6 multiple choice questions
1. What is flux?
| | The amount of a quantity passing through an area. (No other answers are correct.) |
| | The amount of a quantity passing through an area per unit time. (No other answers are correct.) |
| | The momentum change of an object per unit time. |
| | The change in charge of an object per unit time. |
| | Both A and B are correct. |
2. Which of the following are examples of closed surfaces?
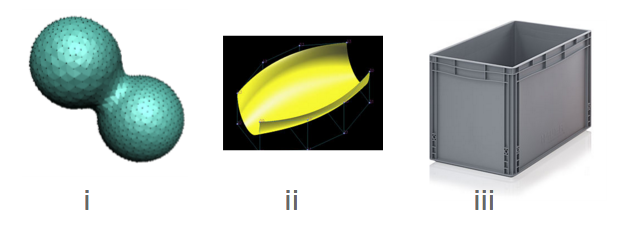
| | i and iii only |
| | i, ii, and iii |
| | i only |
| | iii only |
| | ii and iii only |
3. Which of the following statements is/are true about Gaussian surfaces?i. Gaussian surface is the name for a closed surfaces used when calculating flux in Gauss’ Law
ii. A Gaussian surface can have any shape (as long as it is closed)
iii. Like defining your system in energy problems, you can choose any shape or position of Gaussian surface in a problem
iv. It is easy to calculate flux with any Gaussian surfaces you choose
| | i only |
| | i, ii, iii, and iv |
| | i, ii, and iii only |
| | i and ii only |
| | i and iii only |
4. What is the net electric flux through these Gaussian surfaces?
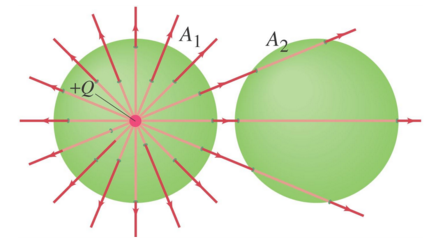
| | A1: 0, A2: 0 |
| | A1: not 0, A2: not 0 |
| | A1: not 0, A2: 0 |
| | A1: 0, A2: 0 |
5. What is the net electric flux within a Gaussian surface is directly related to what physical quantity/quantities?
| | the area chosen (This is the only correct answer.) |
| | the amount of charge enclosed by the area (This is the only correct answer.) |
| | both the amount of charge enclosed by the area and the area chosen |
6. Electric potential and electric potential energy
| | are synonyms for the same physical quantity -- the potential energy per unit charge. |
| | are synonyms for the same physical quantity -- the potential energy of a given charge. |
| | are two different but related physical quantities (electric potential energy is electric potential per unit charge). |
| | are two different but related physical quantities (electric potential is electric potential energy per unit charge). |



