For Catherine Owens
Running head: GREECE 0
Greece
Ashley Robinson
Southern New Hampshire University
Greece
The country chosen for the final project is Greece it is located in the southern part of Europe. It has an extensive coastline and shares its borders with Albania, the Republic of Macedonia, Bulgaria, and Turkey. The reason behind this choice is the rich history and culture the nation has with significant influences in art, philosophy, language, politics and sports. The nation was the originator for the Olympic Games that is estimated to have started in 776 BC and ended in 393 BC before it was reinstated in 1896, after more than one millennium (Finley, 2012). Currently, it is one of the world's most visited countries, ranked amongst the top 20 tourist destinations. According to the Greek Ministry of Tourism, the country received over ten million tourists in the year 2015 (Turner, 2015). This has allowed the country’s foreign exchange generation to increase significantly from US$17 billion in 2014 to US$ 29 billion (Turner, 2015). Compared to ancient Greece, modern Greece has had several economic stagnations. The nation joined the then called “European Community” which later was renamed to the “European Union (E.U.)” in 1981. During the same period, the country suffered economic inertia; however, the E.U. come to the country’s aid leading to the nations noteworthy economic, growth of the 1990s. The increased heavy investments, trade, aid from the E.U. and promotion of entrepreneurship drove this growth (Petrakis, 2014). Nonetheless, the country is mostly recognized for its remarkable geological and archeological sites. With eighteen UNESCO World Heritage sites as well as long coastline, many islands such as Rhodes and Mykonos the nation is a rich geographically defined region (Katsoni, & Stratigea, 2016). The country is rich in information economically, geographically, socially and politically.
Geographical Map of Greece 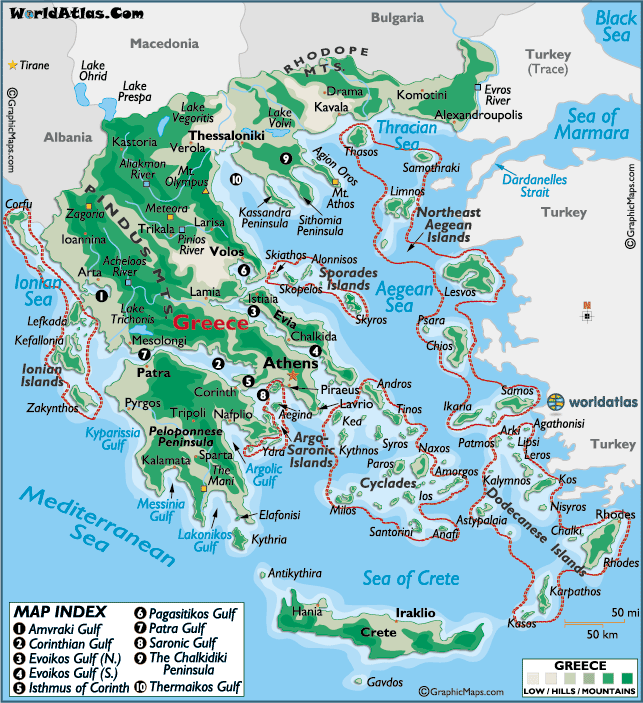
(World Atlas, 2017)
Statistics of the Nation (Central Intelligence Agency, 2017)
Geographic Elements
| Location | Southern Europe, bordering the Aegean Sea, Ionian Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea, between Albania and Turkey. |
| Climate | Temperate climate with mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers |
| Bordering Countries | with Albania, the Republic of Macedonia, Bulgaria, and Turkey |
| Terrain | mountainous with ranges that extend into the sea as chains of islands otherwise known as Peninsulas |
| Elevation | mean elevation: 498 m, elevation extremes: lowest point: Mediterranean Sea 0 m, highest point: Mount Olympus 2,917 m |
| Natural Resources | lignite, petroleum, iron ore, bauxite, lead, zinc, nickel, magnesite, marble, salt, hydropower potential |
| Land Use | over 60% of the land is used for agriculture, and approximately 30% is under forestation |
Country Composition
| Population Composition | 93% of the nation’s population are Greek nationals and 7% being foreigners |
| Religion | Greek Orthodox 98%; Islam 1.3%; Christianity 0.7% |
| Language | 99% Greek; 1% French and English |
| Literacy | 97.7% of total population; Male – 95.5%; Female – 96.9% |
| Rate of Urbanization | 0.47% (2010-2015); 78% of the total population |
| Educational Expectancy | Males 17 years; Female 17 years |
Reasoning from the Statistics
From the statistical analysis, it is clear that majority of the population of Greece comprises of the youth. Therefore, the nation has a high number of unemployed citizens who can qualify for various upcoming tourist resorts that will be created by the government. Secondly, the nation has several tourist attraction sites from the terrain to the UNESCO world heritage sites. Finally, the country’s major Greek Orthodox religion promotes unity, resulting in no religious based violence that may affect the foreigners. However, the country is facing tense times, as the population wants political figures to step down from office resulting in political violence (Michaletos, 2016). The nation has been going through severe economic problems some of which contributed to the economic depression of 2008-2009. This resulted in fewer exports from the country; fewer exports mainly because many companies were facing foreclosure due to the lack of currency circulation. The foreclosures also resulted in the majority of the working population to lose their occupations contributing to the increase in violence in the main parts of the country. Currently, the significant risks that face the country include political violence and economic instability due to poor reforms did by the government (Michaletos, 2016). The E.U. has stepped in to help the country twice in the past decade; this has resulted in the E.U. creating terms and conditions that the Greek government will have to follow if they are to receive a bailout.
Reference
Central Intelligence Agency. (2017). The World Factbook: Greece. Cia.gov. Retrieved 11 May 2017, from https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/gr.html
Finley, M. (2012). Olympic Games (1st ed.). Mineola, NY: Dover Publications.
Katsoni, V., & Stratigea, A. (2016). Tourism and culture in the age of innovation (1st ed.). New York, NY: Springer.
Michaletos, I. (2016). In First Nine Months of 2016, Urban Violence and Crime Rise in Greece - Greece. Balkanalysis.com. Retrieved 11 May 2017, from http://www.balkanalysis.com/greece/2016/10/11/in-first-nine-months-of-2016-urban-violence-and-crime-rise-in-greece/
Turner, R. (2015). The Authority on World Travel & Tourism Travel Economic impact 2015 Greece (1st ed.). Athens: Oxford Economics. Retrieved from https://www.wttc.org/-/media/files/reports/economic%20impact%20research/countries%202015/greece2015.pdf
World Atlas. (2017). Greece Map. Worldatlas.com. Retrieved 11 May 2017, from http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/europe/gr.htm



