Complete pages 6-14 exclude page 9 and show work
Chapter 7: Gases
Choose the most correct answer.
Show the calculations, wherever needed, to arrive at the answer.
Which of these is not a characteristic of gases?
compressibility
expansion to fill their containers
formation of homogeneous mixtures
All of these are characteristics of gases.
As a helium-filled balloon rises, its volume increases. This is an example of _______ Law.
Avogadro’s
Boyle’s
Charles’s
Gay-Lussac’s
A balloon filled with hot air rises. This is an example of _______ Law.
Avogadro’s
Boyle’s
Charles’s
Gay-Lussac’s
Avogadro’s Law states that the volume of a sample of a gas is proportional to the _______ of the gas.
number of moles
mass
pressure
temperature
Standard temperature and pressure (STP) equals (X) atmosphere(s) and (Y) degrees Celsius.
X = 0, Y = 25
X = 1, Y = 0
X = 1, Y = 25
X = 0, Y = 0
A sample of 2.0 moles of nitrogen (N2) gas at STP occupies a volume of _______ liters.
11.2
22.4
44.8
89.6
A sample of 4.0 grams of methane (CH4) gas at STP occupies a volume of _______ liters.
5.6
11.2
22.4
44.8
A gas sample with a mass of 88.0 mg occupies 50.0 mL at 750 Torr and 27 degrees Celsius. The gas is _______.
CO
CO2
SO2
SF6
The kinetic-molecular theory of gases states that the average kinetic energy of the gas particles is proportional to the _______ of the gas.
Kelvin temperature
Celsius temperature
number of moles
pressure
Which observation illustrates “average kinetic energy is proportional to absolute temperature”?
Most gases will liquefy under intense pressure.
Tire pressure is greater after a car has traveled some distance.
A spray can feels cold to the touch after use.
Gases expand to fill their container.
In a lung ailment such as emphysema, there is a decrease in the ability of oxygen to diffuse into the blood. How would the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood change?
The partial pressure of oxygen will be lower than normal.
The partial pressure of oxygen will be higher than normal.
The partial pressure of oxygen cannot be predicted.
The partial pressure of oxygen will be the same as it normally is.
Why is water used to sterilize surgical equipment heated to 1200C at 2.0 atm in an autoclave?
As the pressure inside the autoclave is higher than 1.0 atm, water boils below 1000C, sterilizing the equipment faster.
As the pressure inside the autoclave is higher than 1.0 atm, water boils above 1000C, sterilizing the equipment faster.
As the pressure inside the autoclave is lower than 1.0 atm, water boils below 1000C, sterilizing the equipment faster.
As the pressure inside the autoclave is lower than 1.0 atm, water boils above 1000C, sterilizing the equipment faster.
A flexible container is filled with He(g) to a volume of V1 at a temperature of 150.K. The container is then heated at constant pressure to a temperature of 300. K. What is the final volume of the container?
V1/3
V1/2
V1
2V1
Assuming constant n and T, which of the following graphs correctly represents the relationship between P and V for an ideal gas?
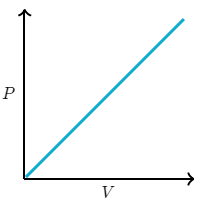
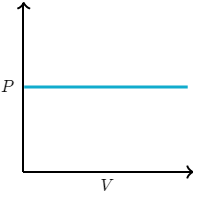
A mixture containing 4.0 moles of He(g), 2.5 moles of N2(g) and 3.5 moles of Ar (g) exerts a total pressure of 1.2 atmospheres. What is the partial pressure of He(g)?
0.30 atm
0.48 atm
0.72 atm
1.2 atm
A 0.0733 L balloon contains 0.00230 moles of I2 vapor at a pressure of 0.924 atm. What is the temperature in Kelvin of the I2 in the balloon?
300. K
359 K
86 K
319 K
A piece of dry ice, CO2(s), is placed into an evacuated 2.00 L rigid container and allowed to sublime. After complete sublimation, the pressure inside the container is 5.60 atm at 250C. Calculate the number of moles of CO2 in the container.
0.458 moles
0.548 moles
2.18 moles
5.46 moles
A 40.8 mol sample of methane gas, CH4 (g), is placed in a 1020 L container at 298 K. What is the pressure, in atmospheres, of the methane gas?
1.02 atm
0.00689 atm
0.979 atm
0.0821 atm
All of the following are properties of ideal gases except:
Small amounts of energy are lost during collisions between gas molecules
Volume occupied by molecules is negligible compared to the volume occupied by the gas
Gas molecules do not interact with each other except during collisions
Collisions between gas molecules are completely elastic
How many diagrams showing relationships between pressure, volume, and temperature below is/are incorrect for ideal gases?
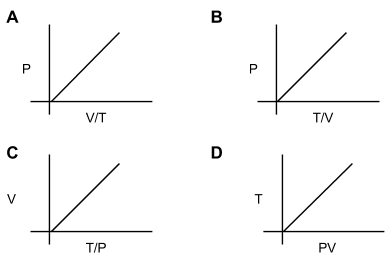
None
Only one
Only two
Only three
At a given temperature T and pressure P, a person's lung holds a set volume of V of air. Given that air is roughly 20% oxygen, how many moles of oxygen are in his lungs?
0.2 * (PT/RV)
5 * (PT/RV)
0.2 * (PV/RT)
5 * (PV/RT)
Gases found in the environment are most likely to exhibit properties similar to that of ideal gases under conditions of:
low temperatures and high pressures
high temperatures and high pressures
high temperatures and low pressures
low temperatures and low pressures
Assume an experiment vessel which is well fitted with a piston. The airtight piston has negligible mass and can move up and down freely. There is 1 mol of an ideal gas contained within the vessel under the piston at pressure of 100 kPa. The piston rests at 10 cm from the base of the vessel. The pressure in the vessel increases to 200 kPa as force is applied to the piston. What would be the new resting position of the piston from the base of the vessel? Assume the temperature is held constant at 300 K throughout the experiment.
5 cm
2 cm
1 cm
8 cm
The behavior of which of these real gases will be reflected most closely with the ideal gas law?
CO2
Ar
He
CH4
Assuming ideal gas properties, which of the following occupies the most volume at 273 K and 1 atm of pressure?
One mole of hydrogen gas
They all occupy the same volume
One mole of oxygen gas
One mole of nitrogen gas
Atmospheric air is comprised, roughly, of 80% nitrogen and 20% oxygen. A 100 L sample of atmospheric air is kept at 300 K and 100 kPa. How many moles of oxygen molecules are found in this gas sample? Use R = 10 (L.kPa/mol.K)
2/3
4/5
3/2
1/5
A gas kept in a closed container has a volume of 4.0 L. Indicate what changes in pressure must have occurred if the volume is compressed to 2L at constant temperature?
The pressure doubles
The pressure becomes one-half of the original pressure
There will be no change in pressure
The pressure becomes one-third of the original pressure
A gas kept in a closed container has a volume of 4.0 L. Indicate what changes in pressure must have occurred if the volume is allowed to expand to 12 L at constant temperature?
The pressure falls to one-third of the initial pressure.
The pressure rises by one-third of the initial pressure.
The pressure increases by three times of the original pressure.
The pressure decreases by three times of the original pressure.
The air in a 5.00 L tank has a pressure of 1.20 atm. What is the new pressure of the air, when the air is contained in the tank have a volume of 1.00 L, if there is no change in temperature?
0.240 atm
6.00 atm
1.20 atm
5.00 atm
The air in a 5.00 L tank has a pressure of 1.20 atm. What is the new pressure of the air, when the air is contained in the tank have a volume of 2500.mL, if there is no change in temperature?
0.00240 atm
0.600 atm
2.40 atm
600. atm
A sample of methane (CH4) has a volume of 25 mL at a pressure of 0.80 atm. What is the volume of the gas if the pressure is 0.40 atm with no change in temperature?
0.500 L
50. mL
500 mL
5.0 mL
The volume of air in a person’s lungs is 615 mL at a pressure of 760 mm of Hg. Inhalation occurs as the pressure in the lungs drops to 752 mm of Hg. To what volume did the lungs expand?
622 mL
609 mL
929 mL
589 mL
A sample of neon initially has a volume of 2.50 L at 150C. What is the new temperature, in 0C, when the volume of the sample is changed at constant pressure to 5.00 L?
5760C
2730C
3030 C
300C
A sample of neon initially has a volume of 2.50 L at 150C. What is the new temperature, in 0C, when the volume of the sample is changed at constant pressure to 1250 mL?
-1290 C
1440C
7.50C
4170C
An air bubble has a volume of 0.500 L at 180C. If the pressure does not change, what is the volume, in Liters, at 00C?
0.469 L
0 L
0.0278 L
0.00172 L
An air bubble has a volume of 0.500 L at 180C. If the pressure does not change, what is the volume, in Liters, at -120C?
0.725 L
0.0206
0.557
0.448 L
Why is there an increased danger of the tires of a car having a blowout when the car is driven on hot pavement in the desert?
An increase in temperature decreases the pressure inside the tires. When the pressure is the same as the pressure limit of the tires, it can blow out.
An increase in temperature increases the pressure inside the tires. When the pressure is less than the pressure limit of the tires, it can blow out.
An increase in temperature increases the pressure inside the tires. When the pressure exceeds the pressure limit of the tires, it can blow out.
An increase in temperature has no effect in the pressure inside the tires. When the pressure is the same as the pressure limit of the tires, it can blow out.
A gas mixture containing oxygen, nitrogen and helium exerts a total pressure of 925 torr. If the partial pressures are oxygen 425 torr and helium 75 torr, what is the partial pressure in torr of the nitrogen in the mixture?
425 torr
75 torr
925 torr
760 torr
Calculate the new temperature, in degree Celsius, when the pressure is changed, with n and V as constants. A sample of air at 40.00C and 745 mm Hg is cooled to give a pressure of 685 mm of Hg.
43.50C
340.0C
36.80 C
14.80 C
Solve for the new pressure, with n and V being constants. A gas with a pressure of 1.20 atm at 750C is cooled to -220C.
0.866 atm
0.352 atm
4.02 atm
1.67 atm
A scuba diver inhales 50.0 mL of compressed air in a scuba tank at a pressure of 3.00 atm and a temperate of 80C. What is the pressure of air in the lungs if the gas expands to 150.0 mL at a body temperature of 370C?
1.20 atm
1.10 atm
8.71 atm
4.68 atm
A sample containing 1.50 moles of neon gas has a volume of 8.00 L. What is the new volume of gas in Liters, when a leak allows one-half of the neon atoms to escape, at constant pressure and temperature?
4.00 L
2.00 L
16.0 L
12.0 L
A sample containing 1.50 moles of neon gas has a volume of 8.00 L. What is the new volume of gas in Liters when a sample of 25.0 g of neon is added to the 1.50 moles of neon gas in the container, at constant pressure and temperature?
14.7 L
133 L
2667 L
15.5 L
Calculate the volume in Liters of 6.40 g of O2 at STP.
22.4 L
4.48 L
2.24 L
44.8 L
4Al (s) + 3O2 (g) → 2Al2O3 (s)
How many grams of Al will react with 12.0 L of O2 at STP?
9.3 g of Al
14.5 g of Al
19.3 g of Al
57.8 g of Al
A 25.0 g sample of N2 gas, has a volume of 50.0 L and a pressure of 630. mm of Hg. What is the temperature of the gas? Universal Gas Constant, R = 62.4 L.mm Hg/mole.K
2920C
5650C
2650C
1520C
An oxygen gas container has a volume of 20.0 L. How many grams of oxygen are in the container if the gas has a pressure of 845 mm of Hg at 220C?
Universal Gas Constant, R = 62.4 L.mm Hg/mole.K
29.4 g of oxygen
0.918 g of oxygen
14.7 g of oxygen
20.8 g of oxygen
Calculate the pressure in atmospheres, of 2.00 moles of He in a 10.0 L container at 270C. Universal Gas Constant, R= 0.0821 L.atm/mole.K
4.93 atm
0.443 atm
3.74 atm
4.43 atm
In a gas mixture, the partial pressures are nitrogen 425 torr, oxygen 115 torr and helium 225 torr. What is the total pressure in torr exerted by the gas mixture?
765 torr
669 torr
651 torr
761 torr
Calculate the number of moles of O2 in 44.8 L of O2 gas.
2.00 moles of oxygen
4.00 moles of oxygen
1.00 moles of oxygen
22.4 moles of oxygen
11



