Comp 230 iLab week 6
VBScript IP File Lab
ObjectivesIn this lab, students will complete the following objectives.
Create a VBScript program using NotePad++.
Write a two-dimensional array of IP addresses to a text file.
Read the IP Addresses text file into a script.
Append new Room/PC/IP address data to the text file.
Use the object Scripting.FileSystemObject.
During your session you will have access to the following lab configuration.
For this lab, we will only need to connect to Vlab-PC1.
Vlab-PC1
To start simply click on the named Workstation from the device list (located on the left hand side of the screen) and click the Power on from the in tools bar. In some cases the devices may power on automatically.
During the boot up process an activity indicator will be displayed in the name tab:
Black - Powered Off
Orange - Working on your request
Green - Ready to access
If the remote console is not displayed automatically in the main window (or popup) click the Connect icon located in the tools bar to start your session.
If the remote console does not appear please try the following option:
Switch between the HTML 5 and Java client versions in the tools bar.
In the event this does not resolve your connectivity problems please visit our Help / Support pages for additional resolution options.
Task 1: Create the IP_FileWrite.vbs Program
Note: All captures must be text only—DO NOT capture the NotePad++ application window or the command prompt window. Use copy and paste of text only.
1) Open NotePad++ and from the menu, select File/Open. Open the file IP_File_start.vbs in the C:\comp230 directory. If you do not see this file, you can download it and extract it from the eCollege Doc Sharing file IP_File_start.zip.
Modify the Programmer Header as needed and Save As the VBScript file as IP_FileWrite.vbs.
We are using the array of IP addresses that was used in Lab 4. The line dim ipAddress(5,3) declare 6x4 two-dimensional array. The 5 and 3 give the maximum index value. Since indices always start at 0, this is a 6x4 array.
The lines that follow initialize the array locations with IP addresses. The first index (0..5) represents the rooms 100 through 105. The second index (0..3) represent the four computers in each room.
The IP address of the third computer in room 104 can be found in the array element or component ipAddress(4,2). This value is “192.168.10.45”. Look at the array carefully to determine the meaning of the index values.
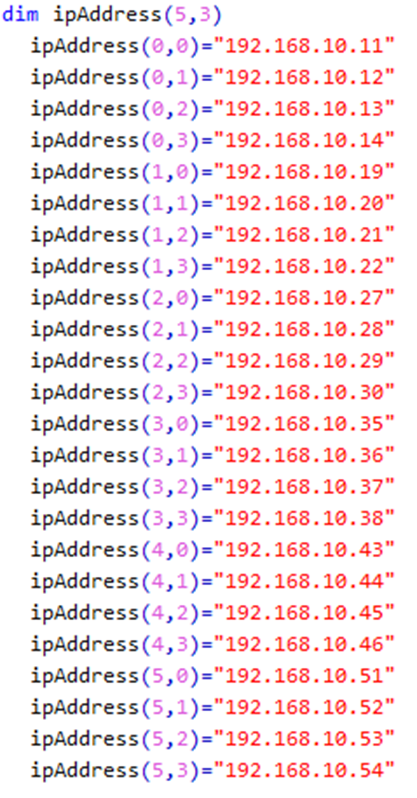
Use SAVE AS to save this file as IP_FileWrite.vbs.
2) Add the code indicated by the pseudocode shown below to write the Array to a text file. Actual code and identifiers for variables and methods within the pseudocode will be in bold font. Carefully read the comments directly below the pseudocode.
Pseudocode
Define the following constants that will be used in your program
CONST READ = 1, WRITE = 2, APPEND = 8, ASCII = 0
We are going to create a text file with the IP address data in it. Define the variable fileName and initialize it to
“c:\comp230\IP_Addresses.csv”
Define the variable ipAddrStr and initialize it to “”
Set fso to the “Scripting.FileSystemObject” using CreateObject
We now want to create the file.
Set ipFileObj = fso.CreateTextFile(filename,True,ASCII)
We will use nested FOR loops to read the data from the two-dimensional array and store it in the text file. Each line of the file will have the room number, computer number, and ip address. Each line of data is first stored in the string variable ipAddrStr, and that data is then written to the file.
For room = 0 to 5
For computer = 0 to 3
ipAddrStr = CStr(room+100) & "," & CStr(computer+1) _
& "," & ipAddress(room,computer)
Use ipFileObj to WriteLine(IpAddrStr)
Next
Next
Use ipFileOjb to close the file
Now we want to read and print the data from the text file. We have to re-open it for reading.
Set ipFileObj = fso.OpenTextFile(fileName,READ,ASCII)
WScript.Echo ipFileObj.ReadAll
ipFileObj.Close
Comments
Named constants should be all caps and the Const prefix should be used to differentiate it from a variable whose value can change.
fileName is a variable that contains the name of the file we will write.
ipAddrStr will be used later to store individual records that we will write to the file “C:\comp230\IP_Addresses.csv”.
You always need to use “Scripting.FileSystemObject” to read, write, or append files.The CreateTextFile method has one required argument and two optional arguments.The first argument value is the file name as string constant or variable. The argument set to True means we will over-write the file if it exists. The third argument specifies the textfile format -1=Unicode, 0=ASCII, 1= system default format.
Note the use of the variable filename. Once ipFileObj is linked to a file, it can be used just like WScript.StdOut. You can use the Write( ), WriteLine( ), and WriteBlankLines( ) methods.
Nested For loops are used to access the two-dimensional array of IP addresses. The outside loop specifies the room 0..5 (representing rooms 100..105) and the inside loop specifies the computer 0..3 (representing computers 1..4). In the first pass through the loop when room = 0 and computer = 0, ipAddrStr is set to the value”100,1,192.168.10.11<CrLf>”.
Close the IP_Addresses.csv file using ipFileObj.Close
3) Save your program with <Ctrl>S. Run your program from a command window using cscript IP_FileWrite.vbs (from the comp230 directory).

4) Execute the dir *.csv command from the command window to verify the existence of the IP_Addresses.csv file.
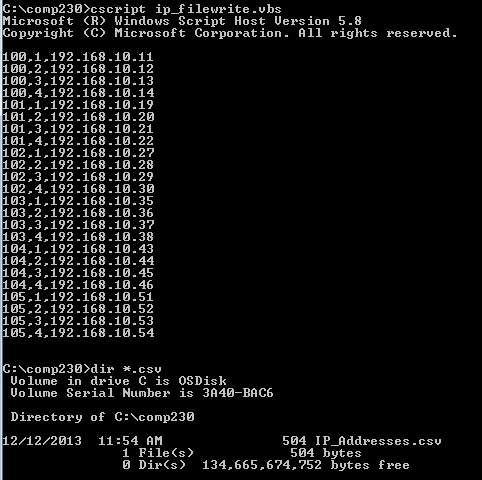
5) If your run has any errors or your file does not contain the data shown above, debug your program and re-run it until you have the correct results.
When you have achieved the correct results, copy and paste your IP_FileWrite.vbs program from NotePad++ into the specified textbox in your lab-report document. Also copy the Windows command prompt run and file verification into the specified textbox into your lab-report document.
Task 2: Create the IP_AppendRead.vbs Program
The IP_AppendRead.vbs program will create data for a new room with four computers with assigned IP addresses. The program will append these four records (one for each IP address) to the IP_Addresses.csv file. Then the program will open the IP_Addresses.csv file and display the contents of the file in a one record per line descriptive format. The new room records that were appended should be displayed.
1) Open NotePad++ and create a new file called IP_AppendRead.vbs. Save this new script file in the C:\comp230 directory. Do not copy and paste any code from your IP_FileWrite.vbs program. This program should be written from scratch.
2) Add the code indicated by the pseudocode shown below to append the new room data to IP_Addresses.csv. Actual code and identifiers for variables and methods within the pseudocode will be in bold font. Carefully read the comments directly below the pseudocode.
Pseudocode
Add an appropriate programmer header
Define the following constants
Const READ = 1, WRITE = 2, APPEND = 8, ASCII = 0
Define the variable fileName and initialize it to "c:\comp230\IP_Addresses.csv"
Define the variable ipAddrStr and initialize it to ""
Define newRoom and initial it to "106"
Define comp1_IP and initialize it to "192.168.10.59"
Define comp2_IP and initialize it to "192.168.10.60"
Define comp3_IP and initialize it to "192.168.10.61"
Define comp4_IP and initialize it to "192.168.10.62"
Set fso to the object “Scripting.FileSystemObject”
Comments
Named constants should be all caps and the const prefix should be used to differentiate it from a variable whose value can change.
fileName is a variable that contains the name of the file we will write.
ipAddrStr will be used to build the record string that will be written to the file “C:\comp230\IP_Addresses.csv”.
The variables newRoom, comp1_IP, comp2_IP, comp3_IP, and comp4_IP are set to values that represent a new room (106) that contains four computers with specific IP addresses.
Use the CreateObject( ) method to Set fso as an object of type: “Scripting.FileSystemObject”.
Add the following using appropriate vbscript commands:
Create a single string that represents the data for the four new rooms.
ipAddrStr = _
newRoom & ",1," & comp1_IP & vbCrLf & _
newRoom & ",2," & comp2_IP & vbCrLf & _
newRoom & ",3," & comp3_IP & vbCrLf & _
newRoom & ",4," & comp4_IP
Pseudocode
If file identified by fileName does not exist Then
Beep Speaker Twice
Display Message:
"File Does Not Exist!!!" & vbcrlf &
"You Must Create the File Before You can Read the File !!"
Quit Program
End If
Set File object ipFileObj using fso.OpenTextFile( )
make sure file is set APPEND and ASCII format
Use ipFileObj object to append ipAddrStr to end of the file identified by filename using WriteLine
Close the file
Comments
ipAddrStr is set to a value that represents the four PCs in the new room 106. Note the use of the Line continuation character _ .
Files can be checked for existence using the fso method FileExists().The NOT Boolean operator may be useful here.
If C:\comp230\IP_Addresses.csv does not exist,
Beep speaker twice and display error message.
Exit the program with WScript.Quit.
Set ipAddrFile to file fileName for APPEND and ASCII.
Set ipFileObj = fso.OpenTextFile(fileName,APPEND,ASCII)
Once ipFileObj is linked to a file, it can be used just like WScript.StdOut. You can use the Write( ), WriteLine( ), and WriteBlankLines( ) methods.
Use the Close method of ipFileObj
3) At this point, Save your IP_AppendRead.vbs script using <Ctrl>S. Run your from a command window using cscript IP_AppendRead.vbs from the Windows Command Prompt in the C:\comp230 directory.
4) After running your program, use the type IP_Addresses.csv command from the Windows Command Prompt in C:\comp230 or open the file in NotePad++ to verify that the new data for room 106 has been written.
C:\c>type IP_Addresses.csv
100,1,192.168.10.11
100,2,192.168.10.12
100,2,192.168.10.13
100,2,192.168.10.14
101,1,192.168.10.19
101,2,192.168.10.20
101,3,192.168.10.21
101,4,192.168.10.22
102,1,192.168.10.27
102,2,192.168.10.28
102,3,192.168.10.29
102,4,192.168.10.30
103,1,192.168.10.35
103,2,192.168.10.36
103,3,192.168.10.37
103,4,192.168.10.38
104,1,192.168.10.43
104,2,192.168.10.44
104,3,192.168.10.45
104,4,192.168.10.46
105,1,192.168.10.51
105,2,192.168.10.52
105,3,192.168.10.53
105,4,192.168.10.54
106,1,192.168.10.59
106,1,192.168.10.60
106,1,192.168.10.61
106,1,192.168.10.62
Return to your program in NotePad++ and finish writing the remainder of your program using the pseudocode found on the next page.
Important Note: After you have verified that the room 106 data has been successfully written to IP_Addresses.csv, re-run your previously written IP_FileWrite.vbs program to restore the original data.
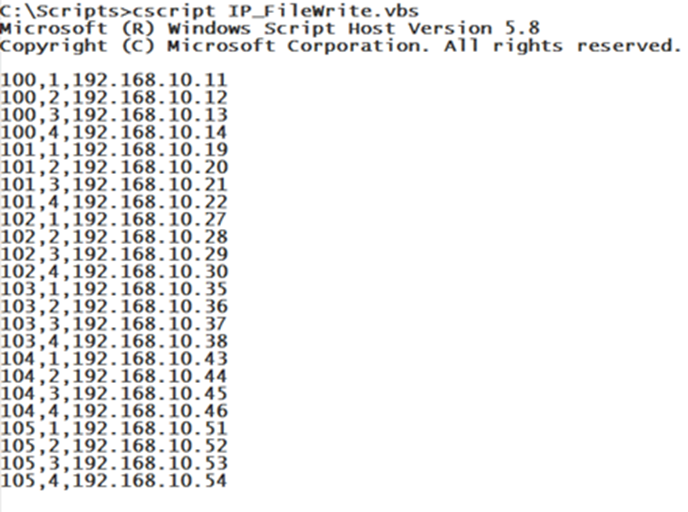
5) The pseudocode shown below will the steps needed to open and read the appended file IP_Addresses.cvs and display the information in the format:
”The IP Address in Room ” room# ” for Computer ” computer# ” is ” ipAddress
where room#, computer# and ipAddress are values read from the IP_Addresses.csv file.
Pseudocode
Using fso.OpenTextFile(), create the ipFileObj object that opens filename for Reading in ASCII format.
Do Until ipFileObj is at EndOfStream
room = ipFileObj.Read 3 characters
ipFileObj.Skip 1 character (the comma)
computer = ipFileObj.Read 1 character
ipFileObj.Skip 1 character (the comma)
ipAddress = ipFileObj.Read 13 characters
ipFileObj.SkipLine
Display Message: "The IP Address in Room " & room & " for Computer "
& computer & " is " & ipAddress
End Loop
Close File
Comments
Set ipFileObj to open fileName for Reading in ASCII format.
Set ipFileObj = fso.OpenTextFile(fileName,READ,ASCII)
Once ipFileObj is linked to a file, it can be used just like WScript.StdIn. You can use the Read( ), ReadLine( ), Skip( ) and SkipLine methods.
The Do/Until loop will display all of the IP_Addresses.csv records including the room 106 records that were added.
Use the Close method of ipFileObj
Task 3: Finish Program and Run it Showing Error-Handling
1) Finish writing your program and save it. Run your program using <F6> in NotePad++ or open a Windows Command Prompt and run it from the C:\comp230directory. Your run should look like the following. Note the highlighted records in the run. These are the appended records for room 106.
2) If you did not get the results shown on the right, you will need to debug your program and run it again until you get these results. To remove duplicate records or restore the original data in the IP_Addresses.csv file, re-run the IP_FileWrite.vbs program.

When you have achieved the correct results copy and paste your IP_AppendRead.vbs program from NotePad++ into the specified textbox in your lab-report document. Also copy the run into the specified textbox in your lab-report document.
3) The .csv extension that we used on our IP_Addresses file indicates a Comma Separated Value format. This kind of file can be opened by Microsoft Excel and Microsoft Access. The file could be easily edited using Excel or even made into a database in Access by adding some field names. Below is our IP_Addresses.csv file opened in Excel (left) and Access (right).

COMP230_Wk6_IPFile_Lab 14 Revision Date: 1213



