Final Strategic Plan
Running head: IMPLEMENTATION PLAN
Kaiser Permanente
Implementation Plan, Strategic Controls, and Contingency Plan Analysis
Qiana Reynolds
Lisa Diesel
May 29, 2017
Introduction
The critical steps in starting and developing Kaiser Permanente can be clearly presented in an implementation plan which includes and not limited to objectives, action items, resource allocation, schedule, financial projections, budget and organizational structure adjustments. The prima ry purpose of this implementation plan is providing a guide which managers of Kaiser Permanente will use so as to achieve their business goals in resource and time efficie nt manner. The implementation plan stipulates how management plans, resource and time required to implement the strategies and core business activities of Kaiser Permanente within the provided time.
Objectives
Kaiser Permanente is an integrated health care delivery whose central mission is a community benefit. The organization believes that good health is a fundamental aspiration of all people. They recognize that good health extends beyond the hospital. Just like their approach to medicine, their work in the community takes an evidence-based and prevention-focused approach. To be healthy, individuals have to access a nutritious and healthy food in their neighborhoods, schools, clean air, playgrounds and safe parks (Kemper, 2014). Good health for the community also needs an emphasis on social and economic well-being as well as equity. Kaiser Permanente focuses their work in three ways i.e. providing access to high-quality healthcare for low incomes, creating healthy and safe environments and communities where individuals work, live and play and finally developing new medical knowledge and also sharing it widely with others (Kemper, 2014).
Functional Tactics
Employees of Kaiser Permanente plays a significant role in achieving the objectives above. The functional tactics include all responsibilities, duties, tasks and activities which are trivial in executing the business strategy. First, Kaiser Permanente’s marketing strategy emphasizes on providing quality healthcare services by outbidding probable competition in the target market. The functional tactics will market and also provide quality health care to the society. It also implements and maintains admission price which is slightly above the market price. The organization can come up with a subscription plan for patients which they can subscribe to those plans. Kaiser Permanente can also use social networking to promote their customers (Kemper, 2014).
Action Items
From the functional tactics and objectives, Kaiser Permanente can establish and implement the following action plan. One of the action plans is developing online promotion campaigns for products and services so as to increase the visitors by 15%. The increase in the rate of customer visit will lead to Kaiser Permanente’s loyal customer base growth in the next few year. Again, Kaiser Permanente will improve the quality of healthcare service they provide to their customers and the order delivery time through improving customer retention and rate of rewards. Customers will be assigned to particular physicians for care plan advice and also current specialty status. Kaiser Permanente will also install a monitoring system which will collect information on service delivery speed, customer satisfaction as well as customer feedback to ensure that the organization reduces order delivery by 5% and then increase the satisfaction of customers by 20%. The information collected will be used to identify areas which need improvement by training nurses and doctors (Kemper, 2014).
Milestones and Deadlines
Kaiser Permanente’s milestones are derived from the objectives, action items, and functional tactics are presented here. The deadline or expected completion date forms a baseline for the implementation plan project (Kemper, 2014).
| Item | Activity of the Milestone | Deadline |
| Submitting the marketing strategy proposal | Monday 5th, June 2017 | |
| Notice the of Strategic Report | Monday 12th June 2017 | |
| Scope Clarification Conference | Wednesday 14th June 2017 | |
| Submitting the Budget Estimate | Thursday 15th June 2017 | |
| Submitting the loyalty program scheme proposal | Friday 16th June 2017 | |
| Submitting the monitoring system proposal | Monday 19th June 2017 | |
| Submitting the training module | Tuesday 20th June 2017 | |
| Installing the monitoring system | Tuesday 27th June 2017 | |
| 9 | Analysis and assessment of the monitoring data | Monday 3rd July 2017 |
| 10 | Training of the employees | Tuesday 4th July 2017 |
Task, task ownership, and resource allocation
Task ownership is among the key elements of employee motivation. It ensures accountability and also makes the members of the team responsible for completing their task (Kemper, 2014).
| Item | Task | Task Ownership | Resource Allocation |
| Developing the marketing strategy | Management team | Marketing | |
| Analyzing the business environment and compile the report | Independent contractor | Research and development | |
| Developing the strategy, including creating strategic goals | Management team | Marketing | |
| Budgeting as well as resource allocation | Accountant | Financial | |
| Developing customer loyalty program | Functional level leaders | Marketing | |
| Identifying and acquiring a monitoring system | Human resource personnel | Human Resources | |
| Developing an employee training module | Independent contractor | Research and development | |
| Implementing the monitoring system | Technical experts | Physical resource | |
| Collecting and analyzing data | Technical Assistant | Operations | |
| 10 | Implementing the process changes according to analysis results | Independent contractors | Operations |
Recommendation
Implementing the plan above requires Kaiser Permanente to perform additional functional levels and also make some n ecessary changes in the organization structure. The organization should explore prospects of additional functional level which can operate, manage and maintain customer service using the monitoring system. The team can also collect and analyze data, train employees on how to improve customer experience and compose reports with recommendations according to the data observed. At the same time, engaging a functional-level team which is a business part which oversees project implementation and an important step towards successfully implementing the project (Lorange, 2017).
Implementing the recommendations will take an extra effort. The main agenda of this implementation plan is improving customer experience, customer service and proving quality healthcare to the community. The organization will move a mile ahead after implementing its strategic plan (Lorange, 2017).
Major success factors and budget
Some of the major success factors which can play a crucial role in the success of Kaiser Permanente includes strategic emphasis with alignment towards optimum performance, development, and management of employees of Kaiser Permanente, value creating in the operations of the organization, finance and equipment, high-end customer relations and availability and efficiency of facilities. The organizational resources, employees, customers, and capabilities are critica l to the competitive abilities and performance of the organization. The feasibility of Kaiser Permanente’s plan relies on the key success factors since they have a confounding impact on customer satisfaction, customer loyalty and sales (Lorange, 2017). The budget which is associated with performance achievement criteria is summarized below.
| Set-up Costs | |
| Business set-up costs | |
| Fee for accountant | $100 |
| Fee for solicitor | $100 |
| Business registration | $30 |
| Registration of the domain name | $10 |
| Insurances | $100 |
| Licenses | $40 |
| Employees remuneration | $120 |
| Setting up of the business premise | |
| Lease deposit and advance rent | $500 |
| Fitting | $150 |
| Utility bills | $100 |
| Stationary as well as other essentials | $100 |
| Equipment | |
| Computer and Software | $600 |
| POS | $300 |
| Starting Operations | |
| Promotions | $100 |
| Supplies | $1000 |
| Working capital | $250 |
| Start-up Capital | |
| Loans | $2500 |
| Equity Investment | $300 |
| Total Set-costs | $4650 |
| Borrowings Required | $1850 |
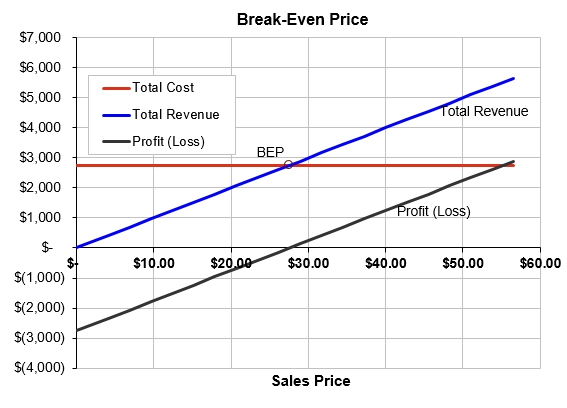
From the break-even chart, the break-even price is $27.57, and it is higher as compared to standard market value. We can also see that break-even sales are $2756.76 and they are higher considering the resources and capacity of Kaiser Permanente as compared the competition of the market (Kemper, 2014).
Risk Management Plan
A risk management plan can be defined as a document which a project manager composes or prepares so as to foresee risks, estimate their impacts and then iden tify the responses to issues. One of the main risks which Kaiser Permanente is likely to face in its implementation plan is achieving the break-even point when providing health care services to its customers. This is because profitability is not the primary objective of the organization since its main goal is providing quality and affordable healthcare to the community. Another risk would be erroneous treatment by the physicians (Melcher, 2011). Kaiser Permanente should consider taking a possible risk management plan, and it includes a qualitative analysis which is based on impacts and estimated probability of the risks. It is good to note that a probable risk response plan would help focus on the unit provision of healthcare services and reduction in wage expenses to reach break-even price. Physicians should also be vigilant to ensure that they do not provide erroneous care services which can cause harm to the patients. Similarly, contingency plan which includes a non-remuneration of the organization owner as well as reducing the wages on expenses or reduction of employees can assist the organization to combat these risks (Subramanian, 2013).
Conclusion
In conclusion, we can see that if Kaiser Permanente executes the implementation plan, it will be in a position to meets its business goals with ease. This is because the management will keep in minds the objectives, action items, functional tactics, and milestones, observe deadlines and understand the task and task ownership. The management will be in a position to monitor operations of the organization using the monitoring system which is brought about by this implementation plan.
ReferencesKemper, D. W. (2014). Kaiser Permanente. Boston: Pearson Education.
Lorange, P. (2017). Implementation of strategic planning. Boston: Pearson Education.
Melcher, H. K. (2011). Strategic planning: development and implementation. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Subramanian, R. &. (2013). Strategic Management: Formulation, implementation, and control. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons.



