Prepare a written case study research paper dealing with a communication problem(s) in his or her place of employment or an organization of choice. From what has been learned in this class, students
Running head: IMPROVING INTERNAL COMMUNICATION
Improving Internal Communication at Griffin Avenue Elementary School
Zalodius Washington
University of La Verne
Introduction 2
Statement of Problem 3
Purpose of Research 3
Research Questions 4
Research Methodology 4
Method of Analysis 4
Method 1: Interactive Communication Process 4
Method 2: Douglas McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y 6
Method 3: Kuhnert and Lewis’ Transactional and Transformational Leadership Theory 8
Method 4: Johari Window Model 10
Method 5: Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory of Motivation 12
Findings to Research Questions 14
Summary of Findings 19
Recommendations 20
References 22
“The history of organizations in all industries suggests that stakeholders must build a cultural foundation that consists of five major elements: shared values, empowerment, communication, service excellence, and rewards for success” (White et al., 2010). These pillars represent a significant paradigm shift in which the unchanging bureaucracy theory of management operates. According to O’Hair et al. 2011, bureaucratic authority structures concentrate a great deal of power at the top of a hierarchy where each subsequent level solely depends on the previous level of authority when adhering to policies, procedures, and dissemination of information. Although bureaucratic structures are considered the most efficient mechanized business approach for providing a transparent chain of command, it impairs the ideology behind transformational leadership. This transformational process begins once the organizational leader effectively articulates his or her vision and inspires others to achieve excellence through the development of a high performing work environment that empowers subordinates and encourages professional growth. (O’Hair et al., 2011).
Griffin Avenue Elementary, a small K-5 school within the Los Angeles Unified School District, is located in Lincoln Heights. Administrators and faculty members are committed to ensuring personalized student instruction and rigorous academic standards in preparation for college readiness. Nonetheless, despite the concerted effort, school administrators ineffectively streamline communication to its faculty; thereby, permeating cultural distrust and undermining the credibility among school leaders.
The rigid bureaucratic structure within the Los Angeles Unified School District does not foster nor encourage transformative leadership at individual school sites. Therefore, school administrators often streamline communication utilizing the downward flow approach when implementing directives and disseminating information from the district headquarters to internal stakeholders. While there are various methods for communicating effectively, organizational leaders should exercise communication competencies that inspire internal stakeholders to support the mission, vision, and values; thus, enhancing interpersonal effectiveness, which serves to improve the cultural and operational foundation of the organization.
Statement of ProblemIt appears that the Administrators of Griffin Avenue Elementary School are highly ineffective in the way they communicate with faculty members.
Purpose of ResearchThe purpose of this research is to identify the factors creating a lack of timelines and substantive communication among Administrators and faculty members at Griffin Avenue Elementary School.
Research QuestionsHow are the Administrators of Griffin Avenue Elementary School highly ineffective in the way they communicate with the faculty?
Why are the Administrators of Griffin Avenue Elementary School highly ineffective in the way they communicate with the faculty?
What can be done to improve the effectiveness of the Administrators of Griffin Avenue Elementary School?
The research methodology for this paper utilizes a review of the literature and theoretical models to support research. Additionally, the research methodology provides assessment substantiated upon personal observations and experiences while on a short-term assignment as a Substitute Teacher at Griffin Avenue Elementary. Finally, the research conducted should provide insight into possible communication deficits within the instructional environment and demonstrate opportunities for course correction strategies to improve internal communication methods.
Method of Analysis Method 1: Interactive Communication ProcessReview of Model:
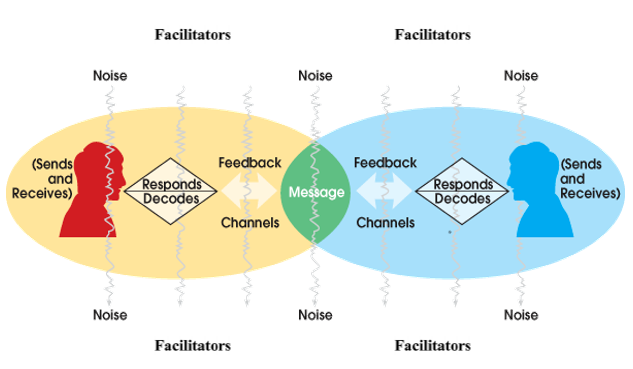
Review of Literature:
Communication focuses on the dissemination and receipt of information in which individuals exchange to accomplish goals and objectives (O’Hair, 2011). The interactive process occurs as follows: First, the encoder (sender) encodes the message, which is transmitted verbally or nonverbally. Next, the message is sent to the decoder (recipient) who decodes the message. The message is conveyed through some medium(channel), which is considered any outlet used to communicate knowledge, data, music, images, emotion, or media to the recipient. Finally, the recipient provides feedback to demonstrate receipt and understanding of the message; thus, completing the interactive communication process. Additionally, O’Hair et al. (2011) describe internal and external factors that interfere with the communication process. The element of noise serves as internal and external factors that potentially distort the ability for either the sender or receiver to encode and decode messages properly. In contrast, facilitators are environmental factors that promote communication; thereby, creating a comfortable environment for encoding and decoding messages.
Moreover, an emphasis during course lectures explains the anthropologic perspective of communication, which comes from the field of linguistics. Post Modernism, structured on linguistics, suggests that one’s language identifies how one sees reality; hence, Social Construction Existential Reality theory. This theory examines shared assumptions about reality as it relates to societal understandings. Further, it expounds on the notions that individuals rationalize their experience by creating models of the social world and share these models through language, which utilizes expression through culture and conventional standards.
Method 2: Douglas McGregor’s Theory X and Theory YReview of Model:

Review of Literature:
The concepts of Theory X and Theory Y were promoted by Douglas McGregor, a social psychologist who expounded on the different theories that explain human motivation and management during the 1960s. Theory X and Theory Y are designed to explain how a manager perceives the motivational behavior of his or her employees. McGregor believed that it was essential to have a firm understanding of the Theory X and Theory Y concept to help managers understand how assumptions regarding employees’ motivation can impact one’s management style. Moreover, McGregor emphasized that one’s management style could be altered appropriately to manage employees effectively based on the manager’s understanding of employee motivation. McGregor argued that Theory Y was the most effective management style as opposed to the Theory X management style that assumes that employees are unmotivated and dislike work. Also, the Theory X management style is based on three assumptions. First, employees have to be controlled or threatened to be productive. Second, employees require supervision at every step. Finally, employees tend to avoid responsibility and often must be directed.
McGregor asserts that the Theory Y management style was most effective based on the following reasons: First, Employees will be self-directed to meet their employment responsibilities when they are committed to them. Secondly, Individuals will be committed to fulfilling their employment responsibilities when a system of rewards are implemented; therefore, addressing the higher-level needs of self-fulfillment. Theory Y managers understand the benefit of having employees who are both creative and demonstrate ingenuity in fulfilling their employment responsibilities. The Theory Y management style operates on the assumption that managerial power should be decentralized, delegating more tasks and responsibilities to various employees. Theory Y managers make full use of a participative management style in which they readily consult their employees for suggestions that consider the creativity and resourcefulness of their employees.
Method 3: Kuhnert and Lewis’ Transactional and Transformational Leadership TheoryReview of Model:
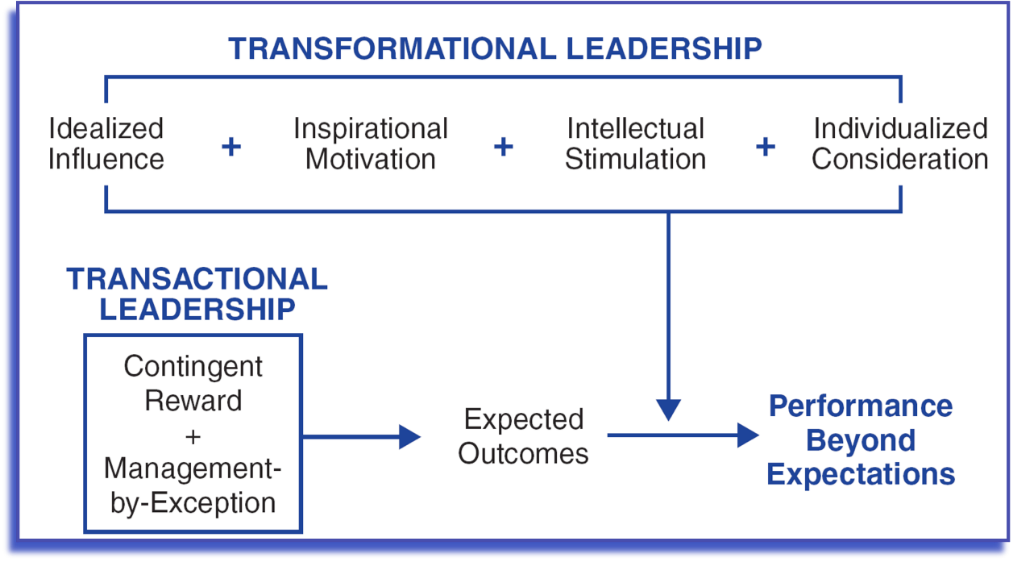
Review of Literature:
The Seminole researchers of Transactional and Transformational Leadership Theory are James MacGregor Burns (1978), Bernard Bass (1985), Kuhnert, and Lewis (1987). The theory expounds on two types of leadership that is, transactional and transformational. First, transactional leadership is a relationship between the superior or organizational leader and subordinates centered on exchanges for mutual gain (O’Hair et al., 2011). For example, the carrot and stick approach where individuals receive rewards in exchange for desired behaviors. These rewards can be monetary, such as sales commissions and merit-based pay. Non-financial rewards include promotions or professional acknowledgment. Conversely, transformational leadership relationships concentrate on goal attainment in which leaders appeal to set values, beliefs, and needs of organizational members; thus, demonstrating social and emotional intelligence. Consequently, the implications of transformational leadership qualities promote empowerment, enhance motivation, improve productivity, and managing change. O’Hair et al. (2011) state the importance of implementing a four-step strategy to manage change in an organizational setting:
Expect the unexpected by the anticipation of problems and having a contingency plan to avoid potential problems.
Concentrate on the organizational vision and identify obstacles to modify or resolve problems.
Evaluate desired outcomes and consider alternative task-related approaches.
Establish a firm yet supportive network committed to accepting change and place those individuals in critical positions to facilitate the process.
Review of Model:
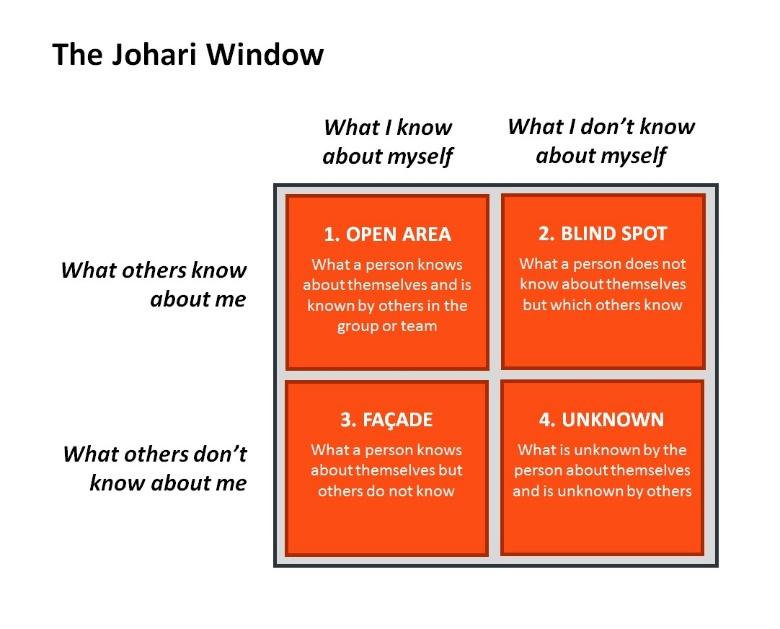
Review of Literature:
The Johari Window is the psychological model developed by Joseph Luft and
Harrington Ingham aims to address the relationship and mutual understanding
between group members. The cognitive psychological tool serves as a communication
model to improve understanding between individuals within a team or in a group setting.
Additionally, the model allows individuals to develop interpersonal communication skills
and relationships. There are two essential ideas in which the Johari Window Model examines: First, individuals can build trust by disclosing information about themselves to counterparts Second, individuals can learn about themselves and come to terms with disregarded issues through constructive feedback from others. The following describes the essence of each quadrant represented in the Johari Window Model:
Open/Free Area quadrant is also known as the ‘area of free activity.’ This is the behavioral and emotional information about the person - is known by the person (‘the self’) and other people. Examples of such information may include trust levels, communication style, competence at work, and leadership effectiveness (https://www.communicationtheory.org/the-johari-window-model/).
The blind area often holds the keys to personal and team progress. When strengths and areas for development are shared in this quadrant, the recipient is better able to make decisions on behavior changes and seeking support or resources for personal development (https://www.communicationtheory.org/the-johari-window-model/).
The hidden area is where we keep personal information that we do not want others to have access to. The reasons for keeping information hidden can range from being personally sensitive, that one would not want to share openly, to information that an employee would like to share, but does not feel there is sufficient trust or safety to do so (https://www.communicationtheory.org/the-johari-window-model/).
The unknown area is information that is unaware of yourselves as well as others. This includes information, feelings, capabilities, talents. This can be due to traumatic past experiences or events which can be unknown for a lifetime. The person will be unaware until he discovers his hidden qualities and capabilities or through observation of others. Open communication is also an effective way to decrease the unknown area and thus to communicate effectively(https://www.communicationtheory.org/the-johari-window-model/).
Review of Model:
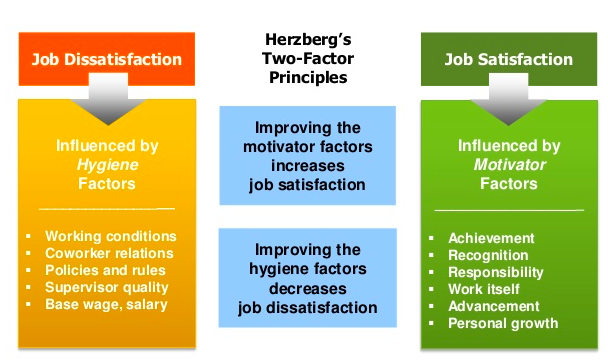
Review of Literature:
Frederick Herzberg, a well-known psychologist, and motivational theorist, developed the Two-Factor theory to determine what motivates human behavior in the workplace. The two key factors are motivating factors and hygiene factors. First, motivating factors can be described as intrinsically rewarding; thus, causing an employee to work harder. These factors are responsibility, achievement, growth, and opportunity (Longest et al., 2014). Hygiene factors represent elements that cause dissatisfaction or negatively impact employees. For example, working conditions, salary, interpersonal relations, and organizational policy. Managerial implications of Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory, according to Longest et al., (2014) suggests that managers should ensure the work remains stimulating and rewarding to increase motivation and performance among employees. Also, managers should consider and support the role in which hygiene factors play to avoid or minimize employee dissatisfaction.
Noticeably, there are distinct similarities between Herzberg’s theoretical model and Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs. Abraham Maslow developed a hierarchical structure of needs for understanding specific factors that motivate human beings. Specifically, Maslow wanted to understand the motivational factors that transcend rewards and unconscious desires. There are five motivational needs outlined in Maslow’s hierarchical structure. The basic needs of humans are listed or explained in the lower portion of this hierarchy. These five motivational needs are the following: Physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization. Maslow posits that it is essential for human beings or individuals to satisfy lower basic needs before advancing to higher-level needs. For example, individuals will not ascend to the higher levels of this structure if there are deficiencies in their basic physiological needs. Hence, Maslow contends that higher level growth needs cannot reach achievement if one does not satisfy the lower level of basic needs in this hierarchy.
Moreover, Maslow contends that every individual has the capability of ascending to the level of self-actualization. Consequently, the same reasoning applies to Herzberg’s model. Meaning, the Two-Factor theory can be used as an indicator to explain advancements and setbacks in one’s personal and professional development.
Findings to Research QuestionsFinding 1:
How are the Administrators of Griffin Avenue Elementary School highly ineffective in the way they communicate with the faculty?
Effective communication plays an integral role in the cultural and operational foundation of an organization. O’Hair et al. (2011) describe three distinct methods for relaying internal communication that is, downward, upward, and horizontal. First, downward communication refers to movement from top to bottom, meaning superiors disseminate information to subordinates to convey messages regarding procedures, organizational goals, and job rationale. The serial communication approach can alter the accuracy of the intended message as the information travels down the chain of command; thus, resulting in misunderstanding, distortion of the message, and reliability of the source (O’Hair et al., 2011). Second, upward communication involves communication from lower-level employees to superiors, which allows expression concerning the acceptance of organizational practices or impending problems that exist within the organization. Moreover, upward communication facilitates a shared decision-making process and provides a sense of empowerment. Last, Horizontal communication flows across the same hierarchical level in an organization where the emphasis on relationship enhances morale and promotes task coordination among departments or teams (O’Hair et al., 2011).
Consequently, through observation, it appears that the relationship between Administrators and Teachers at Griffin Elementary school remains hindered by a deficit in communication. For example, Before the Los Angeles Unified School District (LAUSD) transition to Distance Learning as a result of coronavirus (COVID-19), the Superintendent sent an email providing information and procedures for teachers to follow in preparation for the initial two-week school closure. However, the administrators at Griffin Elementary failed to address the Superintendent’s email nor communicate an instructional plan for teachers to follow at the school site; instead, they waited until two days before the school closure to provide directives. Teachers were in a quandary about the specific course of action to take with the students. Further, on the day leading to school closure, an overwhelming amount of information was circulated through various channels. This undertaking hindered the decoding process, causing frustration and anxiety among teachers. Despite concerted efforts to provide direction, the Administrators’ failure to timely disseminate information negatively affected the communication climate. The implication of an organization’s ability to achieve an ideal communication climate, according to O’Hair et al., (2011), prevents shortcomings such as the example mentioned above. Most importantly, recognizing communication deficits improves situational knowledge and allows for appropriate modifications; therefore, promoting a culture of supportiveness, participative decision making, transparency, and credibility.
Finding 2:
Why are the Administrators of Griffin Avenue Elementary School highly ineffective in the way they communicate with the faculty?
The entire administrative team was newly assigned to Griffin Avenue Elementary School two years ago to implement and improve administrative conditions at the school site. However, it appears that the inexperience of the administrative team reflects a lack of professional development in the area of communication. Although a school’s safety plan exists at the school site, which is implemented by the administrative team, challenges exist in the area of execution of scheduled emergency drills. For example, the school bulletin communicated that a Fire drill was scheduled to take place on a specified date and time; however, it was never carried out. Therefore, teachers were ill-prepared on the actual day of the fire drill. While it can be argued that school staff should be prepared for any emergency drill that might arise, this example clearly shows the administration’s failure to communicate effectively with school stakeholders. In an attempt to ascertain feedback, the administration team distributed an evaluation form following the end of the emergency preparedness drill. Subsequently, the results of the evaluation were not disclosed; thus, resulting in a missed opportunity to address essential protocols about correct emergency procedures. While these examples show the administration’s inability to demonstrate leadership, their actions and approach seem centered on a transactional leadership style rather than transformational. For example, concerning the implementation of emergency procedures at a school site, a transformative leader can use a shared decision-making approach to team with seasoned staff members to assist with the leadership responsibilities.
Finding 3:
What can be done to improve the effectiveness of the Administrators of Griffin Avenue Elementary School?
According to O’Hair et al. (2011), there are five essential components for improving communication skills to promote excellence: First, exercise creative insight by asking the right questions to ensure the organization and team members have the correct information to manage a dynamic workforce effectively. Second, one should demonstrate sensitivity as it plays a vital role in communication skills and increases awareness. Also, active listening can improve one’s ability to evaluate an individual’s nonverbal cues or reactions empathetically. Third, incorporate a vision to inspire, motivate, and build upon the direction of the organization. Fourth, foster an environment based on shared meaning in which the leader and the team establish a connection concerning mutual ideas and perspectives on common goals. Last, an organizational leader should develop a sense of integrity where the emphasis is on building relationships based on trust and respect.
Theoretically speaking, the Johari Window model can be used to improve the effectiveness of the administrative team with regards to communication with faculty members as the model teaches the value of self-disclosure, mutual understanding, and constructive feedback, which are imperatives for building organizational excellence. Further, Theory X and Theory Y support two styles of management, which are authoritarian and participative. Familiarity with McGregor’s theory can provide insight on how to identify and manage individuals based on motivational determinants. For example, a new teacher or substitute may require a Theory X management style, which is considered hands-on or micromanaging to provide guidance and build confidence in the workplace. The administrative team must use discernment to implement interchangeable styles to improve faculty member’s motivation and effectuate the communication climate.
While there are multiple ways to communicate, school administrators at Griffin Elementary must understand the most effective modes for disseminating information and adapt behaviors to promote a healthy communication climate. Most importantly, the onus falls upon the organizational leader or manager to recognize the subordinates’ existential reality and use it to understand values, needs, and effectively empower individuals to participate in the decision-making process. When organizational leaders and managers communicate effectively, it positively impacts the workplace. Implementation of strategic communication and leadership behaviors contributes to a strong organizational foundation resulting in increasing motivation, enhancing productivity, and transparent feedback.
Summary of FindingsThe implementation of communication models and theories in an organization provides a way to improve effectiveness and efficiency. Most importantly, understanding the various communication models and theories allow organizational leaders to identify which one is most applicable under prevailing circumstances. An analysis using five theoretical models showed the following factors contributing to the ineffective communication between the Administration team and faculty at Griffin Elementary School.
Method 1: Interactive Communication Process
Administrator’s improper usage of channels to encode messages; therefore, creating communication barriers such as misunderstanding and distrust among faculty members.
Erroneous assumptions about individuals can impede the encoding and decoding process resulting in communication failure.
Information arriving too early or late and poor quality can impede the communication process.
Method 2: Douglas McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y
Management style and approach as it relates to motivational behavior
Identify self-directed and creative individuals requiring additional responsibilities
Method 3: Kuhnert and Lewis’ Transactional and Transformational Leadership Theory
Transactional leaders operate comparable Carrot and Stick approach where individuals receive rewards in exchange for desired behaviors.
A transformational leader focuses on the organizational vision and goal attainment.
Inspires subordinates through social and emotional intelligence
Method 4: Johari Window Model
Self-awareness
Team collaboration
Demonstrating vulnerability
Mutual understanding
Method 5: Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
Differentiate between hygiene and motivational factors to manage accordingly
Maintain a stimulating work environment
Concentrate on intrinsic motivational factors such as achievement, growth, and opportunity.
Organizational leaders and managers should demonstrate understanding and tolerance, therefore recognizing diverse existential socially constructed realities. This understanding and tolerance will effectively improve communication and allow collaborative efforts in meeting objectives.
The Los Angeles Unified School District should provide joint professional development training for administrators and teachers to address common barriers, ensure clear communication and directives. Implementation of joint professional development training will improve communication competence and create a shared vision in the educational partnership.
Research suggests that organizational leaders can improve interactive listening skills by creating appropriate goals, identifying listening styles, and working to eliminate barriers that can block active listening (O’Hair et al., 2011). School administrators need to establish clear expectations in alignment with the mission, vision, and values of the organization. Moreover, clear and effective communication involves administrators seeking to find effective ways to improve communication at the school site by working to improve interpersonal relationship strategies and eliminate obstacles that hinder communication deficits.
Longest Jr, B. B., & Darr, K. J. (2014). Managing Health Services Organizations and Systems,(MHSOS). Health Professions Press, Inc.
O’Hair, D., Friedrich, G. W., & Dixon, L. D. (2011). Strategic communication in business and the professions. Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
White, K. R., & Griffith, J. R. (2014). The well-managed healthcare organization. Chicago, IL: Health Administration Press.



