Need help with 19 stat questions. Deals with finding hypothesis testing, distribution, and probabilities. Please review attachment for more details.
1. Let x represent the dollar amount spent on supermarket impulse buying in a 10-minute (unplanned) shopping interval. Based on a certain article, the mean of the x distribution is about $40 and the estimated standard deviation is about $8.
(a) Consider a random sample of n = 50 customers, each of whom has 10 minutes of unplanned shopping time in a supermarket. From the central limit theorem, what can you say about the probability distribution of x, the average amount spent by these customers due to impulse buying? What are the mean and standard deviation of the x distribution?
The sampling distribution of x is not normal.
The sampling distribution of x is approximately normal with mean μx = 40 and standard error σx = $8.
The sampling distribution of x is approximately normal with mean μx = 40 and standard error σx = $0.16.
The sampling distribution of x is approximately normal with mean μx = 40 and standard error σx = $1.13.
Is it necessary to make any assumption about the x distribution? Explain your answer.
It is necessary to assume that x has an approximately normal distribution.
It is not necessary to make any assumption about the x distribution because n is large.
It is not necessary to make any assumption about the x distribution because μ is large.
It is necessary to assume that x has a large distribution.
(b) What is the probability that x is between $38 and $42? (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
(c) Let us assume that x has a distribution that is approximately normal. What is the probability that x is between $38 and $42? (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
(d) In part (b), we used x, the average amount spent, computed for 50 customers. In part (c), we used x, the amount spent by only one customer. The answers to parts (b) and (c) are very different. Why would this happen?
The mean is larger for the x distribution than it is for the x distribution.
The standard deviation is smaller for the x distribution than it is for the x distribution.
The x distribution is approximately normal while the x distribution is not normal.
The standard deviation is larger for the x distribution than it is for the x distribution.
The sample size is smaller for the x distribution than it is for the x distribution.
In this example, x is a much more predictable or reliable statistic than x. Consider that almost all marketing strategies and sales pitches are designed for the average customer and not the individual customer. How does the central limit theorem tell us that the average customer is much more predictable than the individual customer?
The central limit theorem tells us that the standard deviation of the sample mean is much smaller than the population standard deviation. Thus, the average customer is more predictable than the individual customer.
The central limit theorem tells us that small sample sizes have small standard deviations on average. Thus, the average customer is more predictable than the individual customer.
2. A new muscle relaxant is available. Researchers from the firm developing the relaxant have done studies that indicate that the time lapse between administration of the drug and beginning effects of the drug is normally distributed, with mean μ = 38 minutes and standard deviation σ = 5 minutes.
(a) The drug is administered to one patient selected at random. What is the probability that the time it takes to go into effect is 35 minutes or less? (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
(b) The drug is administered to a random sample of 10 patients. What is the probability that the average time before it is effective for all 10 patients is 35 minutes or less? (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
(c) Comment on the differences of the results in parts (a) and (b).
The probability in part (b) is part (a) because the
is
for the x distribution.
3. The personnel office at a large electronics firm regularly schedules job interviews and maintains records of the interviews. From the past records, they have found that the length of a first interview is normally distributed, with mean μ = 31 minutes and standard deviation σ = 7 minutes. (Round your answers to four decimal places.)
(a) What is the probability that a first interview will last 40 minutes or longer?
(b) Two first interviews are usually scheduled per day. What is the probability that the average length of time for the two interviews will be 40 minutes or longer?
4. How hot is the air in the top (crown) of a hot air balloon? Information from Ballooning: The Complete Guide to Riding the Winds, by Wirth and Young (Random House), claims that the air in the crown should be an average of 100°C for a balloon to be in a state of equilibrium. However, the temperature does not need to be exactly 100°C. What is a reasonable and safe range of temperatures? This range may vary with the size and (decorative) shape of the balloon. All balloons have a temperature gauge in the crown. Suppose that 51 readings (for a balloon in equilibrium) gave a mean temperature of x = 97°C. For this balloon, σ ≈ 18°C.
(a) Compute a 95% confidence interval for the average temperature at which this balloon will be in a steady-state equilibrium. (Round your answers to one decimal place.)
| lower limit |
|
| upper limit |
|
(b) If the average temperature in the crown of the balloon goes above the high end of your confidence interval, do you expect that the balloon will go up or down? Explain.
It will go down because hot air will make the balloon fall.
It will go down because hot air will make the balloon rise.
It will go up because hot air will make the balloon fall.
It will go up because hot air will make the balloon rise.
5. How much do wild mountain lions weigh? Adult wild mountain lions (18 months or older) captured and released for the first time in the San Andres Mountains gave the following weights (pounds):
| 75 | 103 | 132 | 128 | 60 | 64 |
Assume that the population of x values has an approximately normal distribution.
(a) Use a calculator with mean and sample standard deviation keys to find the sample mean weight x and sample standard deviation s. (Round your answers to one decimal place.)
| x = |
|
| s = |
|
(b) Find a 75% confidence interval for the population average weight μ of all adult mountain lions in the specified region. (Round your answers to one decimal place.)
| lower limit |
|
| upper limit |
|
6. For this problem, carry at least four digits after the decimal in your calculations. Answers may vary slightly due to rounding.
Santa Fe black-on-white is a type of pottery commonly found at archaeological excavations at a certain monument. At one excavation site a sample of 610 potsherds was found, of which 364 were identified as Santa Fe black-on-white.
(a) Let p represent the proportion of Santa Fe black-on-white potsherds at the excavation site. Find a point estimate for p. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
(b) Find a 95% confidence interval for p. (Round your answers to three decimal places.)
| lower limit | |
| upper limit | |
Give a brief statement of the meaning of the confidence interval.
95% of the confidence intervals created using this method would include the true proportion of potsherds.
95% of all confidence intervals would include the true proportion of potsherds.
5% of the confidence intervals created using this method would include the true proportion of potsherds.
5% of all confidence intervals would include the true proportion of potsherds.
(c) Do you think that np > 5 and nq > 5 are satisfied for this problem? Explain why this would be an important consideration.
Yes, the conditions are satisfied. This is important because it allows us to say that p̂ is approximately normal.
No, the conditions are not satisfied. This is important because it allows us to say that p̂ is approximately normal.
No, the conditions are not satisfied. This is important because it allows us to say that p̂ is approximately binomial.
Yes, the conditions are satisfied. This is important because it allows us to say that p̂ is approximately binomial.
7. Suppose you are told that a 95% confidence interval for the average price of a gallon of regular gasoline in your state is from $3.41 to $4.18. Use the fact that the confidence interval for the mean is in the form x − E to x + E to compute the sample mean and the maximal margin of error E. (Round your answers to two decimal places.)
| x = $ | |
| E = $ | |
8. Anystate Auto Insurance Company took a random sample of 364 insurance claims paid out during a 1-year period. The average claim paid was $1555. Assume σ = $230.
Find a 0.90 confidence interval for the mean claim payment. (Round your answers to two decimal places.)
| lower limit | $ |
| upper limit | $ |
Find a 0.99 confidence interval for the mean claim payment. (Round your answers to two decimal places.)
| lower limit | $ |
| upper limit | $ |
9. Three experiments investigating the relation between need for cognitive closure and persuasion were performed. Part of the study involved administering a "need for closure scale" to a group of students enrolled in an introductory psychology course. The "need for closure scale" has scores ranging from 101 to 201. For the 81 students in the highest quartile of the distribution, the mean score was x = 177.30. Assume a population standard deviation of σ = 7.99. These students were all classified as high on their need for closure. Assume that the 81 students represent a random sample of all students who are classified as high on their need for closure. Find a 95% confidence interval for the population mean score μ on the "need for closure scale" for all students with a high need for closure. (Round your answers to two decimal places.)
| lower limit | |
| upper limit | |
10. The Wind Mountain archaeological site is located in southwestern New Mexico. Wind Mountain was home to an ancient culture of prehistoric Native Americans called Anasazi. A random sample of excavations at Wind Mountain gave the following depths (in centimeters) from present-day surface grade to the location of significant archaeological artifacts†.
| 85 | 45 | 120 | 80 | 75 | 55 | 65 | 60 |
| 65 | 95 | 90 | 70 | 75 | 65 | 68 |
(a) Use a calculator with mean and sample standard deviation keys to find the sample mean x and sample standard deviation s. (Round your answers to one decimal place.)
| x = |
|
| s = |
|
(b) Compute a 80% confidence interval for the mean depth μ at which archaeological artifacts from the Wind Mountain excavation site can be found. (Round your answers to one decimal place.)
| lower limit |
|
| upper limit |
|
11. ASK YOUR TEACHER
A research group conducted an extensive survey of 3179 wage and salaried workers on issues ranging from relationships with their bosses to household chores. The data were gathered through hour-long telephone interviews with a nationally representative sample. In response to the question, "What does success mean to you?" 1466 responded, "Personal satisfaction from doing a good job." Let p be the population proportion of all wage and salaried workers who would respond the same way to the stated question. Find a 90% confidence interval for p. (Round your answers to three decimal places.)
| lower limit | |
| upper limit | |
12. Three-circle, red-on-white is one distinctive pattern painted on ceramic vessels of the Anasazi period found at an archaeological site. At one excavation, a sample of 165 potsherds indicated that 62 were of the three-circle, red-on-white pattern.
(a) Find a point estimate p̂ for the proportion of all ceramic potsherds at this site that are of the three-circle, red-on-white pattern. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
(b) Compute a 95% confidence interval for the population proportion p of all ceramic potsherds with this distinctive pattern found at the site. (Round your answers to three decimal places.)
| lower limit | |
| upper limit | |
13. The price to earnings ratio (P/E) is an important tool in financial work. A random sample of 14 large U.S. banks (J. P. Morgan, Bank of America, and others) gave the following P/E ratios.†
| 24 | 16 | 22 | 14 | 12 | 13 | 17 | 22 | 15 | 19 | 23 | 13 | 11 | 18 |
The sample mean is
x ≈ 17.1.
Generally speaking, a low P/E ratio indicates a "value" or bargain stock. Suppose a recent copy of a magazine indicated that the P/E ratio of a certain stock index is μ = 19. Let x be a random variable representing the P/E ratio of all large U.S. bank stocks. We assume that x has a normal distribution and σ = 4.9. Do these data indicate that the P/E ratio of all U.S. bank stocks is less than 19? Use α = 0.01.
(a) What is the level of significance?
State the null and alternate hypotheses. Will you use a left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed test?
H0: μ = 19; H1: μ > 19; right-tailed
H0: μ = 19; H1: μ ≠ 19; two-tailed
H0: μ ≠ 19; H1: μ = 19; two-tailed
H0: μ = 19; H1: μ < 19; left-tailed
(b) What sampling distribution will you use? Explain the rationale for your choice of sampling distribution.
The standard normal, since we assume that x has a normal distribution with known σ.
The standard normal, since we assume that x has a normal distribution with unknown σ.
The Student's t, since we assume that x has a normal distribution with known σ.
The Student's t, since n is large with unknown σ.
Compute the z value of the sample test statistic. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
(c) Find (or estimate) the P-value. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
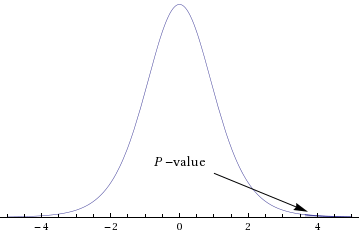
Sketch the sampling distribution and show the area corresponding to the P-value.
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d) Based on your answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Are the data statistically significant at level α?
At the α = 0.01 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
At the α = 0.01 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
At the α = 0.01 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
At the α = 0.01 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
(e) State your conclusion in the context of the application.
There is sufficient evidence at the 0.01 level to conclude that the P/E ratio of all large U.S. bank stocks is less than 19
There is insufficient evidence at the 0.01 level to conclude that the P/E ratio of all large U.S. bank stocks is less than 19
14. A random sample of 46 adult coyotes in a region of northern Minnesota showed the average age to be x = 2.03 years, with sample standard deviation s = 0.76 years. However, it is thought that the overall population mean age of coyotes is μ = 1.75. Do the sample data indicate that coyotes in this region of northern Minnesota tend to live longer than the average of 1.75 years? Use α = 0.01.
(a) What is the level of significance?
State the null and alternate hypotheses.
H0: μ = 1.75 yr; H1: μ ≠ 1.75 yr
H0: μ = 1.75 yr; H1: μ < 1.75 yr
H0: μ > 1.75 yr; H1: μ = 1.75 yr
H0: μ < 1.75 yr; H1: μ = 1.75 yr
H0: μ = 1.75 yr; H1: μ > 1.75 yr
(b) What sampling distribution will you use? Explain the rationale for your choice of sampling distribution.
The Student's t, since the sample size is large and σ is unknown.
The standard normal, since the sample size is large and σ is unknown.
The standard normal, since the sample size is large and σ is known.
The Student's t, since the sample size is large and σ is known.
What is the value of the sample test statistic? (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
(c) Estimate the P-value.
<P-value > 0.250
0.100 < P-value < 0.250
0.050 < P-value < 0.100
0.010 < P-value < 0.050
P-value < 0.010
Sketch the sampling distribution and show the area corresponding to the P-value.
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d) Based on your answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Are the data statistically significant at level α?
At the α = 0.01 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
At the α = 0.01 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
At the α = 0.01 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
At the α = 0.01 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
(e) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application.
There is sufficient evidence at the 0.01 level to conclude that coyotes in the specified region tend to live longer than 1.75 years.
There is insufficient evidence at the 0.01 level to conclude that coyotes in the specified region tend to live longer than 1.75 years.
15. The U.S. Department of Transportation, National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, reported that 77% of all fatally injured automobile drivers were intoxicated. A random sample of 55 records of automobile driver fatalities in a certain county showed that 35 involved an intoxicated driver. Do these data indicate that the population proportion of driver fatalities related to alcohol is less than 77% in Kit Carson County? Use α = 0.10.
(a) What is the level of significance?
State the null and alternate hypotheses.
H0: p = 0.77; H1: p ≠ 0.77
H0: p < 0.77; H1: p = 0.77
H0: p = 0.77; H1: p > 0.77
H0: p = 0.77; H1: p < 0.77
(b) What sampling distribution will you use?
The Student's t, since np > 5 and nq > 5.
The Student's t, since np < 5 and nq < 5.
The standard normal, since np < 5 and nq < 5.
The standard normal, since np > 5 and nq > 5.
What is the value of the sample test statistic? (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
(c) Find the P-value of the test statistic. (Round your answer to four decimal places.)
Sketch the sampling distribution and show the area corresponding to the P-value.
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d) Based on your answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Are the data statistically significant at level α?
At the α = 0.10 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
At the α = 0.10 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
At the α = 0.10 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
At the α = 0.10 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
(e) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application.
There is sufficient evidence at the 0.10 level to conclude that the true proportion of driver fatalities related to alcohol in the county is less than 0.77.
There is insufficient evidence at the 0.10 level to conclude that the true proportion of driver fatalities related to alcohol in the county is less than 0.77.
16. The average annual miles driven per vehicle in the United States is 11.1 thousand miles, with σ ≈ 600 miles. Suppose that a random sample of 31 vehicles owned by residents of Chicago showed that the average mileage driven last year was 10.8 thousand miles. Does this indicate that the average miles driven per vehicle in Chicago is different from (higher or lower than) the national average? Use a 0.05 level of significance.
What are we testing in this problem?
single mean
single proportion
(a) What is the level of significance?
State the null and alternate hypotheses.
H0: μ = 11.1; H1: μ > 11.1
H0: p = 11.1; H1: p > 11.1
H0: p = 11.1; H1: p < 11.1
H0: p = 11.1; H1: p ≠ 11.1
H0: μ = 11.1; H1: μ < 11.1
H0: μ = 11.1; H1: μ ≠ 11.1
(b) What sampling distribution will you use? What assumptions are you making?
The Student's t, since we assume that x has a normal distribution with unknown σ.
The Student's t, since we assume that x has a normal distribution with known σ.
The standard normal, since we assume that x has a normal distribution with known σ.
The standard normal, since we assume that x has a normal distribution with unknown σ.
What is the value of the sample test statistic? (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
(c) Find (or estimate) the P-value.
P-value > 0.500
0.250 < P-value < 0.500
0.100 < P-value < 0.250
0.050 < P-value < 0.100
0.010 < P-value < 0.050
P-value < 0.010
Sketch the sampling distribution and show the area corresponding to the P-value.
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d) Based on your answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Are the data statistically significant at level α?
At the α = 0.05 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
At the α = 0.05 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
At the α = 0.05 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
At the α = 0.05 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
(e) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application.
There is sufficient evidence at the 0.05 level to conclude that the miles driven per vehicle in the city differs from the national average.
There is insufficient evidence at the 0.05 level to conclude that the miles driven per vehicle in the city differs from the national average.
17. Professor Jennings claims that only 35% of the students at Flora College work while attending school. Dean Renata thinks that the professor has underestimated the number of students with part-time or full-time jobs. A random sample of 79 students shows that 35 have jobs. Do the data indicate that more than 35% of the students have jobs? Use a 5% level of significance.
What are we testing in this problem?
single mean
single proportion
(a) What is the level of significance?
State the null and alternate hypotheses.
H0: μ = 0.35; H1: μ > 0.35
H0: p = 0.35; H1: p < 0.35
H0: μ = 0.35; H1: μ ≠ 0.35
H0: p = 0.35; H1: p ≠ 0.35
H0: p = 0.35; H1: p > 0.35
H0: μ = 0.35; H1: μ < 0.35
(b) What sampling distribution will you use? What assumptions are you making?
The standard normal, since np > 5 and nq > 5.
The Student's t, since np < 5 and nq < 5.
The Student's t, since np > 5 and nq > 5.
The standard normal, since np < 5 and nq < 5.
What is the value of the sample test statistic? (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
(c) Find (or estimate) the P-value.
P-value > 0.250
0.125 < P-value < 0.250
0.050 < P-value < 0.125
0.025 < P-value < 0.050
0.005 < P-value < 0.025
P-value < 0.005
Sketch the sampling distribution and show the area corresponding to the P-value.
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d) Based on your answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Are the data statistically significant at level α?
At the α = 0.05 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
At the α = 0.05 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
At the α = 0.05 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
At the α = 0.05 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
(e) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application.
There is sufficient evidence at the 0.05 level to conclude that more than 35% of the students have jobs.
There is insufficient evidence at the 0.05 level to conclude that more than 35% of the students have jobs.
18. The Toylot company makes an electric train with a motor that it claims will draw an average of only 0.8 ampere (A) under a normal load. A sample of nine motors was tested, and it was found that the mean current was x = 1.36 A, with a sample standard deviation of s = 0.46 A. Do the data indicate that the Toylot claim of 0.8 A is too low? (Use a 1% level of significance.)
What are we testing in this problem?
single mean
single proportion
(a) What is the level of significance?
State the null and alternate hypotheses.
H0: μ ≠ 0.8; H1: μ = 0.8
H0: p = 0.8; H1: p > 0.8
H0: μ = 0.8; H1: μ ≠ 0.8
H0: p ≠ 0.8; H1: p = 0.8
H0: μ = 0.8; H1: μ > 0.8
H0: p = 0.8; H1: p ≠ 0.8
(b) What sampling distribution will you use? What assumptions are you making?
The Student's t, since we assume that x has a normal distribution with unknown σ.
The standard normal, since we assume that x has a normal distribution with unknown σ.
The Student's t, since we assume that x has a normal distribution with known σ.
The standard normal, since we assume that x has a normal distribution with known σ.
What is the value of the sample test statistic? (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
(c) Find (or estimate) the P-value.
P-value > 0.250
0.125 < P-value < 0.250
0.050 < P-value < 0.125
0.025 < P-value < 0.050
0.005 < P-value < 0.025
P-value < 0.005
Sketch the sampling distribution and show the area corresponding to the P-value.
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d) Based on your answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Are the data statistically significant at level α?
At the α = 0.01 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
At the α = 0.01 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
At the α = 0.01 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
At the α = 0.01 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
(e) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application.
There is sufficient evidence at the 0.01 level to conclude that the toy company claim of 0.8 A is too low.
There is insufficient evidence at the 0.01 level to conclude that the toy company claim of 0.8 A is too low.
19. A hospital reported that the normal death rate for patients with extensive burns (more than 40% of skin area) has been significantly reduced by the use of new fluid plasma compresses. Before the new treatment, the mortality rate for extensive burn patients was about 60%. Using the new compresses, the hospital found that only 41 of 89 patients with extensive burns died. Use a 1% level of significance to test the claim that the mortality rate has dropped.
What are we testing in this problem?
single proportion
single mean
(a) What is the level of significance?
State the null and alternate hypotheses.
H0: p = 0.6; H1: p > 0.6
H0: p = 0.6; H1: p < 0.6
H0: p = 0.6; H1: p ≠ 0.6
H0: μ = 0.6; H1: μ > 0.6
H0: μ = 0.6; H1: μ < 0.6
H0: μ = 0.6; H1: μ ≠ 0.6
(b) What sampling distribution will you use? What assumptions are you making?
The standard normal, since np > 5 and nq > 5.
The Student's t, since np > 5 and nq > 5.
The standard normal, since np < 5 and nq < 5.
The Student's t, since np < 5 and nq < 5.
What is the value of the sample test statistic? (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
(c) Find (or estimate) the P-value.
P-value > 0.250
0.125 < P-value < 0.250
0.050 < P-value < 0.125
0.025 < P-value < 0.050
0.005 < P-value < 0.025
P-value < 0.005
Sketch the sampling distribution and show the area corresponding to the P-value.
|
|
|
|
|
|
(d) Based on your answers in parts (a) to (c), will you reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis? Are the data statistically significant at level α?
At the α = 0.01 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
At the α = 0.01 level, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
At the α = 0.01 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are statistically significant.
At the α = 0.01 level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude the data are not statistically significant.
(e) Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application.
There is sufficient evidence at the 0.01 level to conclude that the mortality rate has dropped.
There is insufficient evidence at the 0.01 level to conclude that the mortality rate has dropped.