Who can do this Algebra Assignment
Answer all 30 exercises and show all work typed in this document. Provide a graph for #13 a & b.
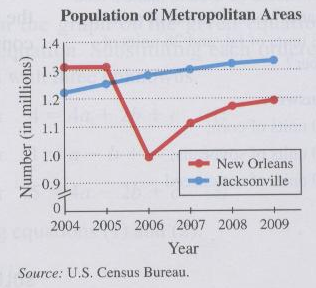
Changes in population—Many factors may contribute to population changes in metropolitan areas. The graph shows the populations of the New Orleans, Louisiana and the Jacksonville, Florida, metropolitan areas over the years 2004–2009.
Use the terms increasing, decreasing, and constant to describe the trends for the population of the New Orleans metropolitan area. [2.5 points]![Who can do this Algebra Assignment 1]()
Solve the system by substitution. (See section 5.1, Example 1.) [2.5 points]
Solve the system by elimination. (See section 5.1, Example 2.) [2.5 points]
Solve each system. State whether it is inconsistent or has infinitely many solutions. If the system has infinitely many solutions, write the solution set with y arbitrary. (See section 5.1, Examples 3and 4.) [5 points]
Solve the system. (See section 5.1, Example 6.) [2.5 points]
Solve the system. State whether it is inconsistent or has infinitely many solutions. If the system has infinitely many solutions, write the solution set with y arbitrary. (See section 5.1, Examples 3, 4, 6, and 7.) [2.5 points]
Solve the system. (Hint: let
and
.) [2.5 points]
Use a system to find the equation of the parabola through the given points. [2.5 points]
Investment decisions—Jane Hooker invests $40,000 received as an inheritance in three parts. With one part she buys mutual funds that offer a return of 2% per year. The second part, which amounts to twice the first, is used to buy government bonds paying 2.5% per year. She puts the rest of the money into a savings account that pays 1.25% annual interest. During the first year, the total interest is $825. How much did she invest at each rate? (See section 5.1, Examples 5 and 9) [2.5 points]
Give all solutions of each nonlinear system of equations, including those nonreal complex components. [10 points]
Unknown numbers—Using a system of equations in two variables, find two numbers whose sum is 17 and whose product is 42. (See section 5.5, Example 6.) [2.5 points]
(Modeling) Circuit gain—In electronics, circuit gain is modeled by
where R is the value of a resistor, t is the temperature, Rt is the value of R at temperature t, and B is a constant. The sensitivity of the circuit to temperature is modeled by
If B = 3.7 and t is 90 K (kelvins), use a system of equations in two variables to find the values of R and Rt that will result in the values of G = 0.4 and S = 0.001. [2.5 points]
Graph each horizontal parabola, and give the domain and range. (See section 6.1, Examples 1 and 2.) [5 points]
Give the focus, directrix, and axis of symmetry for each parabola. (See section 6.1, Example 3.) [5 points]
Write an equation for each parabola with vertex at the origin. (See section 6.1, Example 4.) [5 points]
a. through , opening left
b. through , symmetric with respect to the y-axis
Evaluate each expression. (See section 7.4, Example 1.) [7.5 points]
Determine the binomial coefficient for the fifth term in the expansion of
. [2.5 points]
Write the binomial expansion for the following expression. (See section 7.4, Examples 2–4.) [2.5 points]
Write the indicated term of the binomial expansion. (See section 7.4, Example 5.) [2.5 points]
Twelfth term of
Evaluate each expression. (See section 7.6, Examples 4–8.) [5 points]
Names for a baby—A couple has narrowed down the choice of a name for their new baby to 5 first names and 3 middle names. Using the fundamental principle of counting or permutations, how many different first- and middle-name combinations are possible? (See section 7.6, Examples 1–6.) [2.5 points]
Telephone numbers—Using the fundamental principle of counting or permutations, how many 7-digit telephone numbers are possible if the first digit cannot be 0 and
only odd digits may be used?
the telephone number must be a multiple of 10 (that is, it must end in 0)?
the telephone number must be a multiple of 100?
the first 3 digits are 481?
no repetitions are allowed?
(See section 7.6, Examples 1–6.) [2.5 points]
Marble samples—If a bag of marbles containing 15 marbles has 3 yellow, 4 white, and 8 blue marbles, how many samples of 2 can be drawn in which both marbles are blue? (See section 7.6, Examples 7 and 8.) [2.5 points]
Delegation choices—Seven workers decide to send a delegation of 2 to their supervisor to discuss their grievances.
How many different delegations are possible?
If it is decided that a certain employee must be in the delegation, how many different delegations are possible?
If there are 2 women and 5 men in the group, how many delegations would include at least 1 woman?
(See section 7.6, Examples 7 and 8.) [2.5 points]
Secretary/manager assignments—From a pool of 7 secretaries, 3 are selected to be assigned to 3 managers, 1 secretary to each manager. In how many ways can this be done? (See all methods described in section 7.6, Examples 1–9.) [2.5 points]
Slips of paper marked with the numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4 are placed in a box. A slip is drawn and set aside, its number is recorded, and then a second slip is drawn. Write a sample space with equally likely outcomes for this experiment. [2.5 points]
Referring to the preceding question (no. 26), write each event in set notation and give the probability of the event. (See section 7.7, Example 1.) [2.5 points]
Both slips are marked with even numbers.
Both slips are marked with odd numbers.
Both slips are marked with the same number.
One slip is marked with an odd number, the other with an even number.
Associate each probability in parts (a)–(g) with one of the statements in choices A–F. Choices may be used more than once. [2.5 points]
(a) (b)
(c)
(d)
(e) (f)
(g)
The event is certain occur.
The event cannot occur.
The event is very likely to occur.
The event is very unlikely to occur.
The event is just as likely to occur as not occur.
The event is impossible.
Small business loan—The possibility that a bank with assets greater than or equal to $30 billion will make a loan to a small business is 0.002. What are the odds against such a bank making a small business loan? (Source: The Wall Street Journal analysis of CAI Reports filed with federal banking authorities.) [2.5 points]
U.S. population by region—The U.S. resident population by region (in millions) for selected years is given in the following table.
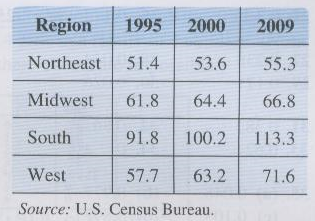
Find the probability that a U.S. resident selected at random satisfies the following. [2.5 points]
Lived in the West in 2000
Lived in the Midwest in 1995
Lived in the Northeast or Midwest in 2000
Lived in the South or West in 2009
What are the odds that a randomly selected U.S. resident in 2009 was not from the South?
WA 6, p. 9