annoted bibliography for e-commerce - 1000 words

CLOUD COMPUTING
Assessment Item 03
(Annotated Bibliography)
Submitted By: Sushant Puri
Student ID: 11588931
Submitted to: Ather Saeed
ABSTRACT
The discovery of cloud computing is expected to bring a big change in the computing was done until now. It will render software as a service which will be more attractive, effective and efficient. It will also equip developers with the capability to develop new internet services without initially having to invest large chunks of money in hardware. The technology is also expected to bring a paradigm shift in the way IT hardware is designed and purchased. Cloud computing marks the inception of an evolution paradigm and is a product of the convergence of three technologies including virtualization, grid computing, and web services. Gradually, the bandwidth at which internet is serviced over to the users is increasing and so is the use of applications which are developed to productively function in this environment. With the ease of access to applications via mobile phones and other handheld portable devices, productivity and efficiency have been greatly improved. But, like any other technology, cloud computing also advances certain issues which inter alia include security, reliability, privacy, interoperability, consistency of services.
INTRODUCTION
With a plethora features, functionalities and advantages over conventional computing, cloud computing provides a conceptualization of utility services that can customize and scaled as per user requirements. Nowadays, working with cloud services is as easy as accessing the internet via browser itself. Collaborative sharing, ease of access and use, productivity, efficiency, efficacy are several factors which offer latitude for expanding adoption of cloud computing by individuals, enterprises, and organizations. Presently, everyone can browse a website, choose a service, select a convenient mode of payment, make payment and commence using a software as a service without having to invest in hardware or obtaining software licenses, absence of human effort, no requirements of maintaining a server, or a backup strategy as all of this is provisioned by the SaaS provider as a part of the package.
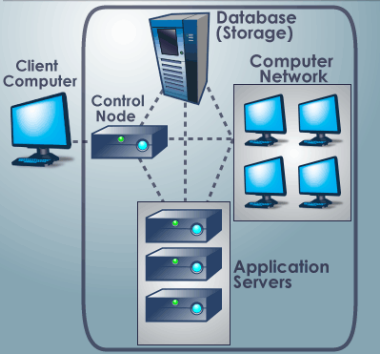
Typical Cloud Computing System
With cloud computing, as many numbers of people can work on the same file in a collaborative fashion and changes made by any authorized person are seamlessly updated at other the end of other users. Plainly speaking, a number of benefits accrue to the user of cloud computing which inter alia include virtualization, on-demand availability of computing resources, the absence of any compulsion to make an upfront commitment with the service provider, and pay-as-you-features.
PROBLEMS/ISSUES
Observing superficially, cloud computing has a multitude of benefits to offer to users but several issues and concerns deter enterprises and organizations from adopting cloud systems. These issues include:
One of the most pressing issues with cloud computing is security and reliability of data stored in remote servers. Loss of data, data corruption, data theft and privacy are among the major issues abound cloud computing. Cloud computing leverages virtualization capabilities and user data is stored in servers located at remote data centers spread across geographically separated locations. These data centers are susceptible to the risk of online data theft, resource crunch due to service or network failure, incorrect data output to user queries. These issues dilute the value proposition associated with cloud computing.
With cloud computing, large organizations tend to be skeptical about the consistency in the availability of cloud services. If due to any cause, the service is interrupted, it may lead to a loss of business, revenue and customers as well on part of such organizations.
Development in the field of information and communication technology and growing needs of users has resulted in the transformation of applications into being more and more data intensive. With applications becoming more data-intensive, large chunks of data need to be transferred over the internet which altogether becomes a costly proposition. Data transfer costs pose as bottlenecks in the transfer of data. This renders it imperative for service providers and service users to deliberate upon the cost implications of data placement, transfer, and traffic at the individual levels of their systems if they are to keep a hold on costs.
Performance unpredictability gives rise to operational issues. Bugs in large scale distributed systems often result in loss of productivity and efficiency. Debugging the application source code at the scale at production datacenters is a .viable solution.
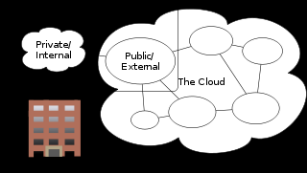
Public Cloud System [6]
Issues of privacy, security, reliability and interoperability make users wary of credibility of cloud systems. Due to the fact that APIs differ from one service provider to the other, compatibility with third-party application emanates as a contentious issue with cloud systems.
Among other problems connected to cloud computing are scaling problems, software licensing and reputation fate sharing.
PROPOSED SOLUTIONS
The main concern that drives organizations to be wary of cloud computing is consistency in the availability of cloud services. Organizations with diversified operations raise skepticism about the adequate availability of utility computing services. Today, users want highest standards of services and in order to keep atone to user expectations of services, SaaS products have also set high standards but consistency in the provisioning of cloud services is very difficult to achieve and maintain [8]. This could be achieved through provisioning of utility services through multiple network providers. The benefit such scheme is that consistency of services is not affected, in case, of a network outage by a single provider. Today, computing communities vouch for, and coincide with, “no single source of failure” as a rule of heuristics yet, in most cases, the single most prevalent cause of failure of Cloud Computing service is provisioning of services by a single service provider. Even if a utility service is provided by multiple service providers exchanging data from data centers based geographically disparate locations, reliance on a single software system and common infrastructure could strike a company out of business [4]. Critically evaluating the foregoing discussion, the incumbent is the need for service providers to lay a business continuity strategy to keep operational threats at bay and to serve as a backup plan should a contingency arises. In order for service providers to ensure continuity in the provisioning of utility services to service users and enhance software dependability, individual stacks of software must be provided by different companies altogether since it would not justified for single companies to have adequate hardware, software and backup infrastructure to ensure service consistency [5].
With cloud computing users also face interoperability issues. The fact that software APIs are different among different service providers raises file compatibility and data extraction issues with third party applications. It is owing to this reason that several enterprises and organizations are unwilling to substitute conventional computing with cloud computing. A rather direct solution to the problem of interoperability is standardization of APIs across all service providers. This will allow utility service developers to share data and services across multiple users to ensure interoperability is achieved [1, 10].
Currently, applications are becoming more and more data heavy. Cloud systems work over the internet and require the exchange of a large amount of data between remote servers and users based on the scale of service provisioned to the user. Costs involved in the transfer are data may cascade to large sums with average transfer costs of $100-$150 per terabyte of data. It is imperative for cloud providers as also cloud users to achieve a robust abstraction of costs at each level of the system to understand implications of data placement and transport having due accord to traffic. An apparent solution to large costs involved in data transfers in physical transportation of disks carrying data or if dismantling the data disks is a problem then, possibly shipping the whole computer system to designated locations via overnight deliveries [9]. This provides a simple yet effective solution to costs associated with the online transfer of large chunks of data. But, this recourse may offer challenges in case data is lost in transit due to damage in transit among other causes and manufacturers do not provide any guarantee on either the disks or computer systems. But, this challenge can be easily tackled by transporting extra disks with redundant data in an RAID-like manner. RAID is a Redundant array of independent disks being a virtualization technology for storage of data wherein components of physical disk drives are stored into a single logical system to achieve both data performance improvement and data redundancy. Yet another radical solution to reduce data transfer costs is to reduce WAN bandwidth costs. A majority portion in the likes of two-third of the bandwidth costs is consummated is setting up of high-end routers and as low as one-thirds can be attributed to fibre costs [11]. Attempts are ongoing to manufacture low-cost and simpler routers using commercial components which are capable of being controlled from a centralized location [12].
Large scale distributed systems often suffer from bugs which could be lead to a loss of productivity and translate proposed benefits of cloud computing into inherent weaknesses further leading to inefficiencies. An opportunity in this area is the reliance on virtual machines (VMs) in cloud computing [2]. It has been the case with most SaaS providers that they developed their service architecture without virtual machines since they either started before commercialization of VMs or the costs associated with VMs were too high at that point in time. Because use of virtual machines is customary in cloud computing and utility services. With virtualization, it is possible to collect valuable as also sensitive information which is not otherwise possible [3].
Cloud systems leverage virtualization, automation, and scheduling of tasks. The elemental underpinning underlying cloud architecture is storage of user data on servers located at remote data centers and on-demand retrieval of data and information upon user request [6]. But, the downside here is the potential risk of loss of data, data theft and data corruption which makes cloud computing an unattractive proposition for the users. However, the bright side to this is the existence of technologies which can devise an effective solution to the problem. “Data encryption”, “virtual local area networks” and “network middleboxes” like data packet filters and firewalls which ensure safety and security of data [7].
CONCLUSION
Cloud computing marks the beginning of a new era in the field of information and communication technology as it brings with an evolution paradigm which has the potential to change the way in which computing was done. Users are still getting acquainted with this technology and a shift from conventional computing to cloud computing will happen but gradually. Owing to this technology, developers with novel ideas about internet services will no longer need to expend large chunks of money in building their software and hardware infrastructural capabilities but rather they could focus on effective provisioning of utility services.
For cloud providers, profitability lies in economies of scale with higher profitability as the user base grows and the ability of the service provider to multiplex among a broad base of users. In contrast to a variety of benefits associated with cloud computing, there are certain challenges as well. These challenges include security, privacy and reliability of data, consistency in the availability of services, interoperability issues due to unstandardized application programming interfaces which are unique to different service providers, issues in assessment and implementation of cloud computing, high costs of data transfers, and bugs in large-scale distributed systems. Intelligent, efficient and effective solutions so devised to overcome challenges associated with cloud computing were enlisted in this report after a critical and exhaustive review of relevant literature. Cloud computing as a recent technology is still at a nascent stage of its development and there is still so much potential which can be realized owing to ongoing research and development in this regard.
REFERENCES
1. Ahmed, M., & Hossain, M. A. (2014). Cloud computing and security issues in the cloud. International Journal of Network Security & Its Applications, 6(1), 25.
2. Antonopoulos, N. & Gillam, L. (2010). Cloud Computing: Principles, Systems, and Applications. Springer Science & Business Media.
3. Armbrust, M., Fox, A., Griffith, R., Joseph, A.D., Katz, R., & Konwinski, A. (2010). A view of cloud computing. Communications of the ACM, 53(4), 50-58.
4. Badie, N., Hussin, A. R. C., & Lashkari, A. H. (2015). Cloud computing data center adoption factors validity by fuzzy AHP. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 8(5), 854-873.
5. BECHTOLSHEIM, A. (2008). Cloud Computing and Cloud Networking. Talk at UC Berkeley.
6. Benatallah, B. (2011). Cloud computing: methodology, systems, and applications. CRC Press.
7. Bindu, B. S., & Yadaiah, B. (2011). Secure data storage in cloud computing. International Journal of Research in Computer Science, 1(1), 63-73.
8. Dawoud, W., Takouna, I., & Meinel, C. (2010). Infrastructure as a service security: Challenges and solutions. Ministry of Education and Higher Education, 1-8.
9. GRAY, J., AND PATTERSON, D. A conversation with Jim Gray. ACM Queue 1, 4 (2003), 8–17.
10. Nazir, M. (2012). Cloud computing: overview & current research challenges. IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering, 2278-0661.
11. HOLZLE ¨ , U. Private communication, January 2009.
12. MCKEOWN, N., ANDERSON, T., BALAKRISHNAN, H., PARULKAR, G., PETERSON, L., REXFORD, J., SHENKER, S., AND TURNER, J. OpenFlow: Enabling innovation in campus networks. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review 38, 2 (April 2008).
0



