G5 -1 Greece Guide Part 1
GUIDE 5 -1 (Part I)Unit 2Art of Ancient Greece

Apollo’s Temple at Delphi
This unit presents an important part of our course for it concerns with the very foundation of the Western civilization. We are going to spend more time in this section and work on two guides devoted to Greek art. Try to learn as much as you can.
Before you open your book, let us define the key term “classical that is being used in several senses.
IN HISTORY
Classical world of Greece and Rome –these two ancient civilizationsdeveloped such high standards and enduring models in art and life that this period in human history was named Classical.
The civilizations of Greece and Rome are called classical
The Greek and Roman cultures are called classical
Greco-Roman art is called classical
Classicalperiod in Greece – one of the periods in the history of Greece marked by the highest artistic and cultural achievements.We will study it in the next Greek Guide (part 2).
IN EVERYDAY LIFE
I am sure these applications are better known to you but I want you to realize how they are related to their Greek origins.
3. We use the word ClassicalStyle when we talk about the taste or style based on the principles of clarity, harmony and order – standards that were set by Greek and Roman art.
4. Finally, the general meaning of classical or classic would be 'first ranking',
'the best of its kind', and 'enduring'. Thus, a classic carmeans the finest and most renowned brand in the industry. Am I correct? A dress can be classic as well as. The Americans also use the word classy as a sort of Argo abbreviation when they talk about people whose demeanor and looks are proper and who hold themselves with dignity.
It is not likely that we think about ancient Greeceand Rome when using these words today, is it? Yet, when we call anything classical we pay homage to the high standards of beauty, harmony, and ideal of perfection. And when we compliment someone’s style or demeanor we refer to the ancient Greeks and Romans who claimed the importance of responsibility,duty and integrity prescribed for every good person and citizen.
Now let us begin reading about the celebrated civilizations that set the high classical standards for the millennium to come. Set a goal to learn as much as possible. Take advantage of any extracurricular opportunity. Thus, I would encourage you to watch this introductory video. It will be also helpful for the purpose of orientation in this extensive unit.
Extra Credit Project: Sum up 8 minutes of video in 8 statements (1 bonus point)
 Greek Art History from Goodbye-Art Academy
Greek Art History from Goodbye-Art Academy
Ancient Greek Art: 8-statement Review
Notice that they start with the Classical period and after that go back to the beginning.
Reminder: When you hear something that you want to put on paper, simply stop the video.
Try a CC feature for subtitles/close captions and see if you findthem helpful (right lower corner).
…
.
One more thing to keep in mind if you want to be scholarly minded students of history. Thereal story of Greece started earlier – in the Aegean world covered in the previous chapter.
/Now it is the time to open Chapter 3
CLASSICAL ART:
GREECE AND ROME
“… the glory that wasGreece …
/Complete the well known line by Edgar Allan Poe (on top of page)
The preface is so important that we will go though it together and in detail.
“No other culture has had as far-reaching influence….(p. 45)
/Name the areas in which Greek influence can be felt in our modern world.
*…
"Greece has asserted itself time and again over the 3,000 years since its birth"(p. 45)
This phrase means that there were several revivals of the Classical style in the Western culture since it had developed 2,500 years ago in the Mediterranean world. You should know three major revivals of Greco-Roman culture.
Renaissance:“During the___century, there was a revival of Greek art and culture…”
/Indicate the century/(Renaissance began in Italy in the 1400s)Neo-classical style:“On the eve of French Revolution of 1789…”
What source of inspiration the artists turn to? Complete the phrase.
You remember, of course, that the word neo means new.
3. Greek Revival style:“Our founders ….
/What our founders looked to when building the new American cities and towns?
Next time when you go to Washington, look around to notice that you are surrounded by the Greek and Roman architecture – the National Gallery and other buildings along the Pennsylvania avenuelook exactly like classical temples. But you do not even go that far - there are many houses with the Greek columns in your own town as well.
* * * * * * * * *
Describe the historical relationship between Greece and Rome after Greece was conquered and absorbed by Rome.
*…
Hellenism– *[look up in Glossary]
Let me add to this:
Hellenes - This is how the Greeks called themselves (after the mythical ancestorHellen).
Hellas – this is how they called Greece.
GREECE
To claim that we can get along without …
/You are welcome to type yet another wise saying by the 19th century French artist Ingres.The ideas of HUMANISM and DEMOCRACY were the most important contributions of the Greek thought to the Western civilization. The first time in the history the value was put on the individual.
Besides these contributions there were another fundamental concepts that were introduced by the Greeks and have been used in European culture ever since. Define these basic concepts.
Try to do it in a simple and clear way. Verbalize the notions how you understand them from the text.
| Concept | Major Concern | Define Concept |
| HUMANISM | MAN | * |
| RATIONALISM | REASON | * |
| REALISM / NATURALISM | REALITY | * |
| IDEALISM | BEAUTY/ PERFECTION | * |
This section ends with an interesting thought true through the entire history of humankind.
“As with many civilizations, the development of Greece…(p. 46) /Complete
Four major periods in the art history of ancient Greece spanned together about 1,000 years:
GEOMETRIC period - Birth
ARCHAIC period - Maturation
CLASSICAL period - Perfection (Peak)
HELLENISTIC period - Decline
Geometric Period
| WHEN/ Dates | WHEN /Century | Historical Landmarks |
| * | 9th-8thB.C. |
|
Why is this period called Geometric? – *
The Dipylon Vase as an example of the Geometric Style in Greek Art. (8th century B.C.)
|
What are the decorative motifs? – * What scene is depicted in the central wider bands? – * |
What do they mean when they say that the human figures are renderedin a “conceptual manner” and are “highly abstracted”? Depict how the human figureslook? –
7th CENTURYB.C. (700 - 600 B.C) – Aspan between Geometric and Archaic periods.
(This period is not in your book)
The Greeks undertook the expanded sea travels, visited Egypt and the Near East.
This influence could be easily traced in Greek art of the followingArchaic period.
For example, when you will be looking at the kouros(soon) see whether this statue of nude youth reminds you the Egyptian statues.
Archaic Period
| WHEN/ Dates | WHEN /Century | Historical Landmarks |
| 6th century B.C. This is approximate. late 7th - early 5th centuriesB.C. | Persian invasions 480 B.C. Burning of Acropolis by the Persians Greece expanded its trade |
Type in the dates in the left column and make sure you understand why these centuries and
why “late 7th” and “early 5th.” I will not ask you this on the exam but take a chance to practice.
Archaic– *…
/What does this word means in Greek and why was it assigned to this particular period? (seeGlossary)
Vase PaintingArchaic period
An impressive number of painted vases of various forms came down to us from ancient Greece.
I put together a few most common types (not in your book)
| Kraters– a vessel used for mixing the traditional Greek drink of wine mixed withwater. By the way, this is how they would often drink wine in France
| |
| Amphora - a type of ceramic vase with two handles and a long neck narrower than the body. Was used by the ancient Greeks and Romans | |
| Lekythos - a vessel forstoring oil Note: it has one handle and narrow neck. | |
| Kylix - a wine-drinking cup on a stem Tondo- acircularpainted surface (in this case, inside the cup) “As the representations would be covered with wine, the scenes would only be revealed in stages as the wine was drained. They were often designed with this in mind, with scenes created so that they would surprise or titillate the drinker as they were revealed….” (Wikipedia) | A couple of interesting facts: The word kylix is from theGreek kulix, "cup," which is cognate with Latin calix, the source of the English word "chalice." Image: Greek kylix (inside). |
On term vases
There were a great variety of different types of Greek vessels traditionally called vases.
Thisis not exactly the right term because these "vases" were not used for flowers or house decoration but had various functions (see terms 'krater' and 'lekythos').
The term came about only in the 18th century when there was a huge “fashion on Greeks”, the collected Greek vessels were used for decorating the palaces’ interiors, and they provided the models for the vase industry.This is why the shape of the vases that you have at home, look so much like the Greek vessels.
When you look next time at the modern vase, think about its historical ancestor - Greek amphora that 3,000 years ago was in use in every Greek house for such a basic need as storing oil and wine.
We observe the crucial changes in rendering the human figure in art of this period compared to the previous one - Geometric period.
Vasewith Women working Wool on a Loom.Greek, c. 540 B.C. Archaic Period
From the Metropolitan Museum of Art[“A Closer Look”on page 48]
| *… - This type of the vessel was used forstoring oil. Observe a beautiful composition, read the text and
Athenawas the patron goddess of *__ (In addition to being one of the major divinities in Penelope - tell a story about this smart woman – a wife of legendary Odysseus. - * |
Start reading “Vase Painting” section
“During the Geometric period the human figurewas subordinated to decorative motifs, but in the Archaic period it became *___/Complete/
Francois Vasepainted by Kleitias. Greek, c. 570 B.C. ____ Archaic Period
|
| What type of vessel is it? -* /Sum up 1st paragraph/
Observe the human and animal figures on this vase and compare them to the figures on the Dipylon Vase(from Geometric period). What is new? -* |

Francois Vase.Boar hunting scene (detail)
Black-Figure Vasesof theArchaic period
It is pretty clear why such a name came about, right?
Figures are*… (color)
Background is -*… (color) /Read paragraphs 2- 3 and describe technique/
|
| Black-figured painting technique Three-stage firing process in the kiln: Stage 1:* Stage 2:* Stage 3:* Achilles and Ajax playing a dice game painted by Exekias. c. 530 bc Vatican Museums, Rome |
Red-Figure Vasesof theClassical period
The next stage in the history of vase-painting:
Figures are *… (color)
Background is - *… (color)
|
Kylix by Chairias, ca. 510-500 BC. Ancient Agora Museum in Athens. |
*… -wine-drinking cup /Name/ When this reversal technique was invented? - * Which figures look more realistic |
ArchitectureArchaic Period
During theArchaic period, the major principles for architecture had been developed that continued to exist throughout ancient Greece as well as throughout the entire history of Western civilization.
/Sum up first paragraph/
Temple architecture
Megaron- *___
Cellain Greek temple is*___
The overall shape of the temple was*___ (Model)
(Model)
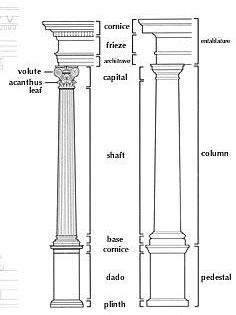
GREEK ARCHITECTURAL ORDERS
For all unknown terms look in the Glossary at the end of your handbook and write down the definitions. This is a “must know” vocabulary.
Three orders (or styles) in Greek architecture:
*
*
*
| | Doric order was [Describe] *…… *…. *…. |
| | Ionic order has a capital made of scroll-shaped volutes and…. |
| | Corinthian order: * most complex base, * capitalis made of carved acanthus leaves ending in volutes. Whose favorite order was it? [You will also see a lot of it in the American architecture]
|
Note: it is the shape of capital that allows you to identify the order
Try to find a building built in the Classical style in your own town. My guess would be that it is bank or court house.
ARCHITECTURAL ORDER
Define architectural terms. (Look up in Glossaryat the end of the book).
Example: Pediment - any triangularspace surrounded by cornices.
|
entablature
| Cornice- *
Frieze- * Architrave- * Entablature- * cornice + frieze + architrave altogether make entablature Capital (head of the column) - * Shaft- *. Stylobate- *. Stereobate- *. /Look in the book for these twoelements/ |
SCULPTURE Archaic period
"In the Archaic period, sculpture emerged as a principal art form."
* /What changed?/
Fallen Warriorfrom the temple at Aegina. C. 500 B.C.



Which part of the temple was decorated by this sculpture? - *
Stylization – By this moment you are supposed to come across this word thatyou have already met in the previous chapter.You should remember that this term is also related to theterms “conceptual" (e.g., manner) and “conventional"(e.g., representation”).
What do these terms mean? Use the sculpture ofFallen Warrior from the temple at Aegina
asan example of stylization. Explain how you understand it.
Which part of the figure, do you think, is done more realistically - his body or head?
*
The conventions are most obvious in the sculpting of the “mask-like” face. Describe them.
*
*
Notice a strange smile on his face(not exactly adequate for a dying man). It is called an “archaic smile”. You will come across this new term on the next page. Here we deal again with a conventional approach (not a naturalistic one).
Free-Standing Sculpture began to appear about* _
Kouros
| | What type of statues received this name? - */Who is depicted? What was its possible purpose? - * Stylistic characteristics of kouros: Shape of the body - * Fists are * Position of legs - * The parts of anatomy are * “ Kneecaps and muscles - * Hair - * What about the facial expression? -* |
Archaic Smile- * /Find the term in Glossary/
This facial expression is better seen on Kore. There are several theories explaining the possible meaning of this somewhat mysterious smile.One of them asserts that the sculptors tried to give more live to the human face.
There is yet another hypothesis– it suggests thatthe Greek sculptors intended to pass the state of being blessed and/or these figures could be the representations of gods. As for the warrior's smile, there might be some explanation found in the code of brave behavior, ability to endure physical suffering and value of personal honor by which the Greek men had been raised.
| | Kore What is different about Kore - a female counterpart of Kouros? What was the material that theses statues were made of? Do they look the same way today as they looked 3,000 years ago? |
TERMS
Peplos - *
Encaustic- *
/Read about this unusual and very durable kind of paintin the glossary /
“The Greeks made their gods into men and their men into gods” (page 52)
Indeed, the Greeks pictured their gods very much as human beings. Remember this when you look at the Greek statues and read the myths. At the same time, the humans depicted as perfect beings – the beautiful idealized figures.
When and how did the Archaic period end? Make brief historical notes of the last paragraph.

Naxos Island
In conclusion of Greek Guide 5-1
Major artistic achievements of Archaic Art
| Vase painting | Black-Figure painting |
|
|
|
| Architecture | New architectural format of temple |
Next Guide will continue the Greek theme -it will be devoted to the next two periods - Classical and Hellenistic. Take the Greek QUIZ (# 4) only after completion of both Greek guides.