In your Week 2 Assignment (attached), you displayed data based on a categorical variable and continuous variable from a specific dataset. In Week 3 (attached), you used the same variables as in Week 2
Running head: INRODUCTION TO QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS 1
Introduction to Quantitative Analysis: Visually Displaying Data Results
Walden University
Introduction to Quantitative Analysis: Visually Displaying Data Results
According to Wagner (2016), a categorical variable is often nominal or ordinal variable which provides small values of names and labels, while continuous variable that are known as a large values and factions. In reviewing the High School Longitudinal Study dataset, one categorical and one continuous variable will be identified and placed in the appropriate visual display.
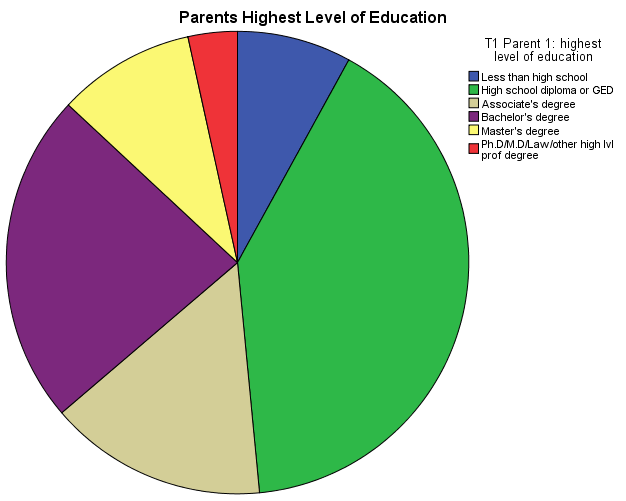
Categorical Variable: Parent Highest Level of Education
For the categorical variable, I will break this down into six categories: less than high school, high school diploma/GED, associate’s degree, bachelor’s degree, master’s degree or decorate.
Continuous Variable: Years Math Teacher Has Taught High School Math
For the continuous variable, I used the years math teacher has taught high school math. This variable is continuous because it can be broken down into decimals which can be infinite (Wagner, 2016).

Analysis of Data
As I examine the data, both visual allowed to get a holistic view of what’s being presented. For example, the first pie chart identify the level of parent’s education. This allows us to see quick data that majority of parents have a least a high school diploma or GED. However, as I examine Wagner (2016) output data, the data can be analyze by using descriptive functions inside SPSS.
| Case Processing Summary | ||||||||
| Cases | ||||||||
| Included | Excluded | Total | ||||||
| Percent | Percent | Percent | ||||||
| T1 Parent 1: highest level of education | 16784 | 71.4% | 6719 | 28.6% | 23503 | 100.0% | ||
| Statistics | ||
| T1 Parent 1: highest level of education | ||
| Valid | 16784 | |
| Missing | 6719 | |
| T1 Parent 1: highest level of education | |||||||
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | ||||
| Valid | Less than high school | 1342 | 5.7 | 8.0 | 8.0 | ||
| High school diploma or GED | 6795 | 28.9 | 40.5 | 48.5 | |||
| Associate's degree | 2562 | 10.9 | 15.3 | 63.7 | |||
| Bachelor's degree | 3893 | 16.6 | 23.2 | 86.9 | |||
| Master's degree | 1614 | 6.9 | 9.6 | 96.6 | |||
| Ph.D/M.D/Law/other high lvl prof degree | 578 | 2.5 | 3.4 | 100.0 | |||
| Total | 16784 | 71.4 | 100.0 | ||||
| Missing | Missing | .0 | |||||
| Unit non-response | 6715 | 28.6 | |||||
| Total | 6719 | 28.6 | |||||
| Total | 23503 | 100.0 | |||||
| Years math teacher has taught high school math | ||
| Valid | 17020 | |
| Missing | 6483 | |
| Years math teacher has taught high school math | ||||||||
| Frequency | Percent | Valid Percent | Cumulative Percent | |||||
| Valid | 1288 | 5.5 | 7.6 | 7.6 | ||||
| 1611 | 6.9 | 9.5 | 17.0 | |||||
| 1700 | 7.2 | 10.0 | 27.0 | |||||
| 1260 | 5.4 | 7.4 | 34.4 | |||||
| 1098 | 4.7 | 6.5 | 40.9 | |||||
| 888 | 3.8 | 5.2 | 46.1 | |||||
| 795 | 3.4 | 4.7 | 50.8 | |||||
| 713 | 3.0 | 4.2 | 55.0 | |||||
| 599 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 58.5 | |||||
| 10 | 692 | 2.9 | 4.1 | 62.5 | ||||
| 11 | 547 | 2.3 | 3.2 | 65.8 | ||||
| 12 | 493 | 2.1 | 2.9 | 68.6 | ||||
| 13 | 447 | 1.9 | 2.6 | 71.3 | ||||
| 14 | 438 | 1.9 | 2.6 | 73.8 | ||||
| 15 | 520 | 2.2 | 3.1 | 76.9 | ||||
| 16 | 357 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 79.0 | ||||
| 17 | 275 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 80.6 | ||||
| 18 | 248 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 82.1 | ||||
| 19 | 276 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 83.7 | ||||
| 20 | 356 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 85.8 | ||||
| 21 | 179 | .8 | 1.1 | 86.8 | ||||
| 22 | 242 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 88.3 | ||||
| 23 | 264 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 89.8 | ||||
| 24 | 144 | .6 | .8 | 90.7 | ||||
| 25 | 219 | .9 | 1.3 | 91.9 | ||||
| 26 | 92 | .4 | .5 | 92.5 | ||||
| 27 | 142 | .6 | .8 | 93.3 | ||||
| 28 | 141 | .6 | .8 | 94.1 | ||||
| 29 | 137 | .6 | .8 | 95.0 | ||||
| 30 | 146 | .6 | .9 | 95.8 | ||||
| 31 | 713 | 3.0 | 4.2 | 100.0 | ||||
| Total | 17020 | 72.4 | 100.0 | |||||
| Missing | Missing | 50 | .2 | |||||
| Unit non-response | 6433 | 27.4 | ||||||
| Total | 6483 | 27.6 | ||||||
| Total | 23503 | 100.0 | ||||||
In examining this data, this longitudinal study explores teenagers as they process through adulthood. We can clearly identify the different levels of education of parents and determine that a high school diploma were common among them. However, if we look more in depth with the analysis of data, some data is missing which can change the percentage of levels. If we had not ran the report with SPSS, we would never realize that some data were missing, can provide strong possibilities but not 100% accuracy. However, in this sample size, it give us a strong indicator that majority of parents have a least a high school diploma.
As observed in the histogram, most math teachers taught high school math for a least three years, but was it a full three year, or three years and two weeks or months, etc. This analysis of data shows how teachers in their field has years of expertise. However, as we examine both data, one thing to consider is that majority of people will finish high school and it’s important to hire the right teachers to educate these individuals. Therefore, one can say that the importance of a child’s high school experience should be fill with intense knowledge of innovation and solutions in increasing positive social change and community awareness.
Reference:
Wagner, W. E. (2016). Using IBM® SPSS® statistics for research methods and social science statistics (6th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.



