mgmt
Answer the following in 250 words each:
a) What is the growth strategy of GE in India? What led to the challenges GE is facing? Critically evaluate the vertical integration and diversification options for GE.
b) How should Raja think about the situation? What are the most important considerations for him to weigh? How should they factor into his course of action?
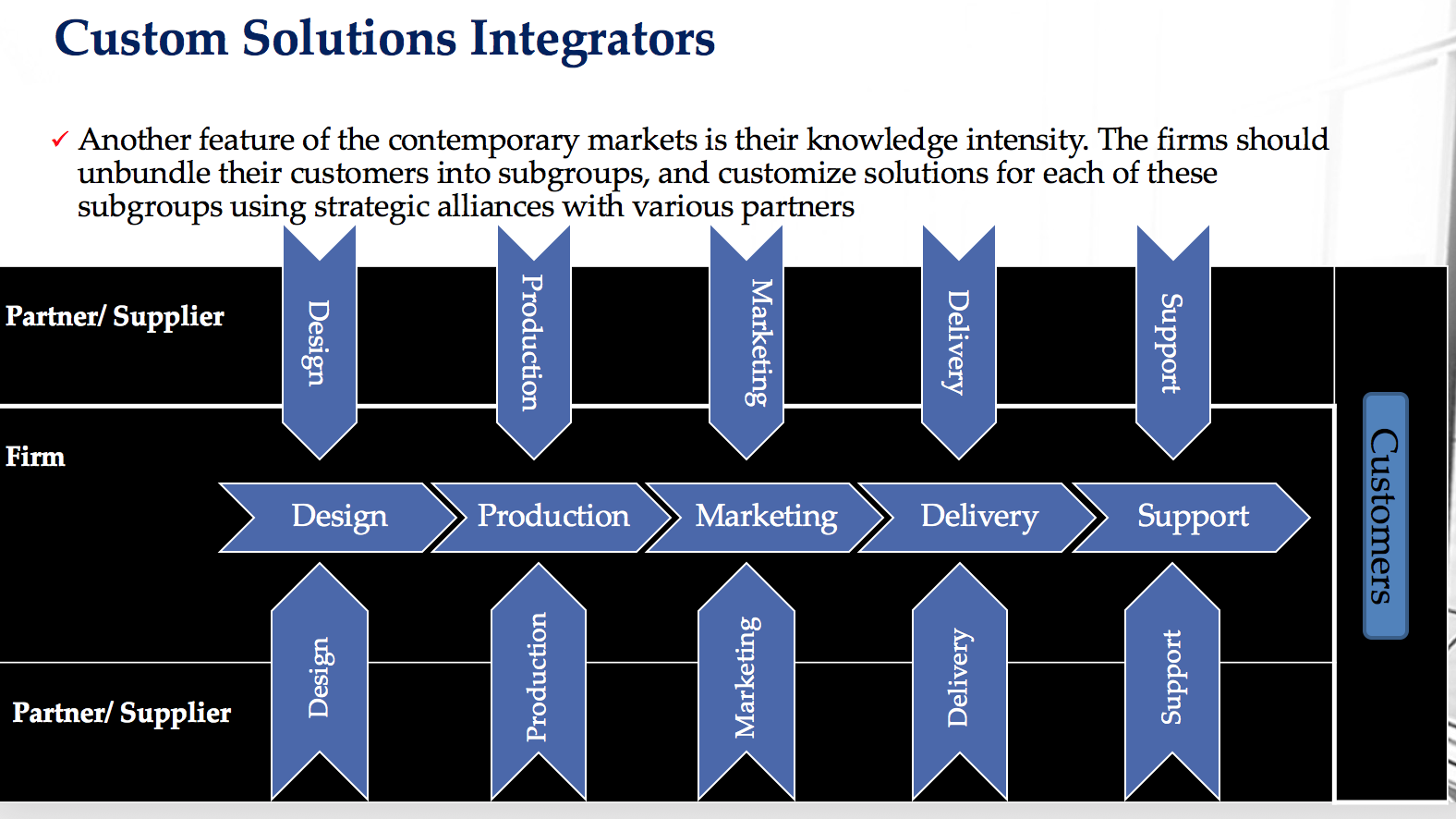
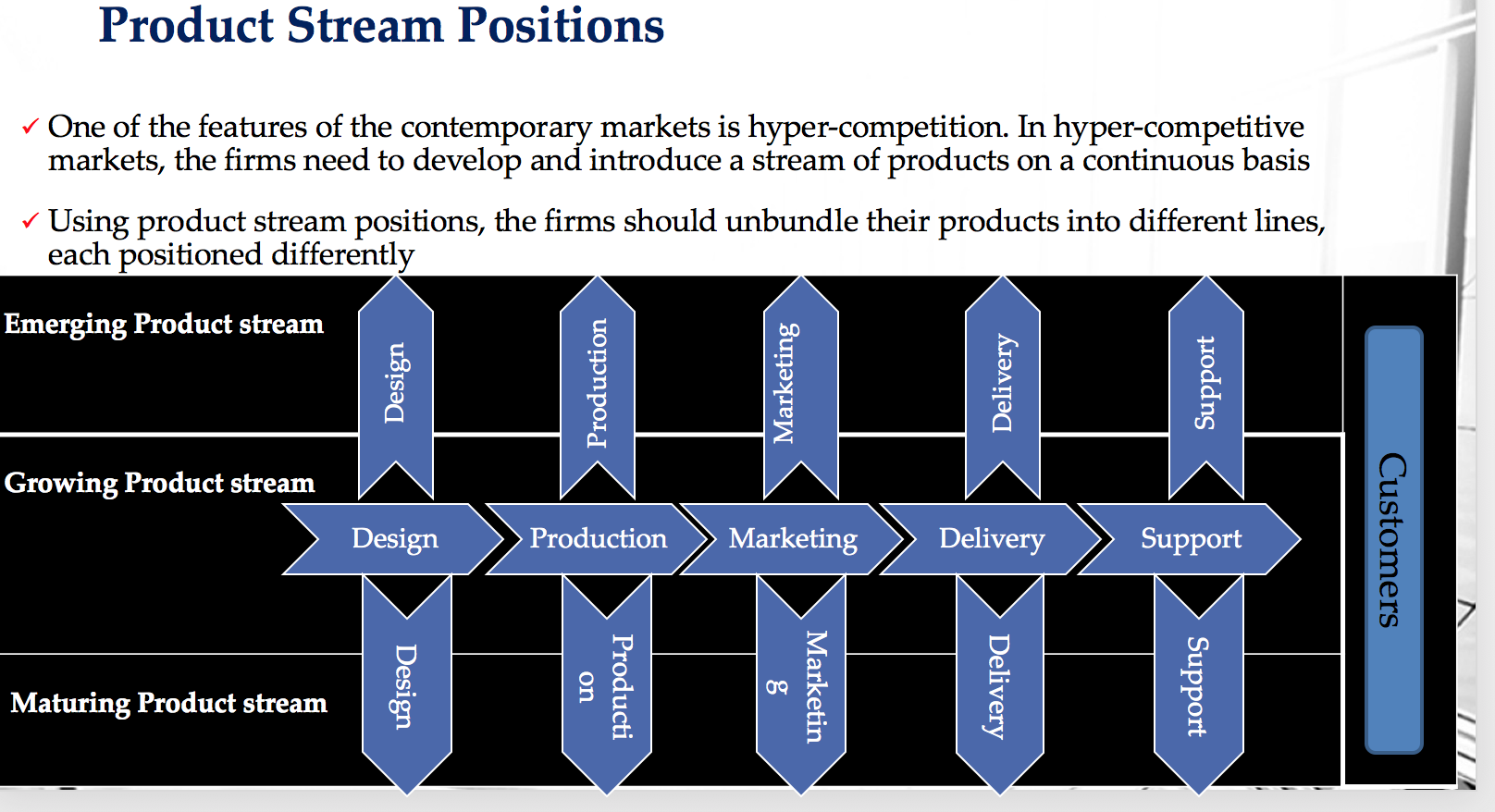
c) Use one of the three value strategies - product stream positions, custom solutions integration, or network exchange system - to identify alternative options for Raja.
Read the case answer the question, here is the Concept you need to use to answer the question. I do not need reference.
Vertical Integration
In an industry value chain, each firm:
Makes its profits
Builds in inefficiencies in the transfer of goods and services from one firm to another
To try saving these transaction costs, firms may vertically integrate
Vertical integration may be
Backward integration: upstream operations closer to the raw materials
Forward integration: downstream operations closer to the customer
Advantages of Vertical Integration
Creates entry barriers for new entrants
Reduces transaction costs (buying, selling, inventory holding, ordering costs)
Offers tighter control and coordination of operations
Allows to spread fixed or overhead costs over a large number of product/ services
Limits of Vertical Integration
Limits flexibility in times of demand/technology shifts; requires innovation and efficiency in each line of business
Requires robust system of organizing, culture building, and performance management, as KSF could vary in different lines of business
E.g., R&D, manufacturing, and marketing in pharmaceuticals have vastly different characteristics
Diversification
Nature of competitive strategies may vary for each business unit
Must create significant value addition by:
Improving core processes (resource capability)
Enhancing structural position (positional capability)
Types of Diversification
Related diversification
Complementary: Entry into new business activity based on shared commonalities in the components of the value chains of the firms
Vertical integration: Entry into the businesses of its suppliers or its customers, to gain control over the supply and delivery systems.
Related (complementary) diversification adds value through economies of scope:
Transferring operational skills or strategic capability from one business to another
Phillip Morris to Miller Brewing
Combining the value chain
P&G’s diaper and power towel businesses
Leveraging strong brand names
Virgin
Stretching core competencies for added value
Terry Berry from graduation rings to corporate incentive programs
Creating stronger capabilities by combining relative strengths of multiple businesses
Daimler and Chrysler
Gaining competitive leverage
For multi-market competition
Unrelated diversification adds value through use of managerial capability when:
Industry is attractive, based on external analysis
Cost of entering the business is lower than the potential benefits, as soft targets for acquisitions exist
Firms with investment constraints in a high growth industry
Firms that are undervalued and could be acquired at low acquisition premiums, and then restructured by breaking them apart and sell off