I have attached the spreadsheet for this assignment and my past two assignments to help. The purpose of this assignment is to review the root causes of the problem and all of the previously tried, as
BENCHMARK ASSIGNMENT 5
Benchmark - Data Collection
Date regarding Noncooperation amongst Managers
|
| Reasons of noncooperation | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Week | Day of the week | Total number of noncooperation amongst managers | Lack of Trust | Individuals shirking their duties | Skewes Influence over Decisions | Stuck in Formation | Others | |
| Monday | ||||||||
| Tuesday | ||||||||
| Wednesday | ||||||||
| Thursday | ||||||||
| Friday | 21 | 16 | ||||||
| Monday | ||||||||
| Tuesday | 19 | |||||||
| Wednesday | 25 | 10 | ||||||
| Thursday | 25 | 12 | ||||||
| Friday | 24 | |||||||
| Monday | 29 | 10 | 10 | |||||
| Tuesday | 19 | |||||||
| Wednesday | 21 | 12 | ||||||
| Thursday | 19 | |||||||
| Friday | 24 | |||||||
| Total | 261 | 97 | 39 | 40 | 54 | 31 | ||
STEP 1: First, check the managers' claim that there is noncooperation on specific days by plotting the combined data day-wise on a histogram.
STEP 2: Plotting a scatter diagram for the total number of noncooperation amongst managers to analyze trends.
The scatter plot is showing that the number of noncooperation amongst managers is increasing with time. This means that there is a presence of an increasing trend.
STEP 3: Creating a Pareto chart a) Counting the total noncooperation in each category. b) Calculating the total cumulative count. C) Calculating the cumulative percentage for each noncooperation cause.
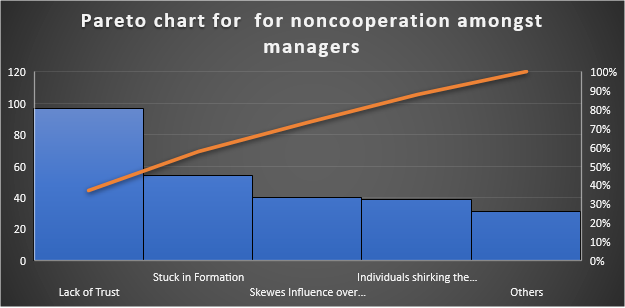
Summary Report
The analysis shows that the primary reason causing noncooperation amongst managers is: Lack of trust is the primary reason with a contribution of 85%. Stuck in information is the second main contribution with a contribution of 45%. Finally, individuals neglect their duties and Skewes Influence over Decisions with a contribution of 30% each.
Mistrust is a significant issue, as illustrated by the analysis. While stuck in information is also a contributing factor, the management must give attention to stuck details and lack of trust to improve the noncooperation among the managers.
References
Dwivedi, Y. K., Shareef, M. A., Mukerji, B., Rana, N. P., & Kapoor, K. K. (2018). Involvement in emergency supply chain for disaster management: a cognitive dissonance perspective. International Journal of Production Research, 56(21), 6758-6773.
Walters, D., Quinlan, M., Johnstone, R., & Wadsworth, E. (2016). Cooperation or resistance? Representing workers' health and safety in a hazardous industry. Industrial Relations Journal, 47(4), 379-395.



