quick practice test (highlight the correct answers)
Normal sea level pressure has a value of
1013.2 millibars.
28.50 inches of lead.
32.01 millibars of mercury.
500 mb.
1222 force per square foot.
2.) The normal range for air pressure at sea level is
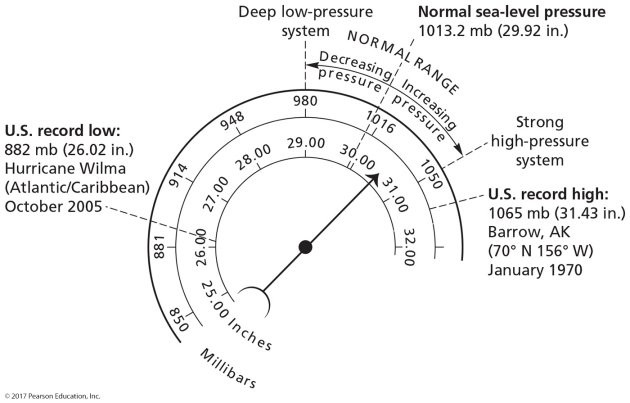
500 to 1000 mb.
100 to 650 mb.
980-1050 mb.
1060-2010 mb.
914-980 mb.
3.) Based on the figure, the Earth's lowest barometric pressures are likely associated with

hurricanes (typhoons).
frontal systems (cold and warm fronts).
cold and dry climates.
sea level.
extreme cold.
4.) The highest surface air pressure in the U.S. ever recorded occurred when the air was

very cold.
very warm.
very wet.
very high above the surface of Earth.
mild.
5.) The two principle properties of wind are
pressure and turbulence.
speed and direction.
pressure and direction.
turbulence and speed.
speed and pressure.
6.) Without the ________ wind would not blow.
Coriolis force
pressure gradient force
friction force
centrifugal force
electromagnetic force
7.) Which of the following is not true of the wind?
Wind is initiated by the pressure gradient force.
Wind blows from regions of high pressure to regions of low pressure.
The direction of flow can be affected by the rotation of Earth.
Air blows from regions of hotter air to regions of colder air.
Winds are named based on the direction from which they blow.
8.) If Earth did not rotate, air would flow
perpendicular to the isobars, i.e., straight across the isobars.
to the right of its direction of motion in the Northern Hemisphere.
to the left of its direction of motion in the Northern Hemisphere.
in a circular pattern.
parallel to the isobars.
9.) The Coriolis reaches maximum deflection at
the equator.
the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn.
30° N and 30° S.
60° N and 60° S.
the poles.
10.) Which of the following is true regarding low-pressure cells in the Southern Hemisphere?
They form a continuous belt of uniform intensity surrounding the periphery of Antarctica.
The air circulation pattern around each low is clockwise.
They are influenced by continental-sized land areas at 60° S.
They are most strongly developed during the summer months (January).
They are known as anticyclones.
11.) The intertropical convergence zone is characterized by
convergence and uplift of warm surface air.
convergence and subsidence of cold surface air.
divergence and uplift of warm surface air.
divergence and subsidence of cold surface air.
a very high pressure cell.
12.) Which of the following is not true of the intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ)?
Consistent high Sun altitude and day length make large amounts of energy available.
Warm, moisture-laden airs converge along the ITCZ.
A band of precipitation is associated with the ITCZ.
The ITCZ is stationary throughout the year.
Surface winds converge along the entire ITCZ region.
13.) Weather is
the climate of a region.
the day-to-day condition of the atmosphere.
the long-term atmospheric condition, including extremes that may occur.
a reference to temperature patterns only.
a classification system used to describe the average temperature and precipitation of an area.
14.) The scientific study of the short-term condition of the atmosphere is
weather.
climate.
meteorology.
geography.
climatology.
15.) The phase changes water and other substances undergo are based on
gravitational energy stored within the electron orbitals of atoms.
the amount of motion of molecules and the strength of the bonds between them.
nuclear fusion processes between atoms of a substance.
nuclear fission processes between atoms of a substance.
diabatic forces acting on the molecules.
16.) When water freezes, its density
increases.
decreases.
remains the same as in the liquid state.
decreases until -4° C, then increases.
is indeterminant due to hydrogen bonding.
17.) When water freezes, its volume
increases.
decreases.
remains the same as in the liquid state.
increases until -4° C, then decreases.
contracts.
18.) Water vapor in the atmosphere is called
water.
deposition.
sublimation.
humidity.
transpiration.
19.) Relative humidity is
the amount of water vapor in the air compared to the normal amount.
the amount of moisture in the air relative to your own sensible feelings.
the amount of water vapor in the air relative to the water vapor capacity of the air.
a basically unused concept when it comes to weather topics.
the amount of water vapor in the air per unit area.
20.) On a typical day, the point of highest relative humidity is associated with
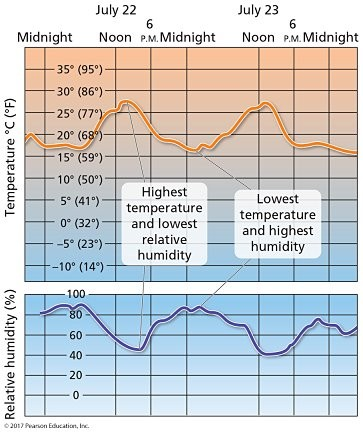
the time of the highest temperature.
the time of the lowest temperature.
solar noon.
dusk.
midmorning.
21.) As temperature increases, the saturation vapor pressure
increases.
decreases.
remains constant.
increases until the dew point is met, then decreases.
decreases until the dew point is met, then increases.
22.) Which of the following is correctly matched?
Normal lapse rate—3.5° C/1,000 m
Environmental lapse rate—6.4 C°/1000 m
Dry adiabatic rate—10 C°/1000 m
Moist adiabatic lapse rate—15 C°/1000 m
Experimental lapse rate—7.2 C°/1000 m
23.) If the amount of water vapor in the air remained constant, but the air temperature increased throughout the day, the relative humidity would
increase.
decrease.
remain constant.
It is impossible to determine which with this information alone.
Changes in a random and irregular manner.
24.) As temperature increases, the amount of energy available for evaporation
increases.
decreases.
remains constant.
Air temperature has no effect on evaporation.
Changes in a random and irregular manner.
25.) In which of the following months would the relative humidity likely be the highest (assuming a Northern Hemisphere station)?
January
March
July
September
May



