HRIS Solution: Strategic Review
HRM Technology Making HRM a Strategic Business Partner
Did you know that HRIS systems were the driving force that transformed HRM from “administrative” to “strategic”? This week we’ll review how that happened and how it is impacting the strategic business plans today.
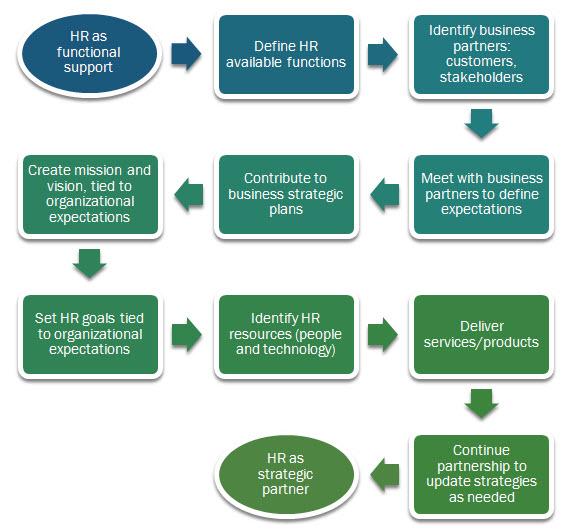
HRM started as a support function, a very low-key, often ignored department that was rarely included in business decisions or strategy planning. After the plans were made for the business, HRM was then told what to do. This focus changed with the entry of technology into the HRM offices. HRM, however, cannot simply become a strategic partner. HRM, now equipped with the means to be a decision maker and frontline contributor to the business, must be a strategic entity within itself first before it can partner with the rest of the business. HRM must reengineer its own processes—how it conducts business itself. To be a strategic contributor, HRM must begin to think strategically. It begins with managing itself more efficiently and creating strategies that align its functions, processes, policies, and resources to the company's strategies. Take a look at the HRM Tutorial in this week's lecture. This tutorial provides just a few ways in which HRM has made itself a strategic department, as well as how it contributes to the business. Think about other ways in which HRM can be a strategic contributor.
HRM now partners with business leaders to become part of the operational strategic process by identifying needed resources based on business plans and then obtaining those resources. HRM and technology transformed the HRM professional’s role. Technology impacts how HRM supports the organization’s overall business strategy and goals. HRM technology trends will be driven by cost control as companies look to optimize investment in employee relations. A challenge today for the HRM professional is to move past the administrative function and become a strategic business partner. HRM must work with the leadership teams to understand the business direction and performance expectations. By actively contributing to business strategies related to talent management, policy creation, and employee relations, HRM can help achieve business goals. For HRM, this requires learning about the business operations, the marketplace, environment, and available labor. Take a look at the flow chart, which provides a review of how HRM has moved from functional support to strategic partner.
As companies reorganize to gain competitive advantage, human resource plays a critical role in helping leadership teams meet these competitive demands through a variety of functions. It begins with hiring and retaining quality employees. How do we create and maintain employee enthusiasm, job satisfaction, and high productivity, instill employee development, and create a fair working environment? HRM technology impacts all of these components and more. The business landscape is constantly changing, which has created a growing need for more effective management of human resources. So how should we manage this human resource capital? What types of functionality should HRM be capable of providing in managing human capital? How can the HRM function add value to this changing business environment? Companies are making dramatic changes focusing on managing the information regarding human capital, which can be addressed through the use of HRIS systems. Through analysis, HRM can provide the necessary information so that business leaders can make the right decisions related to staff.
Companies strive for the highest possible performance from its employees. Organizations want to engage and motivate employees to save time and drive results. HRM technology supports this initiative by providing the information necessary for the business to make educated decisions. HRIS systems have a critical impact on companies that use them. Most times, HRM teams replace several related processes with one HRIS system. This improves the reporting process and how the business manages employees. Think about some HRIS systems that could help improve how your HRM team supports the organization?
Listen
Reengineering HRM

The role of HRM continues to change. Processing employee paperwork manually is no longer a competitive decision. Some companies still have candidates complete a paper application to submit for a job vacancy. This paper application passes through many hands and is finally stored in a paper file. Think about how many paper files your company would need to store for every employee, and don't forget past employees either!
As you have read, HRM's role has drastically changed over the last two decades. You probably recall from Week 1's lecture that business process reengineering (BPR) helped HRM make that transition. HRM continues to create efficiencies through technology, but that requires planning and purpose. How do we optimize HRM processes? BPR is the elemental redesign of a functional process toward improving performance. In a rapidly changing work environment, organizations are changing traditional priorities from planning to innovation. HRM must display the same commitment to meet this key business change. How would you determine if an HRM function would be better served through technology? What are some ways that reengineering, reorganization, and outsourcing can be used? BPR is an essential tool when introducing new technology. It sounds complicated, but it’s not. It’s simply a way of breaking down your processes and procedures and looking to see if there is a way to accomplish the same outcome more efficiently or effectively. How would you begin a BPR process? To accomplish this, HRM must listen to their customers, recognize the need to change, maintain leadership support, understand the organizations’ needs, obtain buy-in, identify the key processes for reengineering, identify the right resources/technology/skills to implement the change, maintain flexibility based on customer feedback, and maintain a continued improvement focus. As with most reengineering, HRM technological changes include the people, the work, and technology. HRM process reengineering’s goal is highlighting congruent process tasks by gathering and communicating information, expediting information and data access, and realigning work accountability.
New technology can really help to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of Human Resources. We must be able to create sound business cases. Once you’ve determined that new technology is the right direction, a needs analysis ensures that the right technology is chosen that best meets the business’s needs. A needs analysis is a process of establishing the validity to change; what is the actual performance versus what it should be (optimal performance). In other words, breaking down the HRM process into specific tasks and then identifying potential areas of efficiency. Once a needs analysis is conducted and identified, that technology can positively impact the HRM function. Choosing the right vendor is an important next step, which we will review in Week 5.
Listen
HRM in the Real World
Although HRIS systems are often seen as simply a way to store employee data, there are a variety of functions that HRIS systems can provide. With this data, HRM can easily retrieve employee information related to attendance, performance, training, benefits, salary, and so on. HRM can then use this information to create strategic plans. For example the sales business within a company is growing dramatically; however, the margin is not. The business is spending more than it is making. How might an HRIS system help identify the core issue? How might staff impact this expense? By analyzing employees' time on the job, this helps to identify potential department inefficiencies. An automated employee time-tracking system can be used to map and measure time spent on specific activities and the resulting costs. In using the HRIS system for the sales organization, information showed that time was spent learning business processes and techniques versus focusing on product delivery. The bottom line was that the sales team did not have the skills necessary to do the work. With this information, the business can train the sales team and go forward by ensuring that new employees have the necessary skills.
Listen
Supplemental Reading
Hot HRIS Issues Now Driving Change reviews how HRM is coveting newer applications of technology to assist in improving long-term workforce planning (3 pages).
How HRIS is Transforming the Workplace reviews how organizations are determined to improve productivity, lower costs, and increase employee satisfaction through technology. It shares how technology impacts HRM’s strategic initiatives (3 pages).
New Roles for HRM Professionals is a little bit longer article but well worth the read. It reviews how technology not only has changed how HRM functions but the new role of HRM professionals. For example, it shares what HRM professionals must now do with the information provided through technology (10 pages).
Moving to a New HRIS shows how the Arizona Department of Administration implemented HRM technology from assembling the project team to testing the HRIS system. This is a good review of what companies go through in automating HRM functions (5 pages).
What's Just Right for You? The automation of HRM functions has made the outsourcing of HRM technology a good candidate. This article reviews the benefits of HRIS outsourcing (4 pages).
Listen
Flashcard Knowledge Review
Please complete the flashcard knowledge review for the week on the Course Resources page.



