Assignment 6: Calculations Do the following on paper, scan or photograph your work, and submit it. You have a room that is 4 m long, 7 m wide, and has a ceiling height of 3 m. The floor is hardwood
Mean Free Path
There are two main factors that affect the rate of decay of reverberation: the distance (and thus time) between reflections, and the amount of energy lost upon each reflection. The average distance traveled between reflections is known as the mean free path, and is dependent on the room size. The larger the room, the longer the mean free path and the longer the decay rate. The mean free path can be calculated using this equation:

Where l is the mean free path, V is the geometric volume of the room, and S is the total surface area of the room. Here is a rectangular room with the dimensions 3 m wide x 5 m long x 2.5 m high.
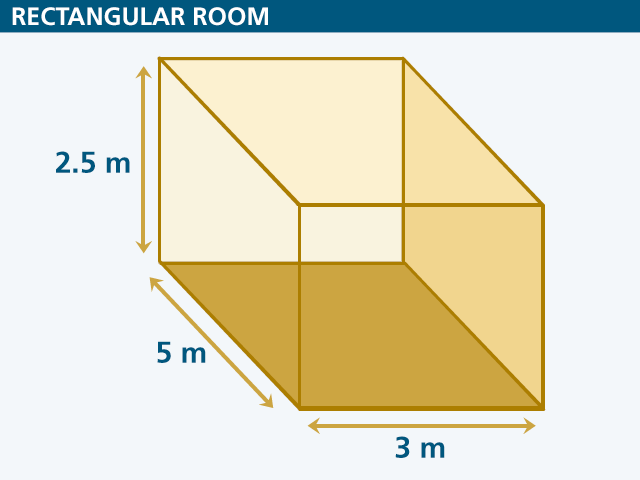
First we'll find the volume of the space: V = 3 m x 5 m x 2.5 m = 37.5 m3. Then, we'll find the total surface area in the room by calculating and summing the areas of each surface:
| Floor | 3 m x 5 m = 15 m2 |
| Ceiling | 3 m x 5 m = 15 m2 |
| Wall 1 | 3 m x 2.5 m = 7.5 m2 |
| Wall 2 | 3 m x 2.5 m = 7.5 m2 |
| Wall 3 | 5 m x 2.5 m = 12.5 m2 |
| Wall 4 | 5 m x 2.5 m = 12.5 m2 |
We can now plug these into our equation to solve for l:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
From this, we can find the average time between reflections by calculating how much time it would take for sound to travel 2.14 m. Remember that sound travels at c = 344 m/s, so the time t to go a distance of d = 2.14 m would be:
![]()
![]()
![]()
So this example room has a very short time between the average sound reflections, 6.2 ms. Again, this result—coupled with the amount of energy lost with each reflection—will determine the room's reverberation decay time.



