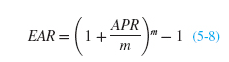Cash Flow Problem Sets
The general equation for computing the future value of multiple and varying cash flows (or payments) is:

The term FVA is used to denote that this is the future value of an annuity. Factoring out the common level cash flow, PMT, we can summarize and reduce the equation as:
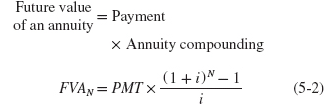
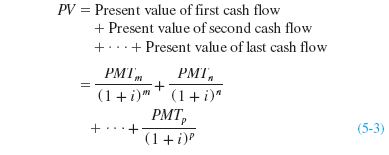
Putting these three individual present value equations together would yield:
PV = [$100 ÷ (1 + 0.07)0] + [$125 ÷ (1 + 0.07)1] + [$150 ÷ (1 + 0.07)2] = $347.84
The general equation for discounting multiple and varying cash flows is:
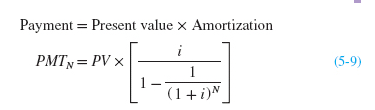
You will find that this present value of an annuity concept will have many business and personal applications throughout your life. Most loans are set up so that the amount borrowed (the present value) is repaid through level payments made every period (the annuity). Lenders will examine borrowers’ budgets and determine how much each borrower can afford as a payment. The maximum loan offered will be the present value of that annuity payment. The equation for the present value of an annuity can be derived from the general equation for the present value of multiple cash flows, equation 5-3. Since each cash flow is the same, and the borrower pays the cash flows every period, the present value of an annuity, PVA, can be written as:
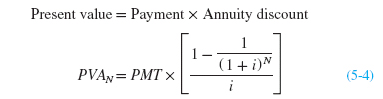
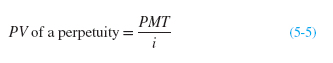
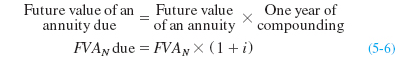
![]()