database multiple questions ch 10,11,13
A(n) ________________________ is one in which all data integrity constraints are satisfied.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A ______________ is a type of lock that restricts database access to the owner of the lock and allows only one user at a time to access the database.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following types of critical events can trigger the database recovery process?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
What type of lock is appropriate when concurrent transactions are granted read access on the basis of a common lock?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A(n) ________________________ is a logical unit of work that must be entirely completed or aborted; no intermediate states are accepted.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following means that a series of concurrent transactions will yield the same result as if they were executed one after another?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
All changes are aborted and the database is set back to the previous consistent state when a __________ statement is reached.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
In concurrency control, in the _____________ approach, the only test for conflict occurs during the validation phase. If a conflict is detected, then the entire transaction restarts.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
In some circumstances, ________-level locks, which require fewer system resources, may produce better overall performance than field-level locks, which require more system resources.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
In concurrency control, the _____________ approach is based on the assumption that the majority of database operations do not conflict.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following processes allows the concurrent execution of transactions, giving end users the impression that they are the DBMS's only users?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A(n) ___________________ is used by the DBMS to keep track of all transactions that update the database.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
____________means that a series of concurrent transactions will yield the same result as if they were executed one after another.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following properties indicates that the database will be in a permanent consistent state after the execution of a transaction?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following is NOT a technique used to control deadlocks in a database?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following is NOT a valid level of lock granularity?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following processes interleaves the execution of the database operations (belonging to several concurrent transactions) to ensure the serializability of transactions, thus guaranteeing that the execution of concurrent transactions will yield the same result as though the transactions were executed one after another?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the ANSI transaction isolation levels is less restrictive?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
The _________________ is a special DBMS process that establishes the order in which the operations are executed within concurrent transactions.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
What type of lock occurs when two transactions wait indefinitely for each other to unlock data?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A(n) _______________ lock exists when access to a data item is specifically reserved for the transaction that locked the object.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following properties means that the data required by an executing transaction cannot be accessed by any other transaction until the first transaction finishes and thus ensures data consistency for concurrently executing transactions?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following properties requires that all parts of a transaction must be completed or the transaction is aborted and ensures that the database will remain in a consistent state?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following properties indicates the permanence of the database's consistent state?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A(n) ________________________ is the equivalent of a single SQL statement in an application program or transaction.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following is NOT one of the main problems with concurrency control?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
All changes are permanently recorded within the database when a ___________ statement is reached.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Each individual transaction must display what is often referred to as the __________ test.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following is NOT a disadvantage of time-stamping methods for concurrency control?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the ANSI transaction isolation levels allows no dirty reads, no non-repeatable reads, and no phantom reads?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
____________________________ is the coordination of simultaneous execution of transactions in a multiuser database system.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
What type of lock is issued only when a transaction must write or update a data item and no locks are currently held on that data item by any other transaction?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A ______________ is a device that guarantees unique or exclusive use of a data item in a particular transaction operation.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
The DBMS does not guarantee that the ________________ of the transaction truly represents the real-world event.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
In the _____________ scheme, the older transaction waits for the younger one to complete and release its locks.
| |||
| |||
| |||
| |||
| atch the following terms with a short description of that term: |
|
For the following two transactions and the initial table values as shown complete the missing blanks in the transaction log below:
| Part_ID | Desrption | OnHand | OnOrder |
| 57 | Assembled Foo | ||
| 987 | Foo Fastener | 12 | |
| 989 | Foo Half |
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
UPDATE Part SET OnHand = OnHand + 7, OnOrder = OnOrder – 7 WHERE Part_ID = 987;
COMMIT;
BEGIN TRANSACTION;
UPDATE Part SET OnHand = OnHand - 4 WHERE Part_ID = 987;
UPDATE Part SET OnHand = OnHand - 2 WHERE Part_ID = 989;
UPDATE Part SET OnHand = OnHand + 1 WHERE Part_ID = 57;
COMMIT
| TRL_ID | TRX_ID | PREV_PTR | NEXT_PTR | OPERATION | TABLE | ROW ID | ATTRIBUTE | BEFORE | AFTER |
| 1787 | 109 | NULL | | START | **** | ||||
| 1788 | 109 | 1787 | | UPDATE | PART | 987 | OnHand | 12 | |
| 1789 | 109 | | | UPDATE | PART | 987 | OnOrder | | |
| 1790 | 109 | | NULL | COMMIT | **** | ||||
| 1791 | 110 | NULL | | START | **** | ||||
| 1792 | 110 | | | UPDATE | PART | 987 | | | |
| 1793 | 110 | | | | | | | ||
| 1794 | 110 | | | | | | | ||
| 1795 | 110 | | NULL | COMMIT | **** | ||||
A(n) _______________ optimizer uses a set of preset conditions and points to determine the best approach to execute a query. The conditions assign a "cost" to each SQL operation; the costs are then added to yield the cost of the execution plan.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
What database statistics measurements are typical of environment resources?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
____________________ describes a process on the server side that will properly configure the DBMS environment to respond to clients' requests in the fastest way possible, while making optimum use of existing resources.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
How are database statistics obtained?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following is NOT a phase the DBMS goes through when processing a query?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A(n) _______________ uses 0s and 1s to represent the existence of a value or condition.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
What database statistics measurements are typical of tables?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
______________ refers to the number of different values a column could possibly have.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
The term __________________ refers to a number of measurements gathered by the DBMS to describe a snapshot of the database objects' characteristics.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following is NOT one of the general guidelines for creating and using indexes?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following phase is where the DBMS runs the SQL query using the chosen plan?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
_____________ database systems are optimized to store large portions (if not all) of the database in primary (RAM) storage rather than secondary (disk) storage.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
In simple terms, the DBMS processes queries in ________ phase(s).
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following phase is where the DBMS analyzes the SQL query and chooses the most efficient access/execution plan?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
RAID level _______________ is when the data and the parity are striped across separate drives, providing good read performance and fault tolerance via parity data.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Optimizer ______ are special instructions for the optimizer that are embedded inside the SQL command text.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following is NOT one of the steps you would follow when formulating a query?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
What query optimization factors should you keep in mind if you intend to write conditional expressions in SQL code?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
What type of SQL statement updates the data dictionary tables or system catalog?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Most performance-tuning activities focus on doing what to the number of I/O operations, which are much slower than reading data from the data cache?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A(n) _______________ optimizer uses sophisticated algorithms based on the statistics about the objects being accessed to determine the best approach to execute a query.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
You use ________________ to provide both performance improvement and fault tolerance, and a balance between them as part of DBMS performance tuning.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following are recommendations you would make for managing the data files in a DBMS with many tables and indexes?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following is an example of an optimizer hint used in standard SQL?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
___________________ describes a process on the client side that will generate an SQL query to return the correct answer in the least amount of time, using the minimum amount of resources at the server end.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
DBMS performance tuning at the server end focuses on setting the parameters used for:
| |||
| |||
| |||
| |||
| Given the following SQL Query, which columns would you recommend to be indexed? SELECT InvoiceNumber, InvoiceDate, Invoice_Total, Invoice_Paid, Drag the correct answers to one of the three pockets. |
invoice Number
| |
Invoice Date
Invoice_Total
Invoice_Paid
Salesman_id
| ou work for a large non-profit that raises money for awareness of and research to cure a very painful childhood disease. They have a database table with over 100,000 names, addresses, and basic demographic information about donors to their cause. Match the following columns in the table based on sparsity. |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The data warehouse is usually a ___________ database optimized for data analysis and query processing.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following are problems when operational data are integrated into the data warehouse?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A(n) ___________________ is an arrangement of computerized tools used to assist managerial decision making.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A(n) ___________________ is a web-based system in BI that presents key business performance indicators or information in a single, integrated view with clear and concise graphics.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
The _______ clause in a materialized view indicates that the view rows are populated right after the command is entered.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
The ____________ is a data-modeling technique used to map multidimensional decision support data into a relational database.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
__________ uses star schemas while _____________ uses data cubes.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
The fact table from the star schema diagram below is ____________.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following is a basic component of the BI architecture?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A(n) _______ in a star schema is a numeric measurement or value that represents a specific business aspect or activity.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which SQL extension is used with the GROUP BY clause to generate aggregates by different dimensions?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following are common characteristics of operational data?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
One of the main characteristics of OLAP is ____________.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following techniques is NOT used to optimize data warehouse design?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
The _______ clause in a materialized view indicates when the rows are actually populated.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which type of OLAP would be best suited for the relational database environment?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A modern BI system provides which of the following distinctive reporting styles?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A(n) _______ in a star schema is a qualifying characteristic that provides additional perspective to a fact.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Decision support data requires managers to _________ and to ________ the data in different situations.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Multidimensional _________________ refers to the processing of data in which data are viewed as part of a multidimensional structure, one in which data are related in many different ways.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
which of the following is NOT a major component of the Business Intelligence framework?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following is NOT a key performance indicator in BI?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A data cube that grows to n number of dimensions is known as a _____________.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
On which level of the BI framework is data analytics used?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A(n) _______ in a star schema provides a top-down data organization that is sued for aggregation and drill-down/roll-up data analysis.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
_______ has a larger database size than __________ .
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
_______ measures the density of the data held in the data cube; it is computed by dividing the total number of actual values in the cube by the total number of cells.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which SQL extension is useful when you want to compute all possible subtotals within groupings based on multiple dimensions?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which SQL extension is used with the GROUP BY clause to generate aggregates by the listed columns, including the last one?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
The ______________ table in the star schema represented below is NOT a dimension.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A(n) _______ in a star schema is often used to search, filter, or classify facts.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A ___________ is a small, single-subject data warehouse subset that provides decision support to a small group of people.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which type of OLAP system works faster for large data sets with predefined dimensions?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
The _______ clause in a materialized view lets you indicate when and how to update the view when new rows are added to the base tables.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following is NOT a dissemination format of BI that started in the 2000s?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A _____ view is a dynamic table that not only contains the SQL query command to generate the rows, it stores the actual rows.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
______ integrates people and processes using technology in order to add value to the business.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
_____ is a framework that allows a business to transform data into information, information into knowledge, and knowledge into wisdom.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
From the data analyst's point of view, decision support data differ from operational data in what three areas?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
A(n) ______________ is an integrated, subject-oriented, time-variant and non-volatile database that provides support for decision-making.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
In the ROLLUP SQL extension, the ____________ of the column list within GROUP BY ROLLUP is very important.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
Which of the following is a basic component of the star schema?
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
The power of multidimensional analysis resides in its ability to focus on specific _______ of the cube.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
The ___________ component of the BI architecture performs data analysis and data-mining tasks using the data in the data store.
| |||
| |||
| |||
|
You have been asked by a client to normalize the driver dimension and to create multiple fact tables for the receipts that a driver collects for each of the new aggregation levels. Fill in the blanks with the field names used in the star schema to accomplish this task.
Facts:
A driver is assigned to one and only one office.
An office is in to only one region and may have many drivers.
A region is located in one and only one country and a country can have many regions.
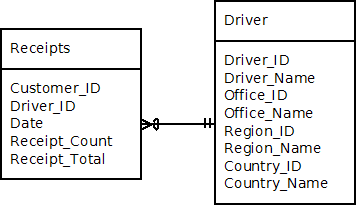
Drag the correct answers in alphabetical order in to corresponding pockets.
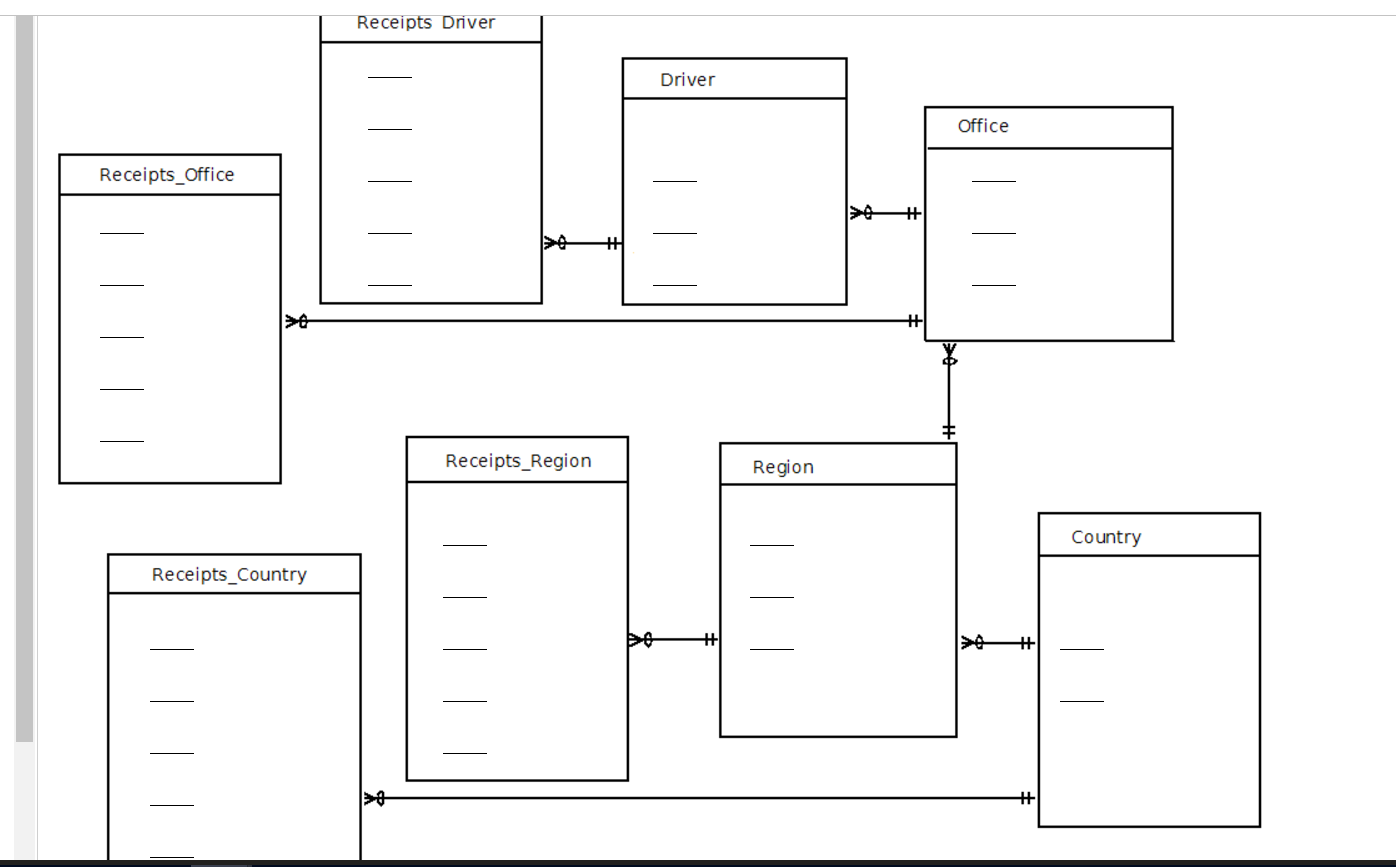
Fill in the blanks with words that would best complete the passage.
Date
Customer_ID
Receipt_Count
Region_ID
Driver_Name
Office_ID
Customer_ID
Receipt_Count
Country_ID
Country_ID
Receipt_Total
Country_ID
Receipt_Total
Office_ID
Office_Name
Country_Name
Customer_ID
Driver_ID
Customer_ID
Receipt_Count
Receipt_Count
Office_ID
Driver_ID
Region_ID
Receipt_Total
Region_ID
Region_Name
Date
Receipt_Total
Date
Date
| Match the following terms with a short description of that term: |
|



