SPSS
College of Doctoral Studies
RES-845: Module 8 Problem Set Solutions
Factorial (2 x 3) MANOVA
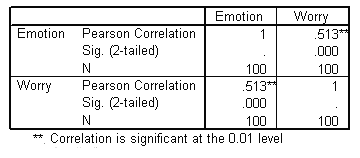
| 1. | Is there a sufficient correlation between the dependent variables to justify the use of MANOVA? |
| 2. | Was the assumption of Equality of Covariance Matrices violated? Explain. |
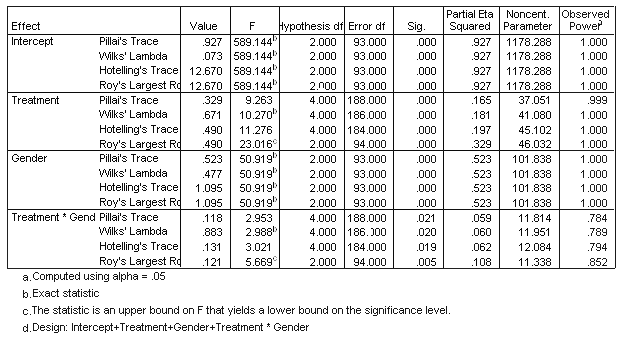
| 3. | Is there a statistically significant multivariate interaction effect? Identify the dependent variable(s) of this interaction effect. |
| 4. | What would be the proper follow-up tests for a statistically significant interaction effect? |
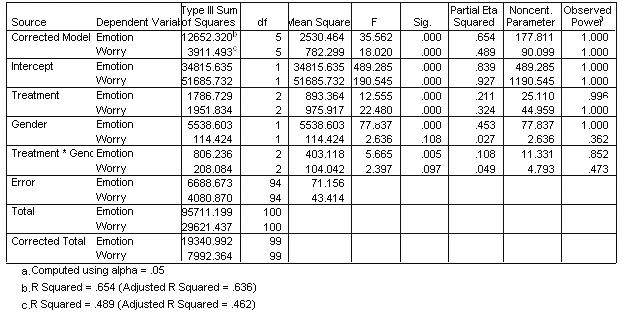
| 5. | Identify the proper post hoc analyses for any statistically significant univariate effects. Explain your answer. |
| 6. | Is there a statistically significant multivariate gender effect on the dependent variate? |
| 7. | Why would a researcher conduct a MANOVA instead of several ANOVAs? |
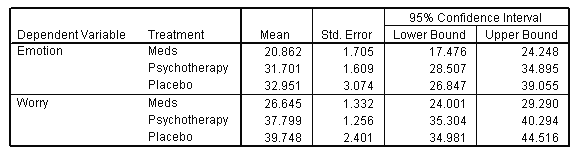
| 8. | Write a Results section for this research. |
| Correlations |
|
|
General Linear Model
| Box's Test of Equality of Covariance Matricesa |
|
|
| Multivariate Tests c |
|
|
| Levene's Test of Equality of Error Variances a |
|
|
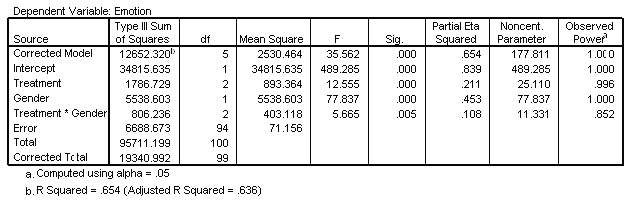
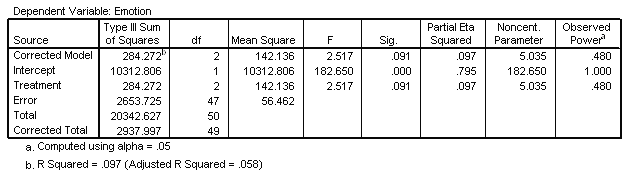
| Tests of Between-Subjects Effects |
|
|
General Linear Model
| 1. Treatment |
|
|
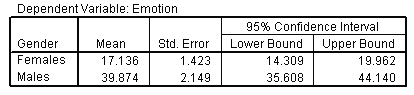
| 2. Gender |
|
|
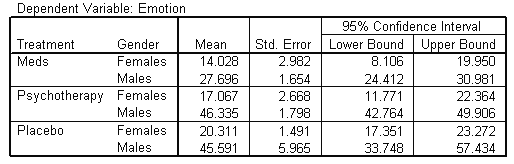
| 3. Treatment * Gender |
|
|
Univariate Analysis of Variance
| Tests of Between-Subjects Effects |
|
|
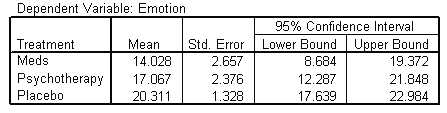
Estimated Marginal Means
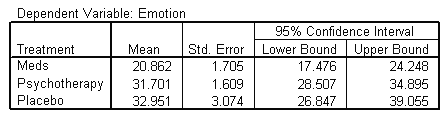
| 1. Treatment |
|
|
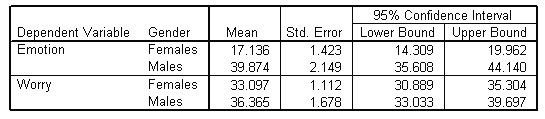
| 2. Gender |
|
|
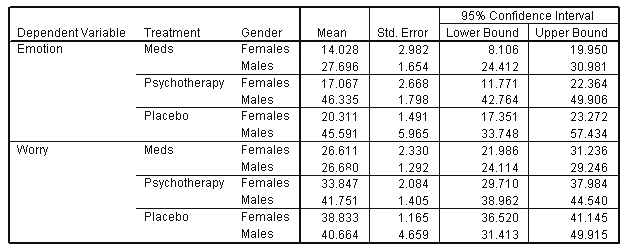
| 3. Treatment * Gender |
|
|
Univariate Analysis of Variance for MALES
| Tests of Between-Subjects Effects |
|
|
Estimated Marginal Means
| Treatment |
|
|
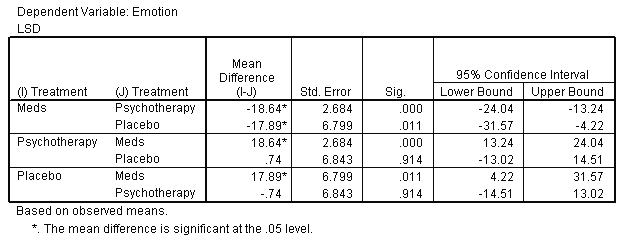
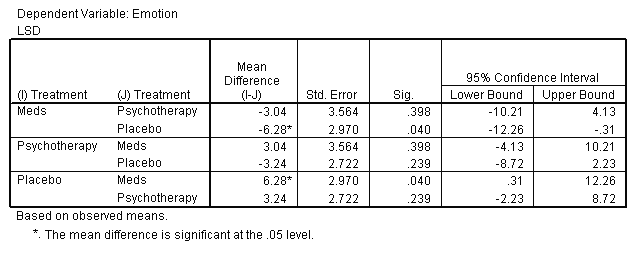
Post Hoc Tests
| Multiple Comparisons |
|
|
Univariate Analysis of Variance for FEMALES
| Tests of Between-Subjects Effects |
|
|
Estimated Marginal Means
| Treatment |
|
|
Post Hoc Tests Treatment
| Multiple Comparisons |
|
|
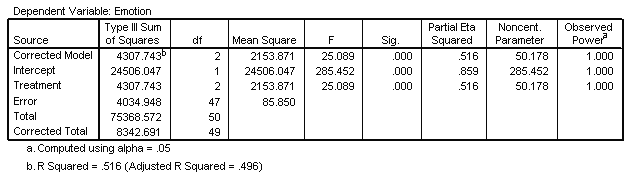
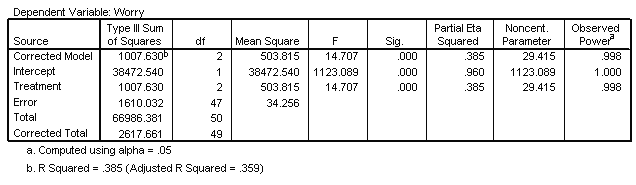
Univariate Analysis of Variance for TREATMENT Main Effect
| Tests of Between-Subjects Effects |
|
|
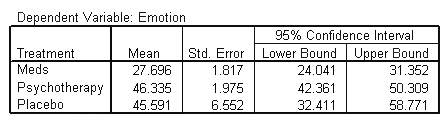
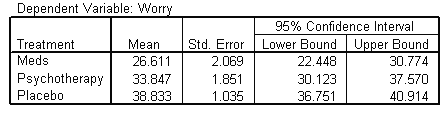
Estimated Marginal Means
| Treatment |
|
|
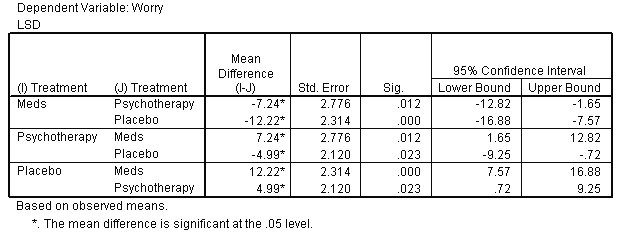
Post Hoc Tests
| Treatment |
|
|