lab assignment
Page 8 of 7
Part One – MineralsThe first part of the activity is about the mineral identification. Watch the following Youtube video in full:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QPKkRRdQLFo
Use your textbook or internet sources to answer the following questions:
First write a summary about the video
(It should contain parts from the beginning, middle, and end of the video - 250 words)Explain the hardness test:
What is cleavage and what is the difference between a cleavage and a crystal face?
Is the color of a mineral and the color of its scratch on a streak plate the same?
Quartz, Calcite, and Clay minerals are the most common minerals on the Earth surface. Explain what is the easiest way to identify them and in what type of rocks or sediments we may find them?
Quartz:
Calcite:
Clay minerals:
Part Two – Major Rock GroupsIGNEOUS ROCKS
The second part of the activity is about the major rock groups. Watch the following Youtube video in full:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Zbz4e-9pjY4
Use your textbook or internet to complete this assignment:First write a summary about the video!
(It should contain parts from the beginning, middle, and end of the video - 250 words)Find the images of the following igneous rocks Basalt, Gabbro, Andesite, Diorite, Rhyolite, Granite, and Peridotite in your textbook or any scientific viable internet source (a good link is https://geology.com) and insert the images in corresponding field.
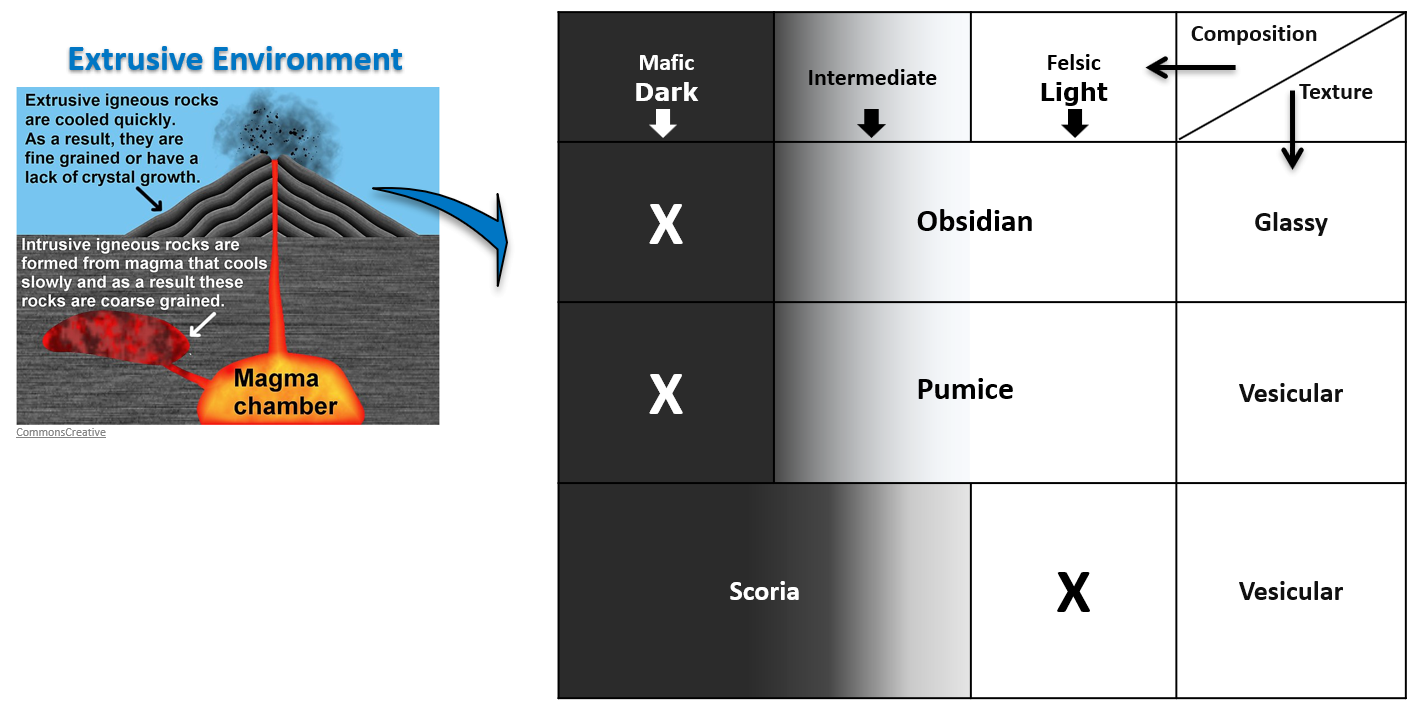
Find the images of the following extrusive igneous rocks Obsidian, Pumice, and Scoria in your textbook or any scientific viable internet source (a good link is https://geology.com) and insert the images in corresponding field.
![lab assignment 1]()
Notice that Obsidian is dark-colored, but it is not mafic!
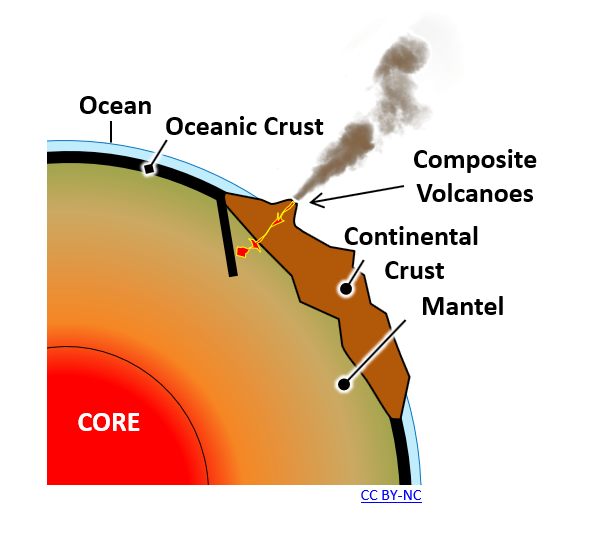
Which rocks or compositions represent the composition of the Earth layers or important geologic features (please see the image below). Use the following compositions to fill out the blanks:
Felsic or granitic | mafic or basaltic | intermediate or andesitic | ultramafic or peridotitic![lab assignment 2]()
The average composition of the
continental crust is represented by
_____________________ composition.The oceanic crust is made of
____________________ rocks.The upper mantel rocks show a ___________
_______________ composition.The strato volcanoes which make up 90%
of all active volcanoes along the margin of
the plates are made of __________________
______________ rocks.
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
Watch the following Youtube video in full:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uozyWZ6XQzM
Use your textbook or internet to answer the following questions:
First write a summary about the above video!
(It should contain parts from the beginning, middle, and end of the video - 250 words)Complete the following blanks:
![lab assignment 3]()
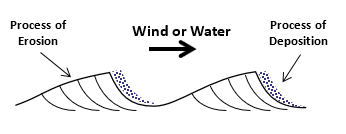
The deposition of sediments generally forms horizontal layers (See the image above) which are called ___________.
The horizontal layering of the sediments obeys the rule or principle of “the law of original horizontally”.
There are exceptions from the rule of Original horizontality, where the layers form asymptotic or ripple-mark shape. This type of layering could be found in the sand dune in deserts and ripple marks in tidal zone. In a very similar way this happens at the mouth of the rivers (Delta). This structure is called ___________.
Consider the size and shape of the grains in the following detrital (or clastic) sedimentary rocks and use ALL the words and environments (the locations where they may have been formed in the past) that may apply:
Round | Gravel | Swamp | Sand | Silt | Clay | Angular | Well-sorted | Poorly-sorted | Landslide | Rocky coast | Desert | Rock fall | Sandy beach | Bottom of a lake | Flood plain | River | Debris from collapse of a cave ceiling | Bottom of an ocean | or Not applicable (NA)
Don’t use number for the size of the grains inside of the clastic sedimentary rocks. Instead use the terms Gravel, Sand, Silt, and Clay (these terms tell you the size of the grains they have nothing to do with the composition!
Hint! Some words may be used in multiple boxes and multiple words may be necessary to correctly


Conglomerate
METAMORPHIC ROCKS
Watch the following Youtube video in full:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ncr-46YX-N0
Use your textbook or internet to answer the following questions:
First write a summary about the video!
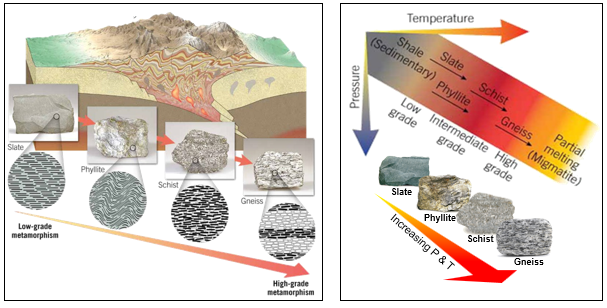
(It should contain parts from the beginning, middle, and end of the video - 250 words)Find the image of the following rocks Slate, Phyllite, Schist, and Gneiss in your textbook or any scientific viable internet source (a good link is https://geology.com) and insert the images in corresponding field.
| Texture | Grain Size | Characteristics | Grade of Metamorphism (low-intermediate-high) | Rock Name |
| Foliated | Slate | |||
| Foliated | Phyllite | |||
| Foliated | Schist | |||
| Foliated | Gneiss | |||
| Non-foliated | Quartzite | |||
| Non-foliated | Marble |
| Texture | Grain Size | Characteristics | Name |
| FOLIATED | Very Fine | Dull Luster Hard Flat Sheets High Frequency “Ping” | SLATE |
| Fine | Wrinkled or Wavy Layers Metallic Luster Few Larger Crystals | PHYLLITE | |
| Medium to Coarse | Visible Sparkling Platy Minerals (Micas) | SCHIST | |
| Medium to Coarse | Alternating Bands of Light and Dark | GNEISS | |
| NON-FOLIATED | Fine to Medium | Calcite (Fizz with HCl) Hardness = 3 | MARBLE |
| Fine to Medium | Quartz Hardness = 7 | META-QUARTZITE |
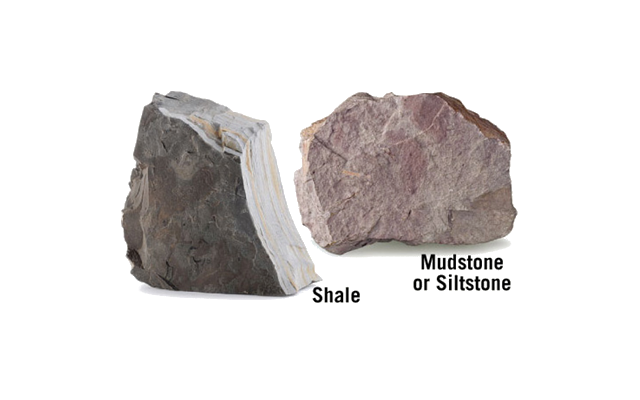
The foliation shows the intensity or grade of metamorphism (the amount of heat and pressure the rocks were exposed to). The image below shows how shale or slate would change at different grade of metamorphism.