answer in simple and clearly
Assignment I (Clinical Enzymology)
Case I (2 Points):
A 63 year old male was brought to the emergency department after complaining of severe chest pain that had lasted for two hours. He had been mowing his lawn when the pain developed, and he became concerned when the pain did not subside after he stopped the activity. He had no previous history of heart disease. On presentation he was moderately overweight, diaphoretic, and in obvious discomfort. He described his chest pain as “beginning in the center of my chest, then my arms, neck, and jaw began to ache too.”
Diagnostic procedures were performed.
Questions:
What is the most important consideration in the triage of this patient?
What tests should be ordered?
Case II (1 Point):
At low concentrations allopurinol acts as a competitive inhibitor of xanthine oxidase and at higher concentrations as a non-competitive inhibitor. However, most of its activity is due to the metabolite oxypurinol which is a non-competitive inhibitor of xanthine oxidase.
Question:
What is the mechanism of action of this medication?
Case III (3 Points):
A 51-year-old male with a history of chest pain with exertion presents with retrosternal chest pressure that radiates to the neck. He has nausea and diaphoresis while at rest. The patient has ST segment elevation and peaked T waves in the inferior ECG leads.
Questions:
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Esophagitis
Acute Myocardial infarction
Pericarditis
Pleural effusion
Hepatitis
Serial Troponin I (TnI) assays were ordered on this patient at admission, 3 hours, and 6 hours afterwards. The samples were collected in heparinized plasma separator tubes. Following are the results (reference range 0-0.03 μg/L)
| Admission = 0.03 µg/L | 3 hours = 0.07 µg/L | 6 hours = 0.02 µg/L |
These results indicate:
A positive test for acute myocardial infarction
Unstable angina
Cardiac injury of severity less than myocardial infarction
Random error with the 3-hour sample
The patient has developed a reinfarction
A specimen from the patient was drawn and creatine kinase (CK) analysis was performed on an automated analyser which gave an error flag indicating substrate depletion. The sample is diluted 1:2 and 1:4 by the serial dilution technique and reassayed. After correcting for the dilution, the results are as follows:
1:2 Dilution = 3,000 IU/L 1:4 Dilution = 3,600 IU/L
Dilutions were made a second time and assayed again but gave identical results. What is the most likely explanation?
The serum became contaminated prior to making the 1:4 dilution
The wrong pipet was used to make one of the dilutions
An endogenous competitive inhibitor is present in the serum
An error has been made in calculating the enzyme activity of one of the two dilutions
An endogenous noncompetitive inhibitor is present in the serum
MCQ 1 (1 Point):
A newborn screening test for galactosemia is positive in your patient. Genetic studies demonstrate the infant harbours a particular mutation in the GALT gene that impairs the activity of galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase. The impaired enzyme cannot convert galactose 1-phosphate and UDP-glucose to UDP-galactose and glucose 1-phosphate. Galactose 1-phosphate accumulates and affects the activity of UTP-dependent glucose-1-phosphate pyrophosphorylase (UGP). Which of the following actions by galactose 1-phosphate proves that it is a competitive inhibitor of UGP?
decreases the apparent Km for glucose 1-phosphate
decreases both the Vmax and the apparent Km for glucose 1-phosphate
decreases the Vmax for glucose 1-phosphate
increases the apparent Km for glucose 1-phosphate
increases the Vmax for glucose 1-phosphate
Lab Experiment (3 Points):
Produce Michaelis Menten and Lineweaver burke plots from the enzyme kinetics lab data in the graph. Make sure to include and check all labels for accuracy, pay special attention to the units. Calculate Km and Vmax for the enzyme.
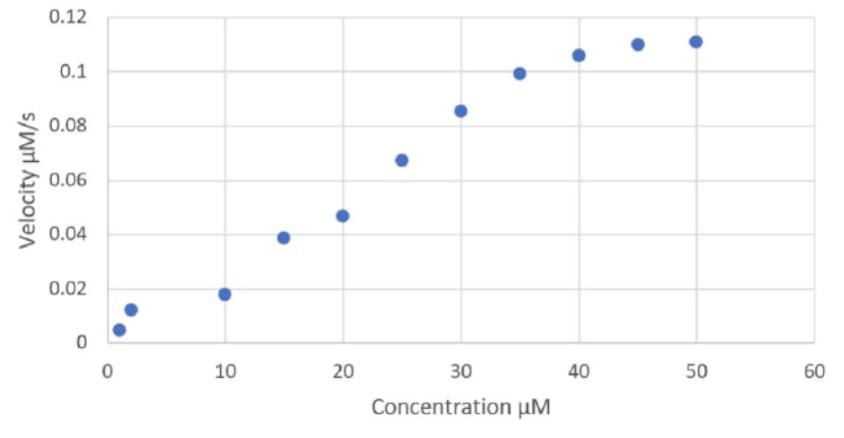
Optimizing the reaction conditions is very important to produce the most accurate kinetic values. List possible factors/conditions that should be tested through repeated trials when designing an optimal activity assay for the enzyme.



