ones kindly)
| is inconsistent with an industrial policy that uses an Export Substitution strategy. | |
| can be consistent with the nascent infant industry strategy in the short run. | |
| is inconsistent with the Lewis model due to the assumption of surplus labour. | |
| is opposed to industrialization of less developed countries. |
A measure that might facilitate strategy switches in the design of a country's industrial policy to further the desired structural transformations in a less developed economy is:
Instruction: You may select more than one answer. Wrong answers and answers that are left blank but should have been marked deduct points from correct marked ones. In any case total points for each question are not below zero.
(please high light the right ones kindly)
| the corruption of government officials in the banking system. | |
| the dependence on world market becomes intensified. | |
| the foreign account that deteriorates which threaten economic stability | |
| the changing composition of imports. | |
| that non-durable consumer imports as a percentage of total imports decline. |
Industrial policies, in a broad sense, go hand and hand with:
Instruction: You may select more than one answer. Wrong answers and answers that are left blank but should have been marked deduct points from correct marked ones. In any case total points for each question are not below zero.
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
The commonality between the Lewis and Big Push models is that both assume:
Instruction: You may select more than one answer. Wrong answers and answers that are left blank but should have been marked deduct points from correct marked ones. In any case total points for each question are not below zero.
| |
| |
| |
| |
|
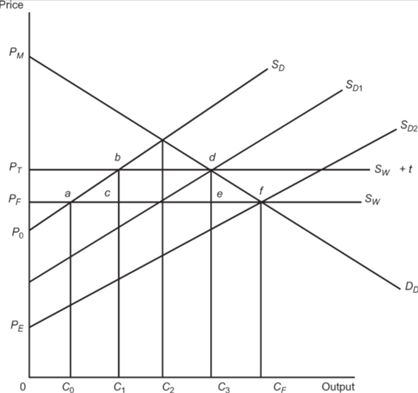
Consider the graph that comes from Cypher's textbook on the promotional tariff strategy. The size of imports that the domestic economy would have when there is no infant domestic industry is
| C2-C0. | |
| zero | |
| C3-C1. | |
| CF-C0. |
State enterprise's operations promote production of
Question 9 options:
| positive externalities accruing to private producers in the economy alleviation of absolute poverty. | |
| private social capital. | |
| efficient structural transformation of economic institutions. | |
| all of the other answers are correct. |
According to Cypher's textbook China's industrialization process after the 1970s can be described up to a certain point as in the
Question 10 options:
| Lewis model. | |
| Nascent infant industry promotional tariff model. | |
| all other options are correct answers. | |
| Big Push model. |
Whenever the state is to some degree "captured" by special interest groups
Question 11 options:
| the nascent infant industry strategy fails to generate efficient allocations in the long run. | |
| promotional tariffs are kept indefinitely. | |
| inefficient allocation of resources remain indefinitely. | |
| all options are correct answers. |

Consider the graph above. The size of imports that the domestic economy would have when there is an infant domestic industry that is fully efficient and the promotional tariff has been eliminated
Question 12 options:
| C2-C0. | |
| zero | |
| none of the other options is a correct answer | |
| CF-C0. | |
| C3-C1 |
Taiwan in the 1950s, during phase of easy Import Substitution Industrialization, state enterprises of all types produced
Question 13 options:
| well over half of all of Taiwanese industrial output. | |
| none of the other options are correct. | |
| almost zero of all Taiwanese industrial output. | |
| below ten percent of all Taiwanese industrial output. |

Consider the graph that comes from Cypher's textbook on the promotional tariff strategy. A neoliberal economist would argue that the promotional tariff to protect the infant industry would
Question 14 options:
| generate a welfare loss in the short run. | |
| reduce indefinitely domestic consumer surplus. | |
| increase the domestic producer surplus of domestic firms at the expense of consumers. | |
| all of the other options are correct. |
An import substitution industrialization process requires
Question 15 options:
| infant industry protectionism. | |
| efficient allocation of resources. | |
| all of the other options are correct. | |
| free international trade. |

Consider the graph that comes from Cypher's textbook on the promotional tariff strategy. The area of the deadweight loss that arises under a promotional tariff to develop a nascent infant industry is
Question 16 options:
| PMPTd | |
| none of the other options are correct. | |
| c+a | |
| c+e |
A nascent infant industry tariff should be
Question 17 options:
| phased out through timely announcements by the government in order for domestic firms to compete with international firms. | |
| kept indefinitely. | |
| none of the other options is a correct answer | |
| eliminated after profits for domestic firms in the industry are zero. | |
| eliminated after one year. |
The infant industry promotional tariff policy can be successful if there
Question 18 options:
| are constant returns to scale in the industry. | |
| are diseconomies of scale in the industry. | |
| is no welfare loss. | |
| are economies of scale in the industry. |
Potential gains from the stage of easy Import Substitution industrialization is that it
Question 19 options:
| develops both specific and general human capital skills as a result of "learning-by-doing". | |
| can provide increasing employment opportunities for an expanding proportion of the labor force. | |
| all options are correct answers. | |
| acts as a training ground for entry-level local capitalists who have an opportunity to develop their own skills in operating profit-oriented and efficiency-focused enterprises. |
Industrialization makes nations less homogeneous in terms of what is consumed, what is read, what is seen on the television and at the cinema and what is learned in schools and in universities.
Question 20 options:
| True | |
| False |
Industrialization is an end in itself and would always increase the capabilities of individuals in Sen's approach.
Question 21 options:
| True | |
| False |
Opposition to industrialization arises from powerful groups who benefit from the status quo of the economy and oppose the possibility of a new order.
Question 22 options:
| True | |
| False |
According to Cypher by 2011 China achieved "upper-middle-income" country status with a PPP adjusted per capita GNI level of US$18,170.
Question 23 options:
| True | |
| False |
Easy Export Substitution Industrialization permits consolidating business elite to come to greater maturity by being forced to remain competitive on price and quality and via continuous upgrading of technological skills and training that maintain productive efficiency.
Question 24 options:
| True | |
| False |
Achieving economic development is inextricably intertwined with the industrialization of an economy according to the heterodox viewpoint of Cypher.
Question 25 options:
| True | |
| False |
For many small nations the limited size of the domestic market as a result of a small population, low average incomes, and a high degree of income inequality can constitute a significant barrier to industrialization.
Question 26 options:
| True | |
| False |
Not all subsequent successful efforts by nations to modernize after Great Britain have involved elements of an import substitution industrialization as a means to promote the expansion of a domestic industrial sector.
Question 27 options:
| True | |
| False |
Historically, import substitution industrialization has been the means by which governments have supported the initial process of structural transformation of an economy.
Question 28 options:
| True | |
| False |
China's explosive growth comes from the Lewis condition of unlimited surplus labour.
Question 29 options:
| True | |
| False |



